
1. Glidiazinamide
2. Glucotrol
3. Glupitel
4. Glydiazinamide
5. Glypidizine
6. K 4024
7. K-4024
8. K4024
9. Melizide
10. Mindiab
11. Minidiab
12. Minodiab
13. Ozidia
1. 29094-61-9
2. Glucotrol
3. Glydiazinamide
4. Melizide
5. Glibenese
6. Glucozide
7. Glupizide
8. Sucrazide
9. Dipazide
10. Glupitel
11. Mindiab
12. Minidiab
13. Minodiab
14. Napizide
15. Ozidia
16. Glucotrol Xl
17. Glibetin
18. Glucolip
19. Aldiab
20. Digrin
21. Glican
22. Glidiab
23. Glipid
24. Minidab
25. Glyde
26. Gluco-rite
27. Glipizida
28. Glipizidum
29. Glipizidum [inn-latin]
30. K 4024
31. Glipizida [inn-spanish]
32. Metaglip
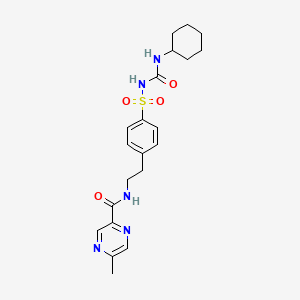
33. N-(4-(n-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide
34. Cp 28720
35. K-4024
36. Cp-28720
37. Tk 1320
38. Cp 28,720
39. N-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide
40. Glipizide Slow Release
41. Glipizide (glucotrol)
42. Cp-28,720
43. 1-cyclohexyl-3-((p-(2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)urea
44. Glide
45. Nsc-759120
46. Chembl1073
47. X7wdt95n5c
48. Mls000069386
49. N-[2-(4-{[(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)amino]sulfonyl}phenyl)ethyl]-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide
50. Pyrazinecarboxamide, N-(2-(4-((((cyclohexylamino)carbonyl)amino)sulfonyl)phenyl)ethyl)-5-methyl-
51. Chebi:5384
52. Cp 28720;k 4024
53. N-(2-{4-[(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl]phenyl}ethyl)-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide
54. N-(4-(beta-(5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamido)ethyl)benzenesulphonyl)-n'-cyclohexylurea
55. Ncgc00015462-07
56. Smr000058455
57. Cas-29094-61-9
58. 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]urea
59. Dsstox_cid_20676
60. Dsstox_rid_79535
61. Urea, 1-cyclohexyl-3-((p-(2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-
62. Dsstox_gsid_40676
63. 29094-66-4
64. 1-cyclohexyl-3-({p-[2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl]phenyl}sulfonyl)urea
65. N-{4-[beta-(5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamido)ethyl]benzenesulphonyl}-n'-cyclohexylurea
66. Glucotrol (tn)
67. Pyrazinecarboxamide, N-[2-[4-[[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-5-methyl-
68. Glipizide (usp/inn)
69. Sr-01000000010
70. Einecs 249-427-6
71. Mfcd00072159
72. Unii-x7wdt95n5c
73. Brn 0903495
74. Glipizide, Solid
75. N-(4-[n-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl]phenethyl)-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide
76. Glipizide [usan:usp:inn:ban]
77. Glipizide/glucotrol
78. Glipizide,(s)
79. Prestwick_242
80. Ks-1068
81. Metaglip (salt/mix)
82. Glipizide [inn]
83. Glipizide [jan]
84. Glipizide [mi]
85. Lopac-g-117
86. Glipizide [usan]
87. Opera_id_1908
88. Prestwick0_000131
89. Prestwick1_000131
90. Prestwick2_000131
91. Prestwick3_000131
92. Glipizide [vandf]
93. G-117
94. Glipizide [mart.]
95. 1-cyclohexyl-3-{4-[2-(5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamido)ethyl]phenylsulfonyl}urea
96. Glipizide [usp-rs]
97. Glipizide [who-dd]
98. Cbiol_001788
99. Lopac0_000621
100. Schembl17094
101. Bspbio_000202
102. Bspbio_001349
103. Kbiogr_000069
104. Kbioss_000069
105. Mls001148176
106. Bidd:gt0476
107. Spbio_002141
108. Bpbio1_000224
109. Gtpl6821
110. Glipizide [orange Book]
111. Dtxsid0040676
112. Glipizide [ep Monograph]
113. Kbio2_000069
114. Kbio2_002637
115. Kbio2_005205
116. Kbio3_000137
117. Kbio3_000138
118. Glipizide [usp Monograph]
119. Bio1_000074
120. Bio1_000563
121. Bio1_001052
122. Bio2_000069
123. Bio2_000549
124. Hms1361d11
125. Hms1568k04
126. Hms1791d11
127. Hms1989d11
128. Hms2089c21
129. Hms2093j09
130. Hms2095k04
131. Hms2233n11
132. Hms3259k12
133. Hms3261n04
134. Hms3369l12
135. Hms3402d11
136. Hms3655g04
137. Hms3712k04
138. Pharmakon1600-01505433
139. Zinc537795
140. Metaglip Component Glipizide
141. Bcp09195
142. Hy-b0254
143. Tox21_110156
144. Tox21_301834
145. Tox21_500621
146. Bbl028143
147. Bdbm50012956
148. Nsc759120
149. Nsc813218
150. S1715
151. Stk631952
152. Akos005564405
153. Glipizide Component Of Metaglip
154. N-[4-(3-cyclohexylureidosulfonyl)phenethyl]-5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxamide
155. Tox21_110156_1
156. Ccg-204710
157. Db01067
158. Lp00621
159. Nc00564
160. Nsc 759120
161. Nsc-813218
162. Sdccgsbi-0050603.p003
163. Idi1_033819
164. N-[2-[4-(cyclohexylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)phenyl]ethyl]-5-methyl-pyrazine-2-carboxamide
165. Glipizide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
166. Ncgc00015462-01
167. Ncgc00015462-02
168. Ncgc00015462-03
169. Ncgc00015462-04
170. Ncgc00015462-05
171. Ncgc00015462-06
172. Ncgc00015462-08
173. Ncgc00015462-09
174. Ncgc00015462-10
175. Ncgc00015462-11
176. Ncgc00015462-12
177. Ncgc00015462-14
178. Ncgc00015462-23
179. Ncgc00016802-01
180. Ncgc00023748-03
181. Ncgc00023748-04
182. Ncgc00023748-05
183. Ncgc00023748-06
184. Ncgc00023748-07
185. Ncgc00255522-01
186. Ncgc00261306-01
187. Ac-15789
188. Sbi-0050603.p002
189. Eu-0100621
190. Ft-0626714
191. Ft-0659737
192. G0369
193. Sw196549-3
194. D00335
195. 094g619
196. Q3108899
197. Sr-01000000010-2
198. Sr-01000000010-5
199. W-107005
200. Brd-k12219985-001-04-8
201. Brd-k12219985-001-15-4
202. Z1880962274
203. Glipizide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
204. Glipizide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
205. Glipizide, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
206. 1-cyclohexyl-3-(4-(2-(2-methylpyrazine-5-carboxamido)ethyl)phenylsulfonyl)urea
207. 1-cyclohexyl-3-{{p=[2-[5-methylpyrazine-carboxamido)-ethyl]phenyl}sulphonyl}urea
208. N-(4-(.beta.-(5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamido)ethyl)benzenesulphonyl)-n'-cyclohexylurea
209. 172964-66-8
210. 2-pyrazinecarboxamide, N-[2-[4-[[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-5-methyl-
211. N-(2-[4-(([(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino)sulfonyl)phenyl]ethyl)-5-methyl-2-pyrazinecarboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 445.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H27N5O4S |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 445.17837553 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 445.17837553 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 139 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 697 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glipizide |
| PubMed Health | Glipizide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glipizide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class.The Chemical Abstracts name of glipizide is 1-Cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]urea. The molecular formula is C21H27N5O4S; the molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Glipizide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Apotex; Accord Hlthcare; Sun Pharm Inds; Sandoz; Par Pharm; Watson Labs; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Zydus Pharms Usa; Mylan |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glucotrol |
| PubMed Health | Glipizide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glipizide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class.The Chemical Abstracts name of glipizide is 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl] phenyl]sulfonyl]urea. The molecular formula is C21H27N5O4S; the molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Glipizide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glucotrol xl |
| PubMed Health | Glipizide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glipizide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class.The Chemical Abstracts name of glipizide is 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl] phenyl]sulfonyl]urea. The molecular formula is C21H27N5O4S; the molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Glipizide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glipizide |
| PubMed Health | Glipizide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glipizide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class.The Chemical Abstracts name of glipizide is 1-Cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]urea. The molecular formula is C21H27N5O4S; the molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Glipizide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Apotex; Accord Hlthcare; Sun Pharm Inds; Sandoz; Par Pharm; Watson Labs; Ivax Sub Teva Pharms; Zydus Pharms Usa; Mylan |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glucotrol |
| PubMed Health | Glipizide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glipizide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class.The Chemical Abstracts name of glipizide is 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl] phenyl]sulfonyl]urea. The molecular formula is C21H27N5O4S; the molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Glipizide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Glucotrol xl |
| PubMed Health | Glipizide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | Glipizide is an oral blood-glucose-lowering drug of the sulfonylurea class.The Chemical Abstracts name of glipizide is 1-cyclohexyl-3-[[p-[2-(5-methylpyrazinecarboxamido)ethyl] phenyl]sulfonyl]urea. The molecular formula is C21H27N5O4S; the molecular... |
| Active Ingredient | Glipizide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg; 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
Indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
FDA Label
Glipizide is a blood glucose-lowering agent. The initial onset of blood glucose-lowering effect occurs around 30 minutes post-administration with the duration of action lasting for about 12 to 24 hours. While the chronic use of glipizide does not result in elevations in the fasting insulin levels over time, the postprandial insulin response, or insulin response to a meal, is observed to be enhanced, even after 6 months of treatment. The main therapeutic actions of glipizide primarily occur at the pancreas where the insulin release is stimulated, but glipizide also mediates some extrapancreatic effects, such as the promotion of insulin signaling effects on the muscles, fat, or liver cells. Due to its action on the endogenous cells, sulfonylureas including glipizide is associated with a risk for developing hypoglycemia and weight gain in patients receiving the drug. Chronic administration of glipizide may result in down-regulation of the sulfonylurea receptors on pancreatic beta cells, which are molecular targets of the drug, leading to a reduced effect on insulin secretion. Like other sulfonylureas, glipizide may work on pancreatic delta () cells and alpha () cells to stimulate the secretion of somatostatin and suppress the secretion of glucagon, which are peptide hormones that regulate neuroendocrine and metabolic pathways. Other than its primary action on the pancreas, glipizide also exerts other biological actions outside of the pancreas, or "extrapancreatic effects", which is similar to other members of the sulfonylurea drug class. Glipizide may enhance the glucose uptake into the skeletal muscles and potentiate the action of insulin in the liver. Other effects include inhibited lipolysis in the liver and adipose tissue, inhibited hepatic glucose output, and increased uptake and oxidation of glucose. It has also been demonstrated by several studies that the chronic therapeutic use of sulfonylureas may result in an increase in insulin receptors expressed on monocytes, adipocytes, and erythrocytes.
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
A10BB07
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BB - Sulfonylureas
A10BB07 - Glipizide
Absorption
Gastrointestinal absorption of glipizide is uniform, rapid, and essentially complete. The absolute bioavailability of glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving a single oral dose was 100%. The maximum plasma concentrations are expected to be reached within 6 to 12 hours following initial dosing. The steady-state plasma concentrations of glipizide from extended-release oral formulations are maintained over the 24-hour dosing interval. In healthy volunteers, the absorption of glipizide was delayed by the presence of food but the total absorption was unaffected.
Route of Elimination
Glipizide is mainly eliminated by hepatic biotransformation, where less than 10% of the initial dose of the drug can be detected in the urine and feces as unchanged glipizide. About 80% of the metabolites of glipizide is excreted in the urine while 10% is excreted in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
The mean volume of distribution was approximately 10 L following administration of single intravenous doses in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In mice and rat studies, the presence of the drug and its metabolites was none to minimal in the fetus of pregnant female animals. Other sulfonylurea drugs were shown to cross the placenta and enter breast milk thus the potential risk of glipizide in fetus or infants cannot be excluded.
Clearance
The mean total body clearance of glipizide was approximately 3 L/hr following administration of single intravenous doses in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Glipizide is subject to hepatic metabolism, in which its major metabolites are formed from aromatic hydroxylation. These major metabolites are glipizide are reported to be pharmacologically inactive. In contrast, an acetylaminoethyl benzine derivative is formed as a minor metabolite which accounts for less than 2% of the initial dose and is reported to have one-tenth to one-third as much hypoglycemic activity as the parent compound.
Glipizide has known human metabolites that include 4-trans-hydroxy-glipizide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The mean terminal elimination half-life of glipizide ranged from 2 to 5 hours after single or multiple doses in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder with increasing prevalence worldwide. Characterized by higher-than-normal levels of blood glucose, T2DM is a complex disorder that arises from the interaction between genetic, environmental and behavioral risk factors. Insulin is a peptide hormone that plays a critical role in regulating blood glucose levels. In response to high blood glucose levels, insulin promotes the uptake of glucose into the liver, muscle cells, and fat cells for storage. Although there are multiple events occurring that lead to the pathophysiology of T2DM, the disorder mainly involves insulin insensitivity as a result of insulin resistance, declining insulin production, and eventual failure of beta cells of pancreatic islets that normally produce insulin. Early management with lifestyle intervention, such as controlled diet and exercise, is critical in reducing the risk of long-term secondary complications, such as cardiovascular mortality. Glipizide, like other sulfonylurea drugs, is an insulin secretagogue, which works by stimulating the insulin release from the pancreatic beta cells thereby increasing the plasma concentrations of insulin. Thus, the main therapeutic action of the drug depends on the functional beta cells in the pancreatic islets. Sulfonylureas bind to the sulfonylurea receptor expressed on the pancreatic beta-cell plasma membrane, leading to the closure of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel and reduced potassium conductance. This results in depolarization of the pancreatic beta cell and opening of the voltage-sensitive calcium channels, promoting calcium ion influx. Increased intracellular concentrations of calcium ions in beta cells stimulates the secretion, or exocytosis, of insulin granules from the cells. Apart from this main mechanism of action, the blood-glucose-lowering effect of glipizide involves increased peripheral glucose utilization via stimulating hepatic gluconeogenesis and by increasing the number and sensitivity of insulin receptors.