
1. Breonesin
2. Ether, Guaiacol Glyceryl
3. Glycerol Guaiacolate
4. Glyceryl Ether, Guaiacol
5. Guaiacol Glyceryl Ether
6. Guaiacolate, Glycerol
7. Guaiphenesin
8. Guaiphenezine
9. Guiatuss
10. Humibid
11. Hytuss
12. My 301
13. My-301
14. My301
15. Scott Tussin
16. Scott-tussin
17. Scotttussin
1. 93-14-1
2. Guaiphenesin
3. Guaiacol Glyceryl Ether
4. Glycerol Guaiacolate
5. Glyceryl Guaiacolate
6. 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propane-1,2-diol
7. Guaiphenesine
8. Methphenoxydiol
9. Aeronesin
10. Breonesin
11. Robitussin
12. Bronchol
13. Mucinex
14. Aresol
15. Propanosedyl
16. Calmipan
17. Cortussin
18. Dorassin
19. Flartussin
20. Guaiacuran
21. Guaiacurane
22. Guaiamar
23. Guaianesin
24. Guaiphesin
25. Hustosil
26. Myocaine
27. Myoscain
28. Creson
29. Gaiamar
30. Hytuss
31. Myocain
32. Reduton
33. Dilyn
34. Resyl
35. Glycerin Guaiacolate
36. Glyceryl Guaiacol
37. Methoxypropanediol
38. Metossipropandiolo
39. Metfenossidiolo
40. Amonidrin
41. Glycotuss
42. Guajacuran
43. Guajamar
44. Guayanesin
45. Guiaphenesin
46. Hustodil
47. Mintosyl
48. Miocaina
49. Miocurin
50. Miorelax
51. Mucostop
52. Muskurelax
53. Myorelax
54. Myoscaine
55. Neuroton
56. Neurotone
57. Reorganin
58. Respenyl
59. Ritussin
60. Tenntuss
61. Glyceryl Guaicolate
62. Glyceryl Guiacolate
63. Guanar
64. Oresol
65. Oreson
66. Respil
67. Sirotol
68. Gvaja
69. Resil
70. Tolyn
71. Tulyl
72. Tulyn
73. 3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol
74. Guaiacol Glycerol Ether
75. Guaiacolglicerinetere
76. Guaia-rom
77. Relaxil G
78. Relaxyl-g
79. Guaicol Glyceryl Ether
80. Gnaifenesin
81. Guaifenesine
82. Glyceryl Guaiacyl Ether
83. Guaiacyl Glyceryl Ether
84. Guaicol Glycerine Ether
85. 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol
86. Organidin Nr
87. O-methoxyphenyl Glyceryl Ether
88. Glycero-guaiacol Ether
89. Guaiacol Glycerin Ether
90. Guaifenesinum
91. Amonidren
92. Pneumomist
93. 1,2-propanediol, 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-
94. Trecid
95. Glycerylguaiacol
96. Glycerin Monoguaiacol Ether
97. Guajacol-glycerinaether
98. Glyceryl Guaiacol Ether
99. 3-o-methoxyphenoxypropane 1:2-diol
100. Glyceryl Guaiacolate Ether
101. Glycerol Mono(2-methoxyphenyl) Ether
102. Actifed C
103. Guaiacolic Acid, Ester With Glycerol
104. My 301
105. Sl-90
106. Xl-90
107. Alpha-glyceryl Guaiacol Ether
108. 1,2-dihydroxy-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propane
109. Guaifensin
110. Alpha-glyceryl Guaiacolate Ether
111. Rac Guaifenesin
112. G 87
113. 1,2-propanediol, 3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-
114. Glycerol-alpha-guajakolether
115. Component Of Quibron
116. 3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-propanediol-1,2
117. Component Of Hycotuss
118. Glycerol .alpha.-guiacyl Ether
119. .alpha.-glyceryl Guaiacol Ether
120. Glycerol .alpha.-guaiacyl Ether
121. Guajacol-.alpha.-glycerin-ether
122. Component Of Brondecon
123. .alpha.-glyceryl Guaiacolate Ether
124. Glycerol .alpha.-monoguaiacol Ether
125. Component Of Quibron Plus
126. Nsc-62112
127. 1,2,3-propanetriol, Ether With 2-methoxyphenol
128. Guaifenesin (guaiphenesin)
129. Glycerol .alpha.-(o-methoxyphenyl)ether
130. Glycerol .alpha.-(2-methoxyphenyl) Ether
131. Component Of Colrex Expectorant
132. 2-g
133. 2/g
134. Cvt-2534
135. Nsc62112
136. 495w7451vq
137. Equicol
138. Glycodex
139. Dsstox_cid_3114
140. Colrex Expectorant
141. Dsstox_rid_76881
142. Dsstox_gsid_23114
143. Guaifenesina
144. Tenntus
145. Tussin
146. Glycerinmonoguaiacol Ether
147. Benylin-e
148. Lufyllin-gg
149. Aether Glycerinoguaiacolicus
150. Guaifenesine [inn-french]
151. Guaifenesinum [inn-latin]
152. Guajacol-alpha-glycerinether
153. Tedral Expectorant
154. (component Of) Deconsal Ii
155. Glycerol Alpha-guiacyl Ether
156. Guaifenesina [inn-spanish]
157. Glycerol Alpha-guaiacyl Ether
158. My-301
159. Glycerol Alpha-monoguaiacol Ether
160. Glycerol-alpha-monoguaiacol Ether
161. Guajacol-glycerinaether [german]
162. Hsdb 3089
163. Sr-01000737186
164. Glycerol Mono(2-methoxyphenyl)ether
165. Einecs 202-222-5
166. Glycerol-alpha-guajakolether [czech]
167. Nsc 62112
168. Glycerol Alpha-(o-methoxyphenyl)ether
169. Glycerol Alpha-(o-methoxyphenyl) Ether
170. Glycerol Alpha-(2-methoxyphenyl) Ether
171. Brn 2049375
172. Glycerin Ether
173. Glyc
174. Ai3-24947
175. Unii-495w7451vq
176. Q-tussin
177. Guaifenesin,(s)
178. Cas-93-14-1
179. Ncgc00016350-01
180. Hustosil (tn)
181. Prestwick_231
182. Entex (salt/mix)
183. Mfcd00016873
184. Humabid
185. Dimacol (salt/mix)
186. Kwelcof (salt/mix)
187. Guaifenesin Dc 95%
188. Hycotuss (salt/mix)
189. Guaifenesin [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
190. Brondecon (salt/mix)
191. Congestac (salt/mix)
192. Triaminic (salt/mix)
193. Dilor G (salt/mix)
194. Guaifenesin-[13c3]
195. Spectrum_000835
196. Pneumomist (salt/mix)
197. Q-tussin (salt/mix)
198. Glycerol-a-guajakolether
199. 3-(2-methoxy-phenoxy)-propane-1,2-diol
200. Mucinex D (salt/mix)
201. Robitussin (tn)
202. Glycerol A-guiacyl Ether
203. Tussar-2 (salt/mix)
204. Brexin Ex (salt/mix)
205. Tussar Sf (salt/mix)
206. Guaifenesin [mi]
207. Guaifenesin(guaiphenesin)
208. A-glyceryl Guaiacol Ether
209. Glycerol A-guaiacyl Ether
210. Mucinex Dm (salt/mix)
211. Prestwick0_000776
212. Prestwick1_000776
213. Prestwick2_000776
214. Prestwick3_000776
215. Spectrum2_001104
216. Spectrum3_000444
217. Spectrum4_000566
218. Spectrum5_000758
219. Guaifenesin [inn]
220. Guaifenesin [jan]
221. Lufyllin-gg (salt/mix)
222. Naldecon-ex (salt/mix)
223. (+-)-3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol
224. Guaifenesin [hsdb]
225. Guaifenesin [usan]
226. Chembl980
227. Theolair Plus (salt/mix)
228. Guaifenesin [vandf]
229. Robitussin Cf (salt/mix)
230. Schembl4321
231. A-glyceryl Guaiacolate Ether
232. Neothylline-gg (salt/mix)
233. Guaifenesin [mart.]
234. Oprea1_193170
235. Pneumotussin Hc (salt/mix)
236. Wln: Q1yq1or Bo1
237. 1, 3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-
238. Bronkaid Caplets (salt/mix)
239. Bspbio_000852
240. Bspbio_002088
241. Glycerol A-monoguaiacol Ether
242. Guaifenesin [usp-rs]
243. Guaifenesin [who-dd]
244. Kbiogr_000972
245. Kbioss_001315
246. Slo-phyllin Gg (salt/mix)
247. 1,2-propanediol, 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)- (+-)-
248. 4-06-00-05576 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
249. Mls000028402
250. 1, 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-
251. Divk1c_000248
252. Spectrum1500321
253. Glycerol-.alpha.-guajakolether
254. Spbio_001208
255. Spbio_002791
256. Pv Tussin Tablet (salt/mix)
257. Tedral Expectorant (salt/mix)
258. Bpbio1_000938
259. Chebi:5551
260. Gtpl7617
261. Guaifenesin (jp17/usp/inn)
262. Dtxsid5023114
263. Guaifenesin [green Book]
264. Tussi-organidin Nr (salt/mix)
265. Hms500m10
266. Kbio1_000248
267. Kbio2_001315
268. Kbio2_003883
269. Kbio2_006451
270. Kbio3_001308
271. Contac Cough Formula (salt/mix)
272. Guaifenesin [orange Book]
273. Ru-tuss De Tablets (salt/mix)
274. Glycerol A-(o-methoxyphenyl)ether
275. Ninds_000248
276. Guaifenesin [ep Monograph]
277. Hms1570k14
278. Hms1920b15
279. Hms2090k20
280. Hms2091h21
281. Hms2097k14
282. Hms2231m20
283. Hms3369e03
284. Hms3369n15
285. Hms3651i17
286. Hms3714k14
287. Isoclor Expectorant C (salt/mix)
288. Pharmakon1600-01500321
289. Polaramine Expectorant (salt/mix)
290. Guaifenesin [usp Monograph]
291. Glycerol A-(2-methoxyphenyl) Ether
292. Hy-b0264
293. Obredon Component Guaifenesin
294. Tox21_110389
295. Tox21_302094
296. Bbl009981
297. Ccg-39687
298. Flowtuss Component Guaifenesin
299. Nsc757052
300. S1740
301. Stk365152
302. Glycerol, 1-(2-methoxyphenyl) Ether
303. Akos005435152
304. Mucinex D Component Guaifenesin
305. Tox21_110389_1
306. Db00874
307. Guaifenesin Component Of Obredon
308. Ks-5306
309. Mucinex Dm Component Guaifenesin
310. Nsc-757052
311. Guaiacol Glyceryl Ether, >=98% (gc)
312. Guaifenesin Component Of Flowtuss
313. Idi1_000248
314. 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1, 2-propanediol
315. Guaifenesin Component Of Hycofenix
316. Hycofenix Component Of Guaifenesin
317. Ncgc00094689-01
318. Ncgc00094689-02
319. Ncgc00094689-03
320. Ncgc00094689-04
321. Ncgc00094689-06
322. Ncgc00255343-01
323. Ac-26819
324. Guaifenesin Component Of Mucinex D
325. Smr000058387
326. Guaifenesin Component Of Mucinex Dm
327. Sbi-0051397.p003
328. Ab00052006
329. Ft-0613565
330. Ft-0669064
331. G0159
332. Sw196538-3
333. (2s)-3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)propane-1,2-diol
334. 1,3-propanetriol, Ether With 2-methoxyphenol
335. D00337
336. D70850
337. 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol, 99+%
338. 3-{[2-(methyloxy)phenyl]oxy}propane-1,2-diol
339. Ab00052006-10
340. Ab00052006-11
341. Ab00052006_12
342. Ab00052006_13
343. A844457
344. Q420682
345. 3 - (2 - Methoxyphenoxy) - 1, 2 - Propanediol
346. Sr-01000737186-2
347. Sr-01000737186-3
348. W-100252
349. (+/-)-3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol
350. Brd-a90515964-001-05-8
351. Brd-a90515964-001-09-0
352. 1,2-propanediol, 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)- (+/-)-
353. Guaifenesin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
354. ( Inverted Exclamation Marka)-3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol
355. Guaifenesin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
356. Guaifenesin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
357. Guaifenesin For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 198.22 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H14O4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 198.08920892 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 198.08920892 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 58.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 151 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Guaifenesin |
| PubMed Health | Guaifenesin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Expectorant |
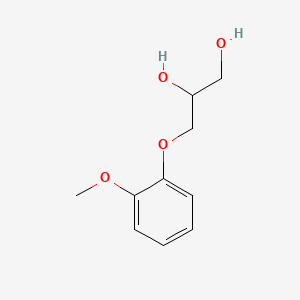
| Drug Label | Guaifenesin (glyceryl guaiacolate) has the chemical name 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol. Its molecular formula is C10H14O4 with a molecular weight of 198.21. It is a white or slightly gray crystalline substance with a slightly bitter aromatic t... |
| Active Ingredient | Guaifenesin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 600mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Perrigo R And D |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mucinex |
| PubMed Health | Guaifenesin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Expectorant |
| Active Ingredient | Guaifenesin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 600mg; 1.2gm |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Reckitt Benckiser |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Guaifenesin |
| PubMed Health | Guaifenesin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Expectorant |
| Drug Label | Guaifenesin (glyceryl guaiacolate) has the chemical name 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol. Its molecular formula is C10H14O4 with a molecular weight of 198.21. It is a white or slightly gray crystalline substance with a slightly bitter aromatic t... |
| Active Ingredient | Guaifenesin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 600mg |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Perrigo R And D |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Mucinex |
| PubMed Health | Guaifenesin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Expectorant |
| Active Ingredient | Guaifenesin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 600mg; 1.2gm |
| Market Status | Over the Counter |
| Company | Reckitt Benckiser |
Expectorants
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Guaifenesin is indicated as an expectorant in the temporary symptomatic management of cough due to minor upper respiratory infections and related conditions, such as sinusitis, pharyngitis, and bronchitis, when these conditions are complicated by viscous mucus and congestion. However, because supporting data are very limited, there is some controversy about its effectiveness. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 1537
VET: Guaifenesin (glyceryl guaiacolate) is a centrally acting muscle relaxant that is believed to depress or block nerve impulse transmission at the internuncial neuron level of the subcortical areas of the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord. It also has mild analgesic and sedative actions. Guaifenesin is given IV to induce muscle relaxation as an adjunct to anesthesia for short procedures. It relaxes both laryngeal and pharyngeal muscles, allowing easier intubation, but has little effect on diaphragm and respiratory function. It may cause transient increases in cardiac rate and decreases in blood pressure. It is also used in treatment of horses with exertional rhabdomyolysis and in dogs with strychnine intoxication.
Kahn, C.M. (Ed.); The Merck Veterinary Manual 9th ed. Merck & Co. Whitehouse Station, NJ. 2005, p. 2018
VET: The drug is used intravenously as a skeletal muscle relaxant in horses. /Gecolate, Glycodex Injection/
US FDA; Database of Approved Animal Drug Products, FDA Center for Veterinary Medicine, VMRCVM Drug Information Lab, CFR Product Abstract for: 030-434, Available from, as of October 24, 2007: https://dil.vetmed.vt.edu/
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) article describing three deaths in U.S. infants aged less than 12 months associated with cough and cold medications /including guaifenesen/. These medications were determined by medical examiners or coroners to be the underlying cause of death. The cases described in this report underscore the need for clinicians to use caution when prescribing and caregivers to use caution when administering cough and cold medications to children aged less than 2 years.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007.
Doses of guaifenesin larger than those required for expectorant action may produce emesis, but GI upset at ordinary dosage levels is rare.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007.
For self-medication, unless directed by a physician, guaifenesin should not be used for persistent or chronic cough such as that occurring with smoking, asthma, chronic bronchitis, or emphysema, or for cough accompanied by excessive phlegm. A persistent cough may be indicative of a serious condition. If cough persists for more than one week, is recurrent, or is accompanied by fever, rash, or persistent headache, a physician should be consulted.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007.
Adverse effects ... indicating need for medical attention only if they continue or are bothersome ... occurring at an incidence less frequent or rare /include/: diarrhea; dizziness; headache; nausea or vomiting; skin rash; stomach pain; urticaria (hives).
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 1537
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for GUAIFENESIN (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
2(?). 2= SLIGHTLY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 5-15 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 PINT & 1 QT FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB).
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-240
Guaifenesin is an expectorant that is indicated for providing temporary symptomatic relief from congested chests and coughs which may be due to a cold, bronchitis, and/or other breathing illnesses.
FDA Label
Guaifenesin is categorized as an expectorant that acts by enhancing the output of phlegm (sputum) and bronchial secretions via decreasing the adhesiveness and surface tension of such material. Furthermore, guaifenesin elicits an increased flow of less viscous gastric secretions that subsequently promote ciliary action - all actions that ultimately change dry, unproductive coughing to coughs that are more productive and less frequent. Essentially, by decreasing the viscosity and adhesiveness of such secretions, guaifenesin enhances the efficacy of mucociliary activity in removing accumulated secretions from the upper and lower airway.
Expectorants
Agents that increase mucous excretion. Mucolytic agents, that is drugs that liquefy mucous secretions, are also included here. (See all compounds classified as Expectorants.)
R05CA03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
R - Respiratory system
R05 - Cough and cold preparations
R05C - Expectorants, excl. combinations with cough suppressants
R05CA - Expectorants
R05CA03 - Guaifenesin
Absorption
Studies have shown that guaifenesin is well absorbed from and along the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration.
Route of Elimination
After administration, guaifenesin is metabolized and then largely excreted in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The geometric mean apparent volume of distribution of guaifenesin determined in healthy adult subjects is 116L (CV=45.7%).
Clearance
The mean clearance recorded for guaifenesin is about 94.8 L/hr (CV=51.4%).
Readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 1537
It is not known whether guaifenesin is distributed into breast milk.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 1537
Elimination /is/ renal, as inactive metabolites.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 1537
Five donkeys and three horses were given guaifenesin, intravenously, by gravity administration, until recumbency was produced. The time and dose required to produce recumbency, recovery time to sternal and standing were recorded. Blood samples were collected for guaifenesin assay at 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 min, and 2, 3, 4 and 6 hr after guaifenesin administration. Serum was analysed for guaifenesin using HPLC and pharmacokinetic values were calculated using a computer software package. In donkeys, heart and respiratory rates and blood pressures were recorded before and at 5-min intervals during recumbency. Arterial blood samples were collected before and at 5 and 15 min intervals during recumbency for analysis of pH, CO2, and O2. ANOVA was used to evaluate dynamic data, while t-tests were used for kinetic values. Respiratory rate was decreased significantly during recumbency, but no other significant changes from baseline occurred. The mean (+/- SD) recumbency dose of guaifenesin was 131 mg/kg (27) for donkeys and 211 mg/kg (8) for horses. Recovery time to sternal (min) was 15 (SD, 11) for donkeys and 34 (SD, 1.4) for horses. Time to standing was 32 min for donkeys and 36 min for horses. Calculation of AUC (area under the concentration-time curve) microgram/mL) (dose-dependent variable) was 231 (SD, 33) for donkeys and 688 (SD, 110) for horses. The clearance (CL) (mL/hr.kg) was 546 (SD, 73) for donkeys, which was significantly different from 313 (SD, 62) for horses. Mean residence time (MRT) (hr) was 1.2 (SD, 0.1) for donkeys and 2.6 (SD, 0.5) for horses. Volume of distribution Vd(area) (mL/kg) was 678 (SD, 92) for donkeys and 794 (SD, 25) for horses. At the rate of administration used in this study, donkeys required less guaifenesin than horses to produce recumbency, but cleared it more rapidly.
PMID:9430767 Matthews N, Peck K et al; J Vet Pharmacol Ther 20 (6): 442-6 (1997)
After the oral administration of 400 mg guaifenesin, the agent experiences rapid hydrolysis (more than 60% of the dose hydrolyzed over a range of seven hours) with -(2-methoxyphenoxy)-lactic acid found as the major urinary metabolite but no parent drug detectable in the urine. Moreover, it has been observed that guaifenesin also experiences both oxidation and demethylation. In particular, the medication is quickly metabolized hepatically by way of oxidation to -(2-methoxyphenoxy)-lactic acid. Furthermore, guaifenesin is also demethylated by O-demethylase in liver microsomes to the point where about 40% of an administered dose is excreted as this metabolite in the urine within 3 hours. In fact, O-demethylase appears to be the primary enzyme for the metabolism of guaifenesin and the primary metabolites of the substance are -(2-methoxyphenoxy)-lactic acid and the demethylated hydroxyguaifenesin, both of which are themselves inactive moieties.
The major urinary metabolite is beta-(2-methoxyphenoxy) lactic acid.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference: Generics 2nd ed p.1474 (1996)
It is excreted in urine principally as glucuronates & sulfates.
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-240
Oxidative o-demethylation of glyceryl guaiacolate ether occurred much more rapidly in ip injected male rats than in females. This sex difference in metabolism was paralleled by corresponding difference in o-demethylase activity between male & female animals.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 272
The half-life in plasma observed for guaifenesin is approximately one hour.
Guaifenesin has a plasma half-life of one hour.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference: Generics 2nd ed p.1474 (1996)
Centrally acting muscle relaxant glyceryl guaiacolate ether was found to have t/2 of 56.5 min in male rats and 88.5 min in female rats following ip administration.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 588
Although the exact mechanism of action of guaifenesin may not yet be formally or totally elucidated, it is believed that expectorants like guaifenesin function by increasing mucus secretion. Moreover, it is also further proposed that such expectorants may also act as an irritant to gastric vagal receptors, and recruit efferent parasympathetic reflexes that can elicit glandular exocytosis that is comprised of a less viscous mucus mixture. Subsequently, these actions may provoke coughing that can ultimately flush difficult to access, congealed mucopurulent material from obstructed small airways to facilitate a temporary improvement for the individual. Consequently, while it is generally proposed that guaifenesin functions as an expectorant by helping to loosen phlegm (mucus) and thin bronchial secretions to rid the bronchial passageways of bothersome mucus and make coughs more productive, there has also been research to suggest that guaifenesin possesses and is capable of demonstrating anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects to some degree possibly by acting as an NMDA receptor antagonist.
Guaifenesin is thought to act as an expectorant by increasing the volume and reducing the viscosity of secretions in the trachea and bronchi. Thus it may increase the efficiency of the cough reflex and facilitate removal of the secretions; however, objective evidence for this is limited and conflicting.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 1537
By increasing respiratory tract fluid, guaifenesin reduces the viscosity of tenacious secretions and acts as an expectorant.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007.
Guaifenesin, a commonly used agent for the treatment of cough, is termed an expectorant since it is believed to alleviate cough discomfort by increasing sputum volume and decreasing its viscosity, thereby promoting effective cough. Despite its common usage, relatively few studies, yielding contrasting results, have been performed to investigate the action and efficacy of guaifenesin. To evaluate the effect of guaifenesin on cough reflex sensitivity. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Fourteen subjects with acute viral upper respiratory tract infection (URI) and 14 healthy volunteers. On 2 separate days, subjects underwent capsaicin cough challenge 1 to 2 hr after receiving a single, 400-mg dose (capsules) of guaifenesin or matched placebo. Measurements and results: The concentration of capsaicin inducing five or more coughs (C(5)) was determined. Among subjects with URI, mean (+/- SEM) log C(5) after guaifenesin and placebo were 0.92 +/- 0.17 and 0.66 +/- 0.14, respectively (p = 0.028). No effect on cough sensitivity was observed in healthy volunteers. /The/ results demonstrate that guaifenesin inhibits cough reflex sensitivity in subjects with URI, whose cough receptors are transiently hypersensitive, but not in healthy volunteers. Possible mechanisms include a central antitussive effect, or a peripheral effect by increased sputum volume serving as a barrier shielding cough receptors within the respiratory epithelium from the tussive stimulus.
PMID:14665498 Dicpinigaitis P, Gayle Y; Chest 124 (6): 2178-81(2003)