


1. Aldiamed
2. Hydroxyethylcellulose
3. Hydroxyethylcellulose, Sodium Salt
4. Hydroxyl Ethyl Cellulose
5. Lacrigel
6. Minims Artificial Tears
7. Natrosol 250
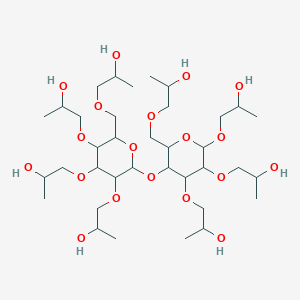
1. Hydroxyethylcellulose
2. Cellulose Hydroxyethyl Ether
3. 2-hydroxyethyl Cellulose Ether
4. Db11602
| Molecular Weight | 806.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C36H70O19 |
| XLogP3 | -3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 19 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 28 |
| Exact Mass | 806.45113000 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 806.45113000 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 263 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 55 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 986 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 18 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For alleviating surface irritation in topical ocular administrations, such as artificial tear solutions. Hydroxyethyl cellulose is also found in topical formulations to aid in more efficient drug diffusion across the membranes.
Hydroxyethyl cellulose acts as a demulcent by relieving inflammation or irritation and dryness of eyes. It acts as one of the key ingredient and viscosity-enhancing agent to prolong corneal contact time and increase intraocular drug levels.
Interacts with the solid surface through hydrogen bonding to thicken and prolong the formation time of a water-retaining film. Hydroxyethyl cellulose acts as a drug carrier or microsphere to entrap other drug molecules and form a viscous gel-like dispersion, enabling drug diffusion across biological membranes.