


1. Diabrezide
2. Diaglyk
3. Diaikron
4. Diamicron
5. Gen Gliclazide
6. Gen-gliclazide
7. Gliklazid
8. Glyade
9. Glyclazide
10. Novo Gliclazide
11. Novo-gliclazide
12. S 1702
13. S 852
14. S-1702
15. S-852
16. S1702
17. S852
1. 21187-98-4
2. Glimicron
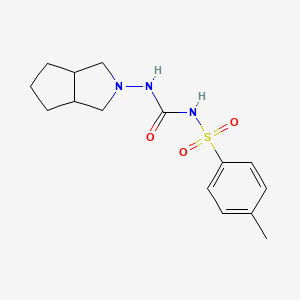
3. 1-(3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydro-1h-cyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2-yl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea
4. 1-(3-azabicyclo(3.3.0)oct-3-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea
5. Chebi:31654
6. 1-(hexahydrocyclopenta(c)pyrrol-2(1h)-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)urea
7. Gliclazidum [inn-latin]
8. Gliclazida [inn-spanish]
9. Gliclazida
10. N-(hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1h)-ylcarbamoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
11. 1-[(4-methylbenzene)sulfonyl]-3-{octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2-yl}urea
12. Nsc-758673
13. Se-1702
14. S1702;se1702
15. Dsstox_cid_3095
16. N-((hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1h)-yl)carbamoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
17. Dsstox_rid_76872
18. Dsstox_gsid_23095
19. S-852
20. S-1702
21. N-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)-n'-(3-azabicyclo(3.3.0)oct-3-yl)urea
22. Glimicron (tn)
23. Smr000542971
24. Sr-01000816184
25. 1-(3-azabicyclo[3.3.0]oct-3-yl)-3-p-tolylsulphonylurea
26. Mfcd00409893
27. J3.151h
28. Gliclazide,(s)
29. Benzenesulfonamide, N-[[(hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1h)-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methyl-
30. Ncgc00016751-01
31. Prestwick_869
32. Cas-21187-98-4
33. Gliclazide (diamicron)
34. Spectrum_001478
35. Specplus_000870
36. Prestwick0_000558
37. Prestwick1_000558
38. Prestwick2_000558
39. Prestwick3_000558
40. Spectrum3_001862
41. Spectrum4_000598
42. Spectrum5_000753
43. Gliclazide (jp17/inn)
44. Schembl16387
45. Bspbio_000635
46. Bspbio_003304
47. Kbiogr_001096
48. Kbioss_001958
49. Mls001215197
50. Mls001304077
51. Mls001304118
52. Divk1c_006966
53. Gliclazide, Powder, >=98%
54. Spectrum1504145
55. Spectrum1505013
56. Spbio_002556
57. Bpbio1_000699
58. Chembl427216
59. Dtxsid9023095
60. Urea, 1-(hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1h)-yl)-3-(p-tolylsulfonyl)-
61. Kbio1_001910
62. Kbio2_001958
63. Kbio2_004526
64. Kbio2_007094
65. Kbio3_002806
66. 1-[3-azabicyclo[3.3.0]oct-3-yl]-3-p-toluenesulfonylurea
67. Hms1569p17
68. Hms1922d15
69. Hms2090k16
70. Hms2096p17
71. Hms2855p09
72. Hms3656c22
73. Hms3713p17
74. Hms3744o13
75. Pharmakon1600-01504145
76. Bcp21240
77. Hy-b0753
78. Tox21_110590
79. Bbl012275
80. Bdbm50103512
81. Nsc758673
82. Nsc813216
83. S2601
84. Se1702
85. Stk803142
86. Akos003237903
87. Akos016340698
88. Tox21_110590_1
89. Ab05958
90. Ccg-213918
91. Db01120
92. Ks-1067
93. Nsc-813216
94. N-[(hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1h)-ylamino)carbonyl]-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
95. Ncgc00095107-01
96. Ncgc00095107-02
97. Ncgc00095107-03
98. Ncgc00095107-04
99. Ncgc00095107-05
100. Ncgc00095107-06
101. Ncgc00095107-09
102. Ncgc00095107-10
103. Ac-12045
104. Sbi-0052662.p002
105. Ab00053165
106. Ft-0626712
107. G0381
108. Sw196994-3
109. D01599
110. D83168
111. Ab00053165-09
112. Ab00053165_10
113. Ab00053165_11
114. 187g984
115. A815188
116. Q290001
117. J-013905
118. J-522753
119. Sr-01000816184-2
120. Sr-01000816184-3
121. Sr-01000816184-4
122. Brd-a61154809-001-04-3
123. Gliclazide, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
124. Gliclazide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
125. 1-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)-3-{octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2-yl}urea
126. 1-(3,3a,4,5,6,6a-hexahydro-1h-cyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2-yl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl-urea
127. Benzenesulfonamide,n-[[(hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1h)-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methyl-
128. Benzenesulfonamide, N-[[(hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1h)-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methyl
| Molecular Weight | 323.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H21N3O3S |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 323.13036271 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 323.13036271 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 497 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of NIDDM in conjunction with diet and exercise.
Based on the pharmacological properties, gliclazide is a second generation sulphonylurea which acts as a hypoglycemic agent. It stimulates β cells of the islet of Langerhans in the pancreas to release insulin. It also enhances peripheral insulin sensitivity. Overall, it potentiates insulin release and improves insulin dynamics.
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
A10BB09
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BB - Sulfonylureas
A10BB09 - Gliclazide
Absorption
Rapidly and well absorbed but may have wide inter- and intra-individual variability. Peak plasma concentrations occur within 4-6 hours of oral administration.
Route of Elimination
Metabolites and conjugates are eliminated primarily by the kidneys (60-70%) and also in the feces (10-20%).
Extensively metabolized in the liver. Less than 1% of the orally administered dose appears unchanged in the urine. Metabolites include oxidized and hydroxylated derivates, as well as glucuronic acid conjugates.
Gliclazide has known human metabolites that include 6-hydroxy-gliclazide, 7-hydroxy-gliclazide, and Methylhydroxygliclazide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
10.4 hours. Duration of action is 10-24 hours.
Gliclazide binds to the β cell sulfonyl urea receptor (SUR1). This binding subsequently blocks the ATP sensitive potassium channels. The binding results in closure of the channels and leads to a resulting decrease in potassium efflux leads to depolarization of the β cells. This opens voltage-dependent calcium channels in the β cell resulting in calmodulin activation, which in turn leads to exocytosis of insulin containing secretorty granules.
