


1. Cystorelin
2. Dirigestran
3. Factrel
4. Fsh Releasing Hormone
5. Fsh-releasing Hormone
6. Gn-rh
7. Gnrh
8. Gonadoliberin
9. Gonadorelin
10. Gonadorelin Acetate
11. Gonadorelin Hydrochloride
12. Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone
13. Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone
14. Kryptocur
15. Lfrh
16. Lh Fsh Releasing Hormone
17. Lh Releasing Hormone
18. Lh-fsh Releasing Hormone
19. Lh-releasing Hormone
20. Lh-rh
21. Lhfsh Releasing Hormone
22. Lhfshrh
23. Lhrh
24. Luliberin
25. Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone
26. Luteinizing Hormone-releasing Hormone
27. Releasing Hormone, Lhfsh
1. Lhrh
2. Lh-rh
3. Gonadoliberin, Luliberin
4. Gnrh
5. 9034-40-6
6. 71447-49-9
7. Lhrh, Human
8. Ncgc00182043-01
9. 6918-09-8
10. Chembl1981292
11. Luteinizing Hormone Releasingfactor
12. Bcp12609
13. Bcp12654
14. Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Factor
15. Syntheticgonadotropin-releasinghormone
16. Db00644
17. Ncgc00389662-01
18. Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone Human
19. Db-057197
20. Ft-0628048
21. C07607
22. A821811
23. L000690
24. Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone Human Acetate Salt;lhrh
25. Lhrh;lh-releasing Factor;gonadorelina;glp-his-trp-ser-tyr-gly-leu-ser-pro-gly-nh2
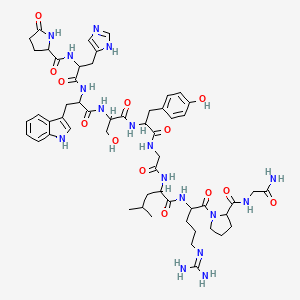
26. N-[1-[[1-[[1-[[1-[[2-[[1-[[1-[2-[(2-azanyl-2-oxidanylidene-ethyl)carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-5-[bis(azanyl)methylideneamino]-1-oxidanylidene-pentan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxidanylidene-pentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxidanylidene-ethyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-o
27. N-[1-[[1-[[1-[[1-[[2-[[1-[[1-[2-[[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]-oxomethyl]-1-pyrrolidinyl]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropa
| Molecular Weight | 1182.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C55H75N17O13 |
| XLogP3 | -2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 16 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 31 |
| Exact Mass | 1181.57302551 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1181.57302551 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 475 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 85 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 2390 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For evaluating the functional capacity and response of the gonadotropes of the anterior pituitary also for evaluating residual gonadotropic function of the pituitary following removal of a pituitary tumor by surgery and/or irradiation.
Gonadorelin is responsible for the release of follicle stimulating hormone and leutinizing hormone from the anterior pitutitary. In the pituitary GnRH stimulates synthesis and release of FSH and LH, a process that is controlled by the frequency and amplitude of GnRH pulses, as well as the feedback of androgens and estrogens. The pulsatility of GnRH secretion has been seen in all vertebrates, and it is necessary to ensure a correct reproductive function. Thus a single hormone, GnRH, controls a complex process of follicular growth, ovulation, and corpus luteum maintenance in the female, and spermatogenesis in the male. Its short half life requires infusion pumps for its clinical use
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed when injected
Rapidly hydrolyzed to inactive peptide components
Very short, initial, 2 to 10 minutes; terminal, 10 to 40 minutes
Systemic - Like naturally occurring gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), gonadorelin primarily stimulates the synthesis and release of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) production and release is also increased by gonadorelin, but to a lesser degree. In prepubertal females and some gonadal function disorders, the FSH response may be greater than the LH response. For the treatment of amenorrhea, delayed puberty, and infertility the administration of gonadorelin is used to simulate the physiologic release of GnRH from the hypothalamus in treatment of delayed puberty, treatment of infertility caused by hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, and induction of ovulation in those women with hypothalamic amenorrhea. This results in increased levels of pituitary gonadotropins LH and FSH, which subsequently stimulate the gonads to produce reproductive steroids.