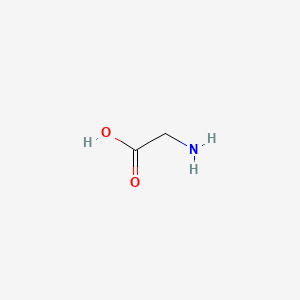

1. Acid, Aminoacetic
2. Aminoacetic Acid
3. Calcium Salt Glycine
4. Cobalt Salt Glycine
5. Copper Salt Glycine
6. Glycine Carbonate (1:1), Monosodium Salt
7. Glycine Carbonate (2:1), Monolithium Salt
8. Glycine Carbonate (2:1), Monopotassium Salt
9. Glycine Carbonate (2:1), Monosodium Salt
10. Glycine Hydrochloride
11. Glycine Hydrochloride (2:1)
12. Glycine Phosphate
13. Glycine Phosphate (1:1)
14. Glycine Sulfate (3:1)
15. Glycine, Calcium Salt
16. Glycine, Calcium Salt (2:1)
17. Glycine, Cobalt Salt
18. Glycine, Copper Salt
19. Glycine, Monoammonium Salt
20. Glycine, Monopotassium Salt
21. Glycine, Monosodium Salt
22. Glycine, Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
23. Hydrochloride, Glycine
24. Monoammonium Salt Glycine
25. Monopotassium Salt Glycine
26. Monosodium Salt Glycine
27. Phosphate, Glycine
28. Salt Glycine, Monoammonium
29. Salt Glycine, Monopotassium
30. Salt Glycine, Monosodium
1. 2-aminoacetic Acid
2. 56-40-6
3. Aminoacetic Acid
4. Glycocoll
5. Aminoethanoic Acid
6. Glycolixir
7. H-gly-oh
8. Glycosthene
9. Padil
10. Aciport
11. Glicoamin
12. Hampshire Glycine
13. L-glycine
14. Amitone
15. Leimzucker
16. Acetic Acid, Amino-
17. Aminoazijnzuur
18. Glycine, Non-medical
19. Sucre De Gelatine
20. Gyn-hydralin
21. Gly (iupac Abbrev)
22. Corilin
23. Glycine [inn]
24. Glycinum [inn-latin]
25. Glicina [inn-spanish]
26. Fema No. 3287
27. Glyzin
28. Gly
29. Acide Aminoacetique [inn-french]
30. Acido Aminoacetico [inn-spanish]
31. Acidum Aminoaceticum [inn-latin]
32. Ccris 5915
33. Hsdb 495
34. Ai3-04085
35. Amino-acetic Acid
36. Mfcd00008131
37. Nsc 25936
38. [14c]glycine
39. 25718-94-9
40. Nsc-25936
41. Chembl773
42. Glycine Iron Sulphate (1:1)
43. Te7660xo1c
44. Chebi:15428
45. Aminoacetate
46. Nsc25936
47. Athenon
48. Glycine-13c
49. Polyglycine
50. Ncgc00024503-01
51. Glicina
52. Dsstox_cid_667
53. Glycine, Free Base
54. Acido Aminoacetico
55. Acide Aminoacetique
56. Dsstox_rid_75720
57. Dsstox_gsid_20667
58. Acidum Aminoaceticum
59. Glykokoll
60. Aminoessigsaeure
61. Hgly
62. Cas-56-40-6
63. Glycine, Labeled With Carbon-14
64. Glycine [usp:inn]
65. Glycine 1.5% In Plastic Container
66. Einecs 200-272-2
67. H2n-ch2-cooh
68. Aminoacetic Acid 1.5% In Plastic Container
69. Unii-te7660xo1c
70. Aminoethanoate
71. 18875-39-3
72. Amino-acetate
73. 2-aminoacetate
74. Glycine;
75. Glycine Usp
76. Glycine Technical
77. [3h]glycine
78. Glycine Usp Grade
79. H-gly
80. L-gly
81. Gly-co
82. Gly-oh
83. L-glycine,(s)
84. [14c]-glycine
85. Corilin (salt/mix)
86. Glycine 1 M Solution
87. Tocris-0219
88. Glycine (h-gly-oh)
89. Glycine [vandf]
90. Nh2ch2cooh
91. Glycine [fhfi]
92. Glycine [hsdb]
93. Glycine [inci]
94. Glycine, >=99%
95. Glycine [fcc]
96. Glycine [jan]
97. Glycine [ii]
98. Glycine [mi]
99. Glycine [mart.]
100. Glycine (jp17/usp)
101. Glycine, 99%, Fcc
102. Glycine [usp-rs]
103. Glycine [who-dd]
104. Biomol-nt_000195
105. Bmse000089
106. Bmse000977
107. Wln: Z1vq
108. Ec 200-272-2
109. Gly-253
110. Glycine [green Book]
111. Gtpl727
112. Ab-131/40217813
113. Glycine [orange Book]
114. Glycine, Electrophoresis Grade
115. Glycine [ep Monograph]
116. Bpbio1_001222
117. Gtpl4084
118. Gtpl4635
119. Glycine [usp Monograph]
120. Dtxsid9020667
121. Bdbm18133
122. Buffer Concentrate, Ph 11.01
123. Azd4282
124. Glycine, >=99.0% (nt)
125. Glycine, 98.5-101.5%
126. Pharmakon1600-01300021
127. Glycine 1000 Microg/ml In Water
128. 2-aminoacetic Acid;aminoacetic Acid
129. Bcp25965
130. Cs-b1641
131. Hy-y0966
132. Zinc4658552
133. Glycine, Acs Reagent, >=98.5%
134. Tox21_113575
135. Glycine, 99%, Natural, Fcc, Fg
136. Nsc760120
137. S4821
138. Stl194276
139. Glycine, Purum, >=98.5% (nt)
140. Glycine, Tested According To Ph.eur.
141. Akos000119626
142. Glycine, For Electrophoresis, >=99%
143. Tox21_113575_1
144. Am81781
145. Ccg-266010
146. Db00145
147. Nsc-760120
148. Glycine, Bioultra, >=99.0% (nt)
149. Glycine, Bioxtra, >=99% (titration)
150. Serine Impurity B [ep Impurity]
151. Glycine, Saj Special Grade, >=99.0%
152. Ncgc00024503-02
153. Ncgc00024503-03
154. Bp-31024
155. Glycine, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
156. Glycine, 0.2m Buffer Solution, Ph 2.5
157. Glycine, 0.2m Buffer Solution, Ph 3.0
158. Glycine, 0.2m Buffer Solution, Ph 3.5
159. Db-029870
160. Ft-0600491
161. Ft-0669038
162. G0099
163. G0317
164. Glycine, Reagentplus(r), >=99% (hplc)
165. A20662
166. C00037
167. D00011
168. D70890
169. M03001
170. L001246
171. Q620730
172. Sr-01000597729
173. Glycine, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
174. Q-201300
175. Sr-01000597729-1
176. Q27115084
177. B72ba06c-60e9-4a83-a24a-a2d7f465bb65
178. F2191-0197
179. Glycine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
180. Z955123660
181. Glycine, Bioultra, For Molecular Biology, >=99.0% (nt)
182. Glycine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
183. Benzene, Diethenyl-, Polymer With 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, Hydrogenated
184. Glycine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
185. Glycine, Analytical Standard, For Nitrogen Determination According To Kjeldahl Method
186. Tris-tricine Buffer; Tris-glycine Buffer;tris Glycine Buffer Concentrate;h-gly-oh
187. Glycine, From Non-animal Source, Meets Ep, Jp, Usp Testing Specifications, Suitable For Cell Culture, >=98.5%
188. Glycine, Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Usp, 99-101% (based On Anhydrous Substance)
189. Glycine, Pharmagrade, Ajinomoto, Ep, Jp, Usp, Manufactured Under Appropriate Gmp Controls For Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production, Suitable For Cell Culture
190. Glycine, Puriss. P.a., Reag. Ph. Eur., Buffer Substance, 99.7-101% (calc. To The Dried Substance)
| Molecular Weight | 75.07 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2H5NO2 |
| XLogP3 | -3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 75.032028402 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 75.032028402 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 5 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 42.9 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
AMINOACETIC ACID HAS BEEN OCCASIONALLY USED IN THERAPY OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS BUT MOST INVESTIGATORS DOUBT THAT THE CMPD HAS ANY VALUE IN THIS DISORDER. ... /IT/ IS ALSO USED IN...ANTACID PREPN, SOMETIMES AS A COMPLEX SALT. HOWEVER.../IT HAS/ LIMITED BUFFERING CAPACITY...
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 963
AMINOACETIC ACID IS USED IN...1.1% SOLN AS AN IRRIGATING FLUID IN TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE. ALTHOUGH A 2.1% SOLN...IS ISOTONIC, IT HAS BEEN FOUND THAT A 1.1% SOLN IS NONHEMOLYTIC.
American Hospital Formulary Service. Volumes I and II. Washington, DC: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, to 1984., p. 40:36
USUALLY FROM 10-15 L OF AMINOACETIC ACID SOLN ARE REQUIRED FOR IRRIGATION DURING TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF PROSTATE.
American Hospital Formulary Service. Volumes I and II. Washington, DC: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, to 1984., p. 40:36
MEDICATION (VET): IV USE IN DOGS INCREASES THEIR TOLERANCE AGAINST CERTAIN TOXIC PARENTERAL AMINO ACID MIXT.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 244
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for GLYCINE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Supplemental glycine may have antispastic activity. Very early findings suggest it may also have antipsychotic activity as well as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
Helps trigger the release of oxygen to the energy requiring cell-making process; Important in the manufacturing of hormones responsible for a strong immune system.
Glycine Agents
Substances used for their pharmacological actions on glycinergic systems. Glycinergic agents include agonists, antagonists, degradation or uptake inhibitors, depleters, precursors, and modulators of receptor function. (See all compounds classified as Glycine Agents.)
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B05 - Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions
B05C - Irrigating solutions
B05CX - Other irrigating solutions
B05CX03 - Glycine
Absorption
Absorbed from the small intestine via an active transport mechanism.
Hepatic
In the CNS, there exist strychnine-sensitive glycine binding sites as well as strychnine-insensitive glycine binding sites. The strychnine-insensitive glycine-binding site is located on the NMDA receptor complex. The strychnine-sensitive glycine receptor complex is comprised of a chloride channel and is a member of the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily. The putative antispastic activity of supplemental glycine could be mediated by glycine's binding to strychnine-sensitive binding sites in the spinal cord. This would result in increased chloride conductance and consequent enhancement of inhibitory neurotransmission. The ability of glycine to potentiate NMDA receptor-mediated neurotransmission raised the possibility of its use in the management of neuroleptic-resistant negative symptoms in schizophrenia.
Animal studies indicate that supplemental glycine protects against endotoxin-induced lethality, hypoxia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation, and D-galactosamine-mediated liver injury. Neutrophils are thought to participate in these pathologic processes via invasion of tissue and releasing such reactive oxygen species as superoxide. In vitro studies have shown that neutrophils contain a glycine-gated chloride channel that can attenuate increases in intracellular calcium and diminsh neutrophil oxidant production. This research is ealy-stage, but suggests that supplementary glycine may turn out to be useful in processes where neutrophil infiltration contributes to toxicity, such as ARDS.
HYPERPOLARIZATION OF MOTONEURONS PRODUCED BY IONTOPHORETIC APPLICATION OF GLYCINE IS RELATIVELY TRANSIENT BUT APPROACHES THE EQUILIBRIUM POTENTIAL FOR THE INDIRECTLY ACTIVATED INHIBITORY POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIAL...TESTS WITH GABA... INDICATE SIMILAR ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS & SIMILAR INCR IN CL- CONDUCTANCE.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 247
MAJOR EVIDENCE THAT FAVORS GLYCINE AS MEDIATOR OF INTRASPINAL POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION IS THE SELECTIVE ANTAGONISM OF ITS EFFECTS BY STRYCHNINE. ... GLYCINE ALSO APPEARS TO BE MOST LIKELY TRANSMITTER FOR INHIBITORY INTERNEURONS IN RETICULAR FORMATION BUT NOT IN CUNEATE NUCLEUS.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 247