


1. 2615-15-8
2. 3,6,9,12,15-pentaoxaheptadecane-1,17-diol
3. Hexagol
4. Hexaoxyethylene Glycol
5. Ho-peg6-oh
6. Peg-6
7. Polyethylene Glycol 300
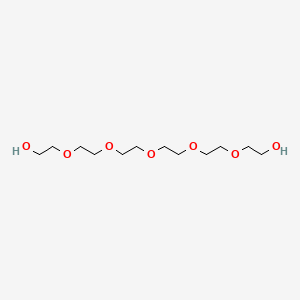
8. 2-[2-[2-[2-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethanol
9. Polyoxyethylene (6)
10. Hexaethyleneglycol
11. Nsc 201209
12. Ethanol, 2,2'-(oxybis(ethyleneoxyethyleneoxy))di-
13. Chebi:49793
14. Mfcd00002877
15. Einecs 220-045-1
16. P6g
17. Oh-peg6-oh
18. Brn 1638281
19. Ai3-01457
20. Hexa[ethylene Glycol]
21. Hexaethylene Glycol, 97%
22. 2,2'-[oxybis(ethyleneoxyethyleneoxy)]bisethanol
23. Schembl38159
24. 4-01-00-02406 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
25. Chembl1235082
26. Dtxsid2058629
27. Wln: Q2/o2/ 5q
28. Amy19025
29. Zinc4521548
30. Nsc201209
31. Akos015839803
32. Nsc-201209
33. Ncgc00159371-02
34. Ncgc00159371-03
35. As-19157
36. Bp-21034
37. Bp-21475
38. Sy024148
39. Trans-2-o-tolylcyclopropanecarboxylic Acid
40. Hy-141230
41. 3,9,12,15-pentaoxaheptadecane-1,17-diol
42. Cs-0115001
43. Ft-0602028
44. H1432
45. Hexaethylene Glycol, Purum, >=95.0% (gc)
46. Ethanol,2'-[oxybis(ethyleneoxyethyleneoxy)]di-
47. A877353
48. J-016283
49. Q27104720
50. Ethanol,2'-[oxybis(oxy-2,1-ethanediyloxy-2,1-ethanediyloxy)]bis-
51. Ethanol, 2,2'-(oxybis(oxy-2,1-ethanediyloxy-2,1-ethanediyloxy))bis-
52. 2-[2-(2-{2-[2-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-ethoxy}-ethoxy)-ethoxy]-ethanol
53. 6529-43-7
| Molecular Weight | 282.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H26O7 |
| XLogP3 | -1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 16 |
| Exact Mass | 282.16785316 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 282.16785316 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 141 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated as a lubricant in over-the-counter ophthalmic solutions to temporarily relieve redness, burning and irritation of the eyes.
PEGs act as nonionic surfactant to decrease surface tension and condition the stratum corneum, thus enhance the diffusion of other molecules or drugs through the skin.
Absorption
PEGs can be absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration with the fraction absorbed being dependent on the molecular weight of the compound. It is likely to display minimal absorption through the intact skin, but may penetrate through injured skin with compromised barrier function.
Route of Elimination
After oral and intravenous exposure, PEGs are excreted mainly unchanged in the urine and faeces.
Volume of Distribution
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Clearance
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Proportion of absorbed PEGs may be metabolized to lower oligomers, glycolic acid, hydroxyglycolic acids and the diglycolic acids homologs, carbon dioxide that is exhaled, and to a minor extent, oxalic acid.
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Due to their physical properties, PEG acts as a surfactant by coating the eye. It provides lubrication and surface protection in dry eyes.