


1. Ethyleneglycolmonosalicylic Acid Ester
2. Glycol Monosalicylate
3. Glycol Salicylate
4. Hydroxyethyl Salicylate
5. Menthoneurin
1. 87-28-5
2. Glycol Salicylate
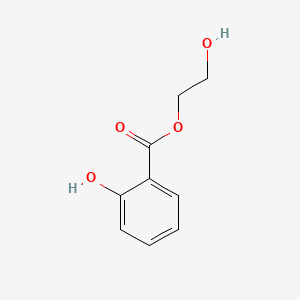
3. 2-hydroxyethyl 2-hydroxybenzoate
4. Ethylene Glycol Monosalicylate
5. Espirosal
6. Glycol Monosalicylate
7. Rheumacyl
8. Sarocol
9. Spirosal
10. Glysal
11. Ethylene Glycol Salicylate
12. Phlogont
13. Monoglycol Salicylate
14. Gl 7
15. Benzoic Acid, 2-hydroxy-, 2-hydroxyethyl Ester
16. Glykolsalicylat
17. Traumasenex
18. Ethylene Glycol, Salicylate
19. Kytta-gel
20. Ethylene Glycol, Monosalicylate
21. 1,2-ethylene Glycol Monosalicylate
22. Aethylenglykolsalicylat
23. Hydroxyethyl Salicylate
24. 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid 2-hydroxyethyl Ester
25. Salicylic Acid, 2-hydroxyethyl Ester
26. Ethylenglycol-monosalicylsaeureester
27. Nsc-72097
28. 3i1vbb7axh
29. .beta.-hydroxyethyl Salicylate
30. Chebi:86541
31. 2-hydroxyethyl 2-oxidanylbenzoate
32. Mfcd00002862
33. Ncgc00159379-03
34. 2-hydroxybenzoic Acid, 2-hydroxyethyl Ester
35. Glycol Salicylate (jan)
36. Glycol Salicylate [jan]
37. Unii-3i1vbb7axh
38. Norgesic (tn)
39. Phlogont (tn)
40. Einecs 201-737-2
41. Nsc 72097
42. Ai3-05033
43. 2-hydroxyethyl-salicylate
44. Bmse000750
45. Dsstox_cid_28913
46. Dsstox_rid_83181
47. Dsstox_gsid_48987
48. Schembl15402
49. Salicylic Acid Ethylene Glycol
50. Glycol Salicylate [mi]
51. Chembl173562
52. Dtxsid4048987
53. Glycol Salicylate [inci]
54. Lvylcbnxhhhpsb-uhfffaoysa-
55. Glycol Salicylate [mart.]
56. Glycol Salicylate [who-dd]
57. Cs-b1707
58. Hy-b2208
59. Nsc72097
60. Zinc1698306
61. Salicylic Acid 2-hydroxyethyl Ester
62. Tox21_113462
63. Akos009075810
64. Db11323
65. Cas-87-28-5
66. Ncgc00159379-02
67. Ncgc00159379-04
68. 2-hydroxy-benzoicacid2-hydroxyethyl Ester
69. Sy032913
70. E0113
71. Ft-0626298
72. Salicylic Acid, 2-hydroxyethyl Ester (8ci)
73. Hydroxyethyl Salicylate [ep Monograph]
74. D01557
75. E78954
76. Ethylene Glycol Monosalicylate, >=98.0% (gc)
77. A842078
78. Q117422
79. Sr-01000944719
80. Sr-01000944719-1
81. W-104034
82. Hydroxyethyl Salicylate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 182.17 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 182.05790880 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 182.05790880 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 66.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 169 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
This drug is only recommended for topical usages for the relief of muscular and rheumatic pain in human and animals.
Temporarily relieves minor to moderate aches and pains. Works with ingredients such as menthol, which has counter-irritant properties. Counter-irritants are externally applied, and lead to irritation or mild inflammation of the skin to relieve pain in muscles or joints by reducing inflammation in deeper adjacent structures. Counter-irritants relieve pain by disrupting the brain from receiving pain signals resulting from conditions such as osteoarthritis (OA) or injuries such as sprains or strains. These agents may cause vasodilatation or skin irritation, leading to a false sensation of heat or warmth.
Absorption
Salicylate absorption follows first-order kinetics with an absorption half-life ranging from 5 to 16 minutes.
Route of Elimination
Salicylates are generally excreted.
The metabolism of glycol salicylate is similar to that of [DB00945] at other salicylates. Metabolism of salicylic acid occurs through glucuronide formation (to produce salicyl acyl glucuronide and salicyl phenolic glucuronide), conjugation with glycine (to produce salicyluric acid), and oxidation to gentisic acid. The rate of formation of salicyl phenolic glucuronide and salicyluric acid are readily saturated at low salicylic acid concentrations and their formation is described by Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The larger the dose administered, the longer it will take to reach steady-state concentrations of salicylates. There is also evidence that enzyme induction of salicyluric acid formation occurs during the metabolism of salicylates.
The serum half-life of [DB00945], a similar salicylate, is 20 min.
Similar to other salicylates. Salicylates and other analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs, particularly the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) mainly used in rheumatology, inhibit cyclooxygenase, therefore reducing prostaglandin synthesis.
