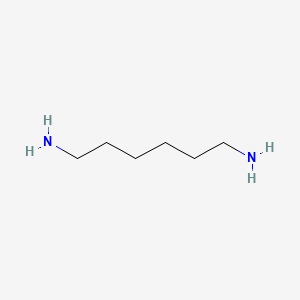

1. 1,6-diaminohexamethylene
2. 1,6-diaminohexane
3. 1,6-diaminohexane Dihydrochloride
4. 1,6-diaminohexane Dihydrochloride, 1-(11)c-labeled
5. 1,6-diaminohexane Dihydrofluoride
6. 1,6-diaminohexane Monohydrochloride
7. 1,6-hexamethylenediamine
8. 1,6-hexane Diamine
9. 1,6-hexanediamine Methanesulfonate
10. 1,6-hexylenediamine
11. Hexamethyldiamine
12. Hexamethylenediamine
13. Hexane-1,6-diamine
14. Hmda Cpd
1. 1,6-diaminohexane
2. Hexamethylenediamine
3. 124-09-4
4. Hexane-1,6-diamine
5. Hmda
6. 1,6-hexylenediamine
7. 1,6-hexamethylenediamine
8. 1,6-diamino-n-hexane
9. Hexamethylene Diamine
10. Hexylenediamine
11. Diaminohexane
12. Nci-c61405
13. 1,6-hexanediamine (solution)
14. Hex-nh2
15. Nsc 9257
16. H2n(ch2)6nh2
17. Zra5j5b2qw
18. Chembl303004
19. Amides, Vegetable-oil, N,n'-hexanediylbis-
20. Chebi:39618
21. Nsc-9257
22. Dsstox_cid_4922
23. Dsstox_rid_77583
24. Dsstox_gsid_24922
25. 73398-58-0
26. Hexane, 1,6-diamino-
27. 16d
28. Cas-124-09-4
29. Ccris 6224
30. Hsdb 189
31. Einecs 204-679-6
32. Unii-zra5j5b2qw
33. Mfcd00008243
34. Un1783
35. Un2280
36. Hexamethylenediamine Solution
37. Brn 1098307
38. Ai3-37283
39. 1,6diaminohexane
40. 6-aminohexylamine
41. 1,6 Diaminohexane
42. 1,6 Hexanediamine
43. 1.6-diaminohexane
44. 1,6-diamino Hexane
45. 1,6-hexamethylene Diamine
46. Hexamethylenediamine, Solid
47. Hexamethylenediamine, 98%
48. Ec 204-679-6
49. Wln: Z6z
50. Hexamethylene Diamine, Solid
51. Nciopen2_002722
52. Schembl15085
53. Hexamethylenediamine, Solution
54. 4-04-00-01320 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
55. Hexanemethylenediamine-
56. Un 1783 (salt/mix)
57. 1,6-hexandiamine, Vegetable Oil Fatty Acids Diamide
58. Hexamethylene Diamine, Solution
59. Hexamethylenediamine, Solution [un1783] [corrosive]
60. Schembl7090279
61. Dtxsid5024922
62. 1,6-hexanediamine [mi]
63. Nsc9257
64. 1,6-hexanediamine [inci]
65. Zinc1543408
66. Hexamethylene Diamine [hsdb]
67. Tox21_202088
68. Tox21_303123
69. Bbl027705
70. Bdbm50323740
71. Stl281875
72. Akos000118875
73. Db03260
74. Un 2280
75. Ncgc00091677-01
76. Ncgc00091677-02
77. Ncgc00257104-01
78. Ncgc00259637-01
79. Bp-21415
80. Vs-08580
81. Hexamethylenediamine, Technical Grade, 70%
82. D0095
83. Ft-0606994
84. Ft-0666352
85. Ag-690/11351767
86. Hexamethylenediamine, Saj First Grade, >=98.0%
87. Q424936
88. Hexamethylenediamine, Solid [un2280] [corrosive]
89. Hexane-1,6-diamine 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
90. J-504038
91. Z966690422
| Molecular Weight | 116.20 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H16N2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 116.131348519 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 116.131348519 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 52 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 8 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 31.5 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
.../HEXAMETHYLENE IS/ ABSORBED THROUGH THE SKIN.
Patty, F. (ed.). Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume II: Toxicology. 2nd ed. New York: Interscience Publishers, 1963., p. 2059
Following oral administration of (14)C-labeled 1,6-diaminohexane to male rats, approx 20% of the administered dose was recovered as (14)CO2 after 72 hr. Urinary and fecal excretion accounted for 47 and 27% of the administered radioactivity, respectively. Of several tissues examined, the highest concn of residual radioactivity were found in the prostate at 24 and 72 hr post-administration.
David RM, Heck HD; Localization of 1,6-(14)C diaminohexane (HMDA) in the prostate and the effects of HMDA on early gestation in Fischer-344 rats; Toxicol Lett 17 (1-2): 49-55 (1983)
An isocyanate generation apparatus was developed and stable isocyanate atmospheres were obtained. At a concn of 5 ug 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (HD) per cu m the precision was found to be 7% (n = 5). Three volunteers were each exposed to the different concn of HI (11.9, 20.5, and 22.1 micrograms/ cu m) and three concns of isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) (12.1, 17.7, and 50.7 micrograms/cu m), in an exposure chamber. The duration of the exposure was 2 hr. Urine and blood samples were collected, and hydrolyzed under alkaline conditions to the HI and IPDI corresponding amines, 1,6-hexamethylene diamine (HDA) and isophorone diamine (IPDA), determined as their pentafluoropropionic anhydride amides (HDA-PFPA and IPDA-PFPA). The HDA- and IPDA-PFPA derivatives were analyzed using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry with thermospray monitoring negative ions. When working up samples from the exposed persons without hydrolysis, no HDA or IPDA was seen. The average urinary excretion of the corresponding amine was 39% for HI and 27% for IPDI . An association between the estimated inhaled dose and the total excreted amount was seen. The average urinary elimination half-time for HDA was 2.5 hr and for IPDA, 2.8 hr. The hydrolysis condition giving the highest yield of HDA and IPDA in urine was found to be hydrolysis wi the 3 M sodium hydroxide during 4 hr. No HDA or IPDA could be found in hydrolyzed plasma (< ca 0.1 micrograms/l) .
PMID:8567087 Tinnerberg H, et al; Int Arch Occup Environ Health 67 (6): 367-74 (1995)
