


1. 1-(2-(4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethylimidazo(4,5-c)pyridin-1-yl)phenyl)ethyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea
2. Aat-007
3. Cj 023,423
4. Cj 023423
5. Cj-023
6. Cj-023,423
7. Cj-023423
8. Mr-10a7
9. Mr10a7
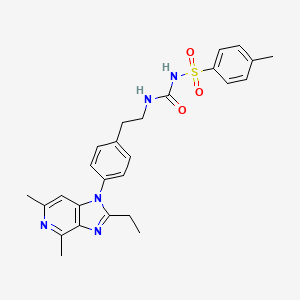
10. N-(((2-(4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-1h-imidazo(4,5-c)pyridin-1-yl) Phenyl)ethyl)amino)carbonyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
11. Rq-00000007
12. Rq-7
1. 415903-37-6
2. Cj-023423
3. Aat-007
4. Cj 023423
5. Rq-7
6. Rq-00000007
7. Mr-10a7
8. Cj-023,423
9. N-((4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-1h-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-1-yl)phenethyl)carbamoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
10. Cj-023
11. Mr10a7
12. J9f5zph7nb
13. Grapiprant (cj-023423)
14. 706802-34-8
15. Cj-023423;rq-00000007;aat-007
16. 1-[2-[4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethylimidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-1-yl)phenyl]ethyl]-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea
17. Benzenesulfonamide, N-(((2-(4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-1h-imidazo(4,5-c)pyridin-1-yl)phenyl)ethyl)amino)carbonyl)-4-methyl-
18. Grapiprant [usan:inn]
19. Unii-j9f5zph7nb
20. 1-(2-(4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethylimidazo(4,5-c)pyridin-1-yl)phenyl)ethyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea
21. N-(((2-(4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-1h-imidazo(4,5-c)pyridin-1-yl)phenyl)ethyl)amino)carbonyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
22. N-[([2-[4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-1h-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-1-yl)phenyl]ethyl]amino)carbonyl]-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide
23. Grapiprant [mi]
24. Grapiprant [inn]
25. Grapiprant (usan/inn)
26. Grapiprant [usan]
27. Grapiprant [who-dd]
28. Schembl120428
29. Gtpl5858
30. Grapiprant [green Book]
31. Chembl3039498
32. Dtxsid60194419
33. Bcp20570
34. Ex-a2544
35. Bdbm50107283
36. S6694
37. Zinc38228051
38. Akos030526811
39. Aat-007cj-023423
40. Cs-5392
41. Db12836
42. Sb18902
43. Ac-36123
44. As-77380
45. Hy-16781
46. A15964
47. D10638
48. D83673
49. A900379
50. Q27077852
51. B0084-470919
52. Cj-023423; Rq-00000007; Aat-007
53. Grapiprant; Rq-00000007; Aat-007; Cj-023423
54. 2-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-1-(4-(2-(((((4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl)amino)carbonyl)amino)ethyl)phenyl)-1h-imidazo(4,5-c)pyridine
55. Benzenesulfonamide,n-[[[2-[4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-1h-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-1-yl)phenyl]ethyl]amino]carbonyl]-4-methyl-
56. N-(((2-(4-(2-ethyl-4,6-dimethyl-1h-imidazo(4,5-c)pyridin-1-yl)phenyl)ethyl)amino)carbonyl)-4-methyl-benzenesulfonamide
| Molecular Weight | 491.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H29N5O3S |
| XLogP3 | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 491.19911098 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 491.19911098 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 114 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 802 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
The effects of grapiprant have been investigated in the area of analgesia and anti-inflammation due to the effects that have been reported about this molecule. This molecule has been approved and widely accepted to be used in veterinary for pain reduction in arthritis. In humans, it has been researched to be used in the control of pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis. The effect of grapiprant can be explained through the function of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) which is a key mediator of swelling redness and pain which are classic signs of inflammation. The effect of PGE2 results from its action through four receptor EP1, EP2, EP3 and EP4 from which the EP4 is the primary mediator of PGE2-driven inflammation.
For the treatment of pain associated with mild to moderate osteoarthritis in dogs.
Preclinical studies have shown that grapiprant is very effective to reduce acute and chronic pain and inflammation. The effect of grapiprant seems to be dose-dependent and it is comparable to the effect of rofecoxib and piroxicam. The effects of grapiprant have been reported to be effective in the relief from arthritic pain in canine patients.
QM01AX92
Absorption
Studies in animals (horse) have shown the presence of a concentration >0.005 ng/ml in serum 72 hours after initial administration of a dose of 2 mg/kg. It is rapidly absorbed and the reported Cmax in this reports was 31.9 ng/ml in a Tmax of 1.5 hours and AUC of 2000 ng.hr/ml. In the case of bioavailability, grapiprant presents a mean bioavailability of 39%. The bioavailability, time for peak concentration and maximal concentration has been reported to be significantly reduced after food.
Route of Elimination
Following an oral dose, the majority of the dose an within the first 72 hours. Studies in animals (horse) have shown the presence of a concentration >0.005 ng/ml in urine 96 hours after initial administration of a dose of 2 mg/kg. From the excreted dose, 55%, 15% and 19% of the administered dose is excreted in bile, urine, and feces respectively.
Volume of Distribution
The reported volume of distribution in animal studies (cats) was reported to be 918 ml/kg.
Clearance
The reported clearance rate in animal studies (cats) was reported to be 173.2 ml/hr.kg.
_In vitro_ studies with dog microsomes have reported the identification of four metabolites, an N-deamination metabolite which is the major metabolite in urine and feces, two hydroxylated metabolites and one N-oxidation metabolite.
The reported elimination half-life in animal studies (horse) is of 5.86 hours.
Grapiprant is an EP4 prostaglandin receptor antagonist and thus the activity of this drug is thought to be completely related to the selective blockade of this receptor. It binds to human and other mammals EP4 prostaglandin receptor with high affinity without interfering with other prostaglandin pathways which are important for a variety of physiological functions. The binding of grapiprant blocks PGE2 binding and hence its biological effect related to the signaling pain and inflammation cascade. Grapiprant has been accepted very greatly in veterinary as its mechanism of action is a targeted approach to pain management by not having any interaction with the production of prostanoids and thus, by not interacting with other prostaglandin receptor pathways.