
1. Daonil
2. Diabeta
3. Euglucon 5
4. Euglucon N
5. Glibenclamide
6. Glybenclamide
7. Hb 419
8. Hb 420
9. Hb-419
10. Hb-420
11. Hb419
12. Hb420
13. Maninil
14. Micronase
15. Neogluconin
1. Glibenclamide
2. 10238-21-8
3. Glybenclamide
4. Glynase
5. Diabeta
6. Micronase
7. Daonil
8. Euglucon
9. Maninil
10. Glybenzcyclamide
11. Semi-daonil
12. Apo-glibenclamide
13. Euglucon 5
14. Azuglucon
15. Bastiverit
16. Benclamin
17. Betanase
18. Duraglucon
19. Euglucan
20. Euglykon
21. Glibenil
22. Glucolon
23. Orabetic
24. Prodiabet
25. Renabetic
26. Yuglucon
27. Dibelet
28. Gilemal
29. Glibens
30. Glibil
31. Glimel
32. Glimide
33. Humedia
34. Libanil
35. Suraben
36. Tiabet
37. Adiab
38. Melix
39. Pira
40. Med-glionil
41. Glibenclamidum
42. Glibenclamida
43. Hb 419
44. Glibenclamidum [inn-latin]
45. Glibenclamida [inn-spanish]
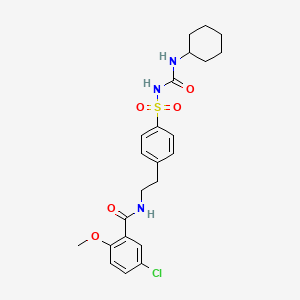
46. 5-chloro-n-(4-(n-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
47. Glyburide (glibenclamide)
48. Hb-419
49. Ur 606
50. Cirara
51. 1-((p-(2-(5-chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-3-cyclohexylurea
52. 1-(p-(2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl)benzenesulfonyl)-3-cyclohexylurea
53. Neogluconin
54. 5-chloro-n-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
55. 5-chloro-n-(2-(4-((((cyclohexylamino)carbonyl)amino)sulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
56. Glibenclamide [inn]
57. U 26452
58. Gewaglucon
59. Glibenbeta
60. Glidiabet
61. Glucobene
62. Glucohexal
63. Glucoremed
64. Hexaglucon
65. Lederglib
66. Lisaglucon
67. Normoglucon
68. Praeciglucon
69. Calabren
70. Cytagon
71. Euclamin
72. Glamide
73. Glibesyn
74. Glibetic
75. Gliboral
76. Glisulin
77. Glitisol
78. Glubate
79. Glucomid
80. Glucoven
81. Glycomin
82. Miglucan
83. Debtan
84. Gliban
85. Gliben
86. Glibet
87. Glicem
88. Gluben
89. Glyben
90. Nadib
91. Sugril
92. Sx6k58tvwc
93. Chembl472
94. Novo-glyburide
95. Nsc-759618
96. Glibenclamid Al
97. 5-chloro-n-[4-(cyclohexylureidosulfonyl)phenethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
98. Gen-glybe
99. Norglicem 5
100. Betanese 5
101. N-(4-(2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl)phenylsulfonyl)-n'-cyclohexylurea
102. Glibenclamid Fabra
103. 5-chloro-n-[2-(4-{[(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)amino]sulfonyl}phenyl)ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
104. Benzamide, 5-chloro-n-(2-(4-((((cyclohexylamino)carbonyl)amino)sulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)-2-methoxy-
105. Mls000069721
106. Chebi:5441
107. Glibenclamid Basics
108. Glibenclamid-cophar
109. Glibenclamid Heumann
110. Semi-euglucon
111. Glibenclamid Genericon
112. Hemi-daonil
113. U-26452
114. Glibenclamid-ratiopharm
115. U-26,452
116. 5-chloro-n-(2-{4-[(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl]phenyl}ethyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
117. Urea, 1-(p-(2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl)benzenesulfonyl)-3-cyclohexyl-
118. Benzamide, 5-chloro-n-[2-[4-[[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxy-
119. Glyburide [usan]
120. Ncgc00015467-11
121. Abbenclamide
122. Diabiphage
123. Glibadone
124. Smr000058229
125. Semi-gliben-puren N
126. Gbn 5
127. Cas-10238-21-8
128. Glibenclamid Riker M.
129. Glyburide (micronized)
130. Urea, 1-((p-(2-(chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-3-cyclohexyl-
131. Dsstox_cid_17237
132. Dsstox_rid_79313
133. Dsstox_gsid_37237
134. U-26,45
135. Micronized Glyburide
136. Glycron
137. 1-[[p-[2-(5-chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]-3-cyclohexylurea
138. 5-chloro-n-(2-{4-[n-(n-cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl]phenyl}ethyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
139. 5-chloro-n-(4-(n-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl)-phenethyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
140. Glyburide (usp)
141. Micronase (tn)
142. 1-{4-[2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl]benzenesulfonyl}-3-cyclohexylurea;1-{4-[2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl]benzenesulfonyl}-3-cyclohexylurea
143. Diabeta (tn)
144. Glynase (tn)
145. Sr-01000000196
146. Glyburide [usan:usp]
147. Einecs 233-570-6
148. Unii-sx6k58tvwc
149. Brn 2230085
150. Amglidia
151. Delmide
152. 5-chloro-n-(4-[n-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl]phenethyl)-2-methoxybenzamide
153. Glibenclamide,(s)
154. Gbm
155. Prestwick_569
156. Glibenclamide B.p.
157. Glyburide (diabeta)
158. Mfcd00056625
159. Rp-1127
160. Spectrum_000250
161. Tocris-0911
162. Glibenclamide - Bio-x
163. Glybenzcyclamide, 99%
164. Glibenclamide; Glyburide
165. Opera_id_801
166. Glyburide [mi]
167. Prestwick0_000316
168. Prestwick1_000316
169. Prestwick2_000316
170. Prestwick3_000316
171. Spectrum2_001816
172. Spectrum3_001327
173. Spectrum4_001199
174. Spectrum5_001631
175. Glyburide [vandf]
176. Lopac-g-0639
177. Probes1_000431
178. Probes2_000378
179. Upcmld-dp006
180. G 0639
181. Glibenclamide [jan]
182. N-p-[2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl]benzenesulfonyl-n'-cyclohexylurea
183. Glyburide [usp-rs]
184. Glyburide [who-ip]
185. Glibenclamide (jp17/inn)
186. N-(4-(beta-(2-methoxy-5-chlorbenzamido)-aethyl)-benzolsulfonyl)-n'-cyclohexyl-harnstoff
187. Cbiol_001790
188. Lopac0_000499
189. Oprea1_764617
190. Schembl22009
191. Bspbio_000312
192. Bspbio_001351
193. Bspbio_003053
194. Kbiogr_000071
195. Kbiogr_001897
196. Kbioss_000071
197. Kbioss_000730
198. Mls001077262
199. Bidd:gt0239
200. Divk1c_000481
201. Glibenclamide [mart.]
202. Spectrum2300229
203. Spbio_001831
204. Spbio_002531
205. Glibenclamide [who-dd]
206. Glibenclamide [who-ip]
207. Bpbio1_000344
208. Gtpl2414
209. Glyburide [orange Book]
210. Dtxsid0037237
211. Upcmld-dp006:001
212. Hms501i03
213. Kbio1_000481
214. Kbio2_000071
215. Kbio2_000730
216. Kbio2_002639
217. Kbio2_003298
218. Kbio2_005207
219. Kbio2_005866
220. Kbio3_000141
221. Kbio3_000142
222. Kbio3_002273
223. Glyburide [usp Monograph]
224. Glybenclamide, >=99% (hplc)
225. Ninds_000481
226. Bio1_000076
227. Bio1_000565
228. Bio1_001054
229. Bio2_000071
230. Bio2_000551
231. Hms1361d13
232. Hms1568p14
233. Hms1791d13
234. Hms1922l08
235. Hms1989d13
236. Hms2089l06
237. Hms2093p04
238. Hms2095p14
239. Hms3259o12
240. Hms3261d19
241. Hms3267a15
242. Hms3402d13
243. Hms3411f16
244. Hms3428d15
245. Hms3651e17
246. Hms3675f16
247. Hms3712p14
248. Pharmakon1600-02300229
249. Zinc537805
250. Bcp05327
251. Glibenclamide [ep Monograph]
252. Glibenclamide For Peak Identification
253. Tox21_110158
254. Tox21_300758
255. Tox21_500499
256. Bdbm50012957
257. Ccg-39618
258. Glucovance Component Glyburide
259. Hd 419
260. Nsc759618
261. Nsc813214
262. Stk362992
263. Glibenclamidum [who-ip Latin]
264. Glyburide - Cas 10238-21-8
265. Akos001487495
266. Tox21_110158_1
267. Bcp9000729
268. Cs-1075
269. Db01016
270. Ks-5326
271. Lp00499
272. Nc00566
273. Nsc 759618
274. Nsc-813214
275. Sb17414
276. Sdccgsbi-0050483.p004
277. Glyburide Component Of Glucovance
278. Idi1_000481
279. Idi1_033821
280. Glibenclamide 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
281. Ncgc00015467-01
282. Ncgc00015467-02
283. Ncgc00015467-03
284. Ncgc00015467-04
285. Ncgc00015467-05
286. Ncgc00015467-06
287. Ncgc00015467-07
288. Ncgc00015467-08
289. Ncgc00015467-09
290. Ncgc00015467-10
291. Ncgc00015467-12
292. Ncgc00015467-13
293. Ncgc00015467-14
294. Ncgc00015467-15
295. Ncgc00015467-16
296. Ncgc00015467-17
297. Ncgc00015467-18
298. Ncgc00015467-20
299. Ncgc00015467-21
300. Ncgc00015467-36
301. Ncgc00015467-37
302. Ncgc00016689-01
303. Ncgc00023447-02
304. Ncgc00023447-04
305. Ncgc00023447-05
306. Ncgc00023447-06
307. Ncgc00023447-07
308. Ncgc00023447-08
309. Ncgc00023447-09
310. Ncgc00023447-10
311. Ncgc00023447-11
312. Ncgc00023447-12
313. Ncgc00254662-01
314. Ncgc00261184-01
315. Bg166164
316. Hy-15206
317. Sbi-0050483.p003
318. Glyburide, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
319. Ab00051949
320. Eu-0100499
321. Ft-0601608
322. G-150
323. G0382
324. Glibenclamide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
325. S1716
326. Sw195828-5
327. A19539
328. C07022
329. D00336
330. D81733
331. M01823
332. Ab00051949-16
333. Ab00051949-17
334. Ab00051949_18
335. Ab00051949_19
336. Q420626
337. Sr-01000000196-2
338. Sr-01000000196-4
339. Sr-01000000196-5
340. Sr-01000000196-6
341. Sr-01000000196-8
342. W-108874
343. Brd-k36927236-001-06-0
344. Brd-k36927236-001-17-7
345. Z277540138
346. Glybenclamide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
347. Glyburide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
348. 1-((p-(2-(5-chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-3-cyclohexyl Urea
349. 5-chloro-n-[4-(3-cyclohexylureidosulfonyl)phenethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
350. 5-chloro-n-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide.
351. 5-chloro-n-[4-({[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino}sulfonyl)phenethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
352. Glibenclamide For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
353. Glyburide (glibenclamide), Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
354. N-(4-(.beta.-(2-methoxy-5-chlorbenzamido)-aethyl)-benzolsulfonyl)-n'-cyclohexyl-harnstoff
355. N1-[4-({[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino}sulfonyl)phenethyl]-5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamide
356. 5-chloro-n-(2-[4-(([(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino)sulfonyl)phenyl]ethyl)-2-methoxybenzamide #
357. 5-chloro-n-[2-[4-[[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]-amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]-ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
358. 5-chloro-n-[2-[4-[[[(cylcohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulphonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide
| Molecular Weight | 494.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H28ClN3O5S |
| XLogP3 | 4.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 493.1438199 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 493.1438199 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 122 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 746 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Diabeta |
| PubMed Health | Glyburide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Diaeta (glyburide) is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. It is a white, crystalline compound, formulated as tablets of 1.25 mg, 2.5 mg, and 5 mg strengths for oral administration. Diaeta tablets USP contain the activ... |
| Active Ingredient | Glyburide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 1.25mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sanofi Aventis Us |
| 2 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glyburide |
| Active Ingredient | Glyburide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1.5mg; 4.5mg; 6mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva; Hikma; Dava Pharms; Mylan |
| 3 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glyburide |
| PubMed Health | Glyburide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glyburide tablets USP contain glyburide, which is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Glyburide is a white, crystalline compound. The chemical name for glyburide is 1-[[p-[2-(5-chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl]phenyl]-sulfonyl]-3-c... |
| Active Ingredient | Glyburide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 1.25mg; 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Corepharma; Teva; Aurobindo Pharma; Heritage Pharms |
| 4 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glynase |
| Drug Label | GLYNASE PresTab Tablets contain micronized (smaller particle size) glyburide, which is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Glyburide is a white, crystalline compound, formulated as GLYNASE PresTab Tablets of 1.5, 3, and 6 m... |
| Active Ingredient | Glyburide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1.5mg; 6mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 5 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glyburide |
| PubMed Health | Glyburide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glyburide tablets USP contain glyburide, which is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Glyburide is a white, crystalline compound. The chemical name for glyburide is 1-[[p-[2-(5-chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl]phenyl]-sulfonyl]-3-c... |
| Active Ingredient | Glyburide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 1.25mg; 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Corepharma; Teva; Aurobindo Pharma; Heritage Pharms |
| 6 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glynase |
| Drug Label | GLYNASE PresTab Tablets contain micronized (smaller particle size) glyburide, which is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. Glyburide is a white, crystalline compound, formulated as GLYNASE PresTab Tablets of 1.5, 3, and 6 m... |
| Active Ingredient | Glyburide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1.5mg; 6mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pharmacia And Upjohn |
| 7 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Diabeta |
| PubMed Health | Glyburide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Diaeta (glyburide) is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class. It is a white, crystalline compound, formulated as tablets of 1.25 mg, 2.5 mg, and 5 mg strengths for oral administration. Diaeta tablets USP contain the activ... |
| Active Ingredient | Glyburide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 1.25mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sanofi Aventis Us |
| 8 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glyburide |
| Active Ingredient | Glyburide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1.5mg; 4.5mg; 6mg; 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva; Hikma; Dava Pharms; Mylan |
Glyburide is indicated alone or as part of combination product with metformin, as an adjunct to diet and exercise, to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Amglidia is indicated for the treatment of neonatal diabetes mellitus, for use in newborns, infants and children.
Sulphonylureas like Amglidia have been shown to be effective in patients with mutations in the genes coding for the -cell ATP-sensitive potassium channel and chromosome 6q24-related transient neonatal diabetes mellitus.
Treatment of neonatal diabetes mellitus
Treatment of large hemispheric infarction
Glyburide is a second generation sulfonylurea that stimulates insulin secretion through the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells, raising intracellular potassium and calcium ion concentrations. Glibenclamide has a long duration of action as it is given once daily, and a wide therapeutic index as patients are started at doses as low as 0.75mg but that can increase as high as 10mg or more. Patients taking glyburide should be cautioned regarding an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality as seen with tolbutamide, another sulfonylurea.
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
A10BB01
A10BB01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BB - Sulfonylureas
A10BB01 - Glibenclamide
Absorption
Elderly patients taking glyburide reached a Cmax of 211-315ng/mL with a Tmax of 0.9-1.0h, while younger patients reached a Cmax of 144-302ng/mL with a Tmax of 1.3-3.0h. Patients taking glyburide have and AUC of 348ng*h/mL.
Route of Elimination
Unlike other sulfonylureas, glyburide is 50% excreted in the urine and 50% in the feces. Glyburide is mainly excreted as the metabolite 4-trans-hydroxyglyburide.
Volume of Distribution
Elderly patients have a volume of distribution of 19.3-52.6L, while younger patients have a volume of distribution of 21.5-49.3L.
Clearance
Elderly patients have a clearance of 2.70-3.55L/h, while younger patients have a clearance of 2.47-4.11L/h.
Glyburide is metabolized mainly by CYP3A4, followed by CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A7, and CYP3A5. These enzymes metabolize glyburide to 4-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M1), 4-cis-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M2a), 3-cis-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M2b), 3-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M3), 2-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M4), and ethylhydroxycyclohexyl glyburide (M5). The M1 and M2b metabolites are considered active, along with the parent molecule.
Glyburide has known human metabolites that include 2-trans-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide, 3-cis-Hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide, 3-trans-Hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide, and 4-cis-hydroxycyclohexyl glyburide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Elderly patients have a terminal elimination half life of 4.0-13.4h, while younger patients have a terminal elimination half life of 4.0-13.9h.
Glyburide belongs to a class of drugs known as sulfonylureas. These drugs act by closing ATP-sensitive potassium channels on pancreatic beta cells. The ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells are known as sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1). Under low glucose concentrations, SUR1 remains open, allowing for potassium ion efflux to create a -70mV membrane potential. Normally SUR1 closes in response to high glucose concentrations, the membrane potential of the cells becomes less negative, the cell depolarizes, voltage gated calcium channels open, calcium ions enter the cell, and the increased intracellular calcium concentration stimulates the release of insulin containing granules. Glyburide bypasses this process by forcing SUR1 closed and stimulating increased insulin secretion.