
1. Cal 101
2. Cal-101
3. Cal101
4. Gs-1101
5. Zydelig
1. 870281-82-6
2. Cal-101
3. Zydelig
4. Gs-1101
5. Cal 101
6. Cal101
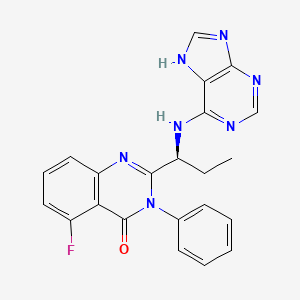
7. (s)-2-(1-((9h-purin-6-yl)amino)propyl)-5-fluoro-3-phenylquinazolin-4(3h)-one
8. 1146702-54-6
9. Idelalisib (cal-101)
10. Cal-101 (idelalisib, Gs-1101)
11. Gs 1101
12. (s)-2-(1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)propyl)-5-fluoro-3-phenylquinazolin-4(3h)-one
13. 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-((s)-1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)-propyl)-3h-quinazolin-4-one
14. Yg57i8t5m0
15. Chembl2216870
16. Chebi:82701
17. Idelalisib; Cal-101
18. 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-((1s)-1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)propyl)-4(3h)-quinazolinone
19. 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-[(1s)-1-(7h-purin-6-ylamino)propyl]quinazolin-4-one
20. 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-[(1s)-1-(3h-purin-6-ylamino)propyl]quinazolin-4(3h)-one
21. 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-[(1s)-1-(7h-purin-6-ylamino)propyl]quinazolin-4(3h)-one
22. 1453810-72-4
23. Idelalisib [inn]
24. Idelalisib [usan:inn]
25. Unii-yg57i8t5m0
26. Idealisib
27. Zydelig (tn)
28. Idelalisib [mi]
29. Idelalisib [jan]
30. Idelalisib [usan]
31. Idelalisib [vandf]
32. Idelalisib [who-dd]
33. Mls006010985
34. Idelalisib (jan/usan/inn)
35. Schembl356400
36. Gtpl6741
37. Idelalisib [orange Book]
38. Schembl16782604
39. Hsdb 8408
40. Amy9239
41. Cal-101/cal101
42. Ex-a330
43. Gs-11cal-101
44. Bcpp000307
45. Dtxsid701007266
46. Bcp02532
47. Ex-a1242
48. Bdbm50403068
49. Mfcd19443647
50. Nsc759224
51. Nsc762828
52. Nsc800771
53. S2226
54. Zinc13986658
55. Akos022186334
56. Idelalisib (cal-101,gs-1101)
57. Bcp9000471
58. Ccg-264949
59. Cs-0256
60. Db09054
61. Nsc-759224
62. Nsc-762828
63. Nsc-800771
64. Cal-101 (gs-1101)
65. Ncgc00262603-01
66. Ncgc00262603-02
67. Ncgc00262603-04
68. Ac-28394
69. Ac-36641
70. Hy-13026
71. Ic489666
72. Smr004702787
73. Sw219823-1
74. A-1138
75. D10560
76. J-517532
77. Q5908266
78. Brd-k60866521-001-01-4
79. (s)-5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-[1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)-propyl]-3h-quinazolin-4-one
80. 4(3h)-quinazolinone, 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-((1s)-1-(1h-purin-6-ylamino)propyl)-
81. 4(3h)-quinazolinone, 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-((1s)-1-(9h-purin-6-ylamino)propyl)-
82. 4(3h)-quinazolinone,5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-[(1s)-1-(1h-purin-6-ylamino)propyl]-
83. 40l
| Molecular Weight | 415.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H18FN7O |
| XLogP3 | 3.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 415.15568639 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 415.15568639 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 99.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 685 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zydelig |
| PubMed Health | Idelalisib (Oral route) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Idelalisib is an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, PI3K.The chemical name for idelalisib is 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-[(1S)-1-(9H-purin-6-ylamino)propyl]quinazolin-4(3H)-one. It has a molecular formula of C22H18FN7O and a molecular weight of 41... |
| Active Ingredient | Idelalisib |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 150mg; 100mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Gilead Sciences |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Zydelig |
| PubMed Health | Idelalisib (Oral route) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Idelalisib is an inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, PI3K.The chemical name for idelalisib is 5-fluoro-3-phenyl-2-[(1S)-1-(9H-purin-6-ylamino)propyl]quinazolin-4(3H)-one. It has a molecular formula of C22H18FN7O and a molecular weight of 41... |
| Active Ingredient | Idelalisib |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 150mg; 100mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Gilead Sciences |
Antineoplastic Agents; Enzyme Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Idelalisib. Online file (MeSH, 2018). Available from, as of March 7, 2018: https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Idelalisib is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of March 7, 2018: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Zydelig is indicated, in combination with rituximab, for the treatment of patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) for whom rituximab alone would be considered appropriate therapy due to other co-morbidities. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
Zydelig is indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsed follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (FL) who have received at least two prior systemic therapies. Accelerated approval was granted for this indication based on Overall Response Rat. An improvement in patient survival or disease related symptoms has not been established. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
Zydelig is indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsed small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) who have received at least two prior systemic therapies. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: HEPATIC. Fatal and/or serious hepatotoxicity occurred in 16% to 18% of Zydelig-treated patients. Monitor hepatic function prior to and during treatment. Interrupt and then reduce or discontinue Zydelig as recommended.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: SEVERE DIARRHEA, COLITIS. Fatal and/or serious and severe diarrhea or colitis occurred in 14% to 20% of Zydelig-treated patients. Monitor for the development of severe diarrhea or colitis. Interrupt and then reduce or discontinue Zydelig as recommended.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: PNEUMONITIS. Fatal and/or serious pneumonitis occurred in 4% of Zydelig-treated patients. Monitor for pulmonary symptoms and bilateral interstitial infiltrates. Interrupt or discontinue Zydelig as recommended.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: FATAL AND SERIOUS TOXICITIES: INFECTIONS. Fatal and/or serious infections occurred in 21% to 48% of Zydelig-treated patients. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection. Interrupt Zydelig if infection is suspected.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Idelalisib (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Idelalisib is indicated in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), relapsed follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (FL), and relapsed small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). For the treatment of relapsed CLL, it is currently indicated as a second-line agent in combination with rituximab in patients for whom rituximab alone would be considered appropriate therapy due to other co-morbidities, while in the treatment of FL and SLL it is intended to be used in patients who have received at least two prior systemic therapies.
FDA Label
Zydelig is indicated in combination with an antiCD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab or ofatumumab) for the treatment of adult patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL):
- who have received at least one prior therapy, or
- as first line treatment in the presence of 17p deletion or TP53 mutation in patients who are not eligible for any other therapies.
Zydelig is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) that is refractory to two prior lines of treatment.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
L01XX47
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EM - Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (pi3k) inhibitors
L01EM01 - Idelalisib
Absorption
Following oral administration, the median Tmax was observed at 1.5 hours.
Route of Elimination
Following a single dose of 150 mg of [14C] idelalisib, 78% and 14% of the radioactivity was excreted in feces and urine, respectively. GS-563117, idelalisib's major metabolite, accounted for 49% of the radioactivity in the urine and 44% in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
23 L
Clearance
14.9 L/hr
Following oral administration of a single 150-mg dose of radiolabeled idelalisib, 78% of the dose was recovered in feces and 14% was recovered in urine; GS-563117 accounted for 44% of the dose recovered in feces and 49% of the dose recovered in urine.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 1175
The administration of a single dose of Zydelig with a high-fat meal (900 calories: 525 calories fat, 250 calories carboydrates, and 125 calories protein) increased idelalisib AUC 1.4-fold relative to fasting conditions. Zydelig can be administered without regard to food.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
The median time to peak concentration (Tmax) was observed at 1.5 hours.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
Idelalisib is metabolized by aldehyde oxidase and CYP3A to its major metabolite GS-563117, which is inactive against P110. Idelalisib is also metabolized to a minor extent by UGT1A4.
Idelalisib, a potent phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase delta (PI3Kd) inhibitor, is metabolized primarily by aldehyde oxidase to form GS-563117 and to a lesser extent by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A and uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase 1A4. In vitro, idelalisib inhibits P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and organic anion transporting polypeptides 1B1 and 1B3, and GS-563117 is a time-dependent CYP3A inhibitor. This study enrolled 24 healthy subjects and evaluated (1) the effect of idelalisib on the pharmacokinetics (PK) of digoxin, a P-gp probe substrate, rosuvastatin, a breast cancer resistance protein, and OATP1B1/OATP1B3 substrate, and midazolam, a CYP3A substrate; and (2) the effect of a strong inducer, rifampin, on idelalisib PK. On treatment, the most common clinical adverse events (AEs) were headache and pyrexia. Grade 3 transaminase increases were observed in 5 of 24 subjects and were reversible. Two subjects had serious AEs after treatment completion (grade 3 pyrexia and/or drug-induced liver injury). Idelalisib coadministration did not affect digoxin and rosuvastatin PK. Coadministration with idelalisib increased plasma exposures of midazolam (138% and 437% for maximum observed plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 extrapolated to infinity (AUCinf), respectively), consistent with the in vitro finding of CYP3A inhibition by GS-563117. Rifampin caused a substantial decrease in idelalisib (58% and 75%, Cmax and AUCinf , respectively) and GS-563117 exposures, indicating an enhanced contribution of CYP3A to idelalisib metabolism under a strongly induced state.
PMID:25760671 Jin F et al; J Clin Pharmacol 55 (8): 909-19 (2015)
Idelalisib is more than 84% bound to plasma proteins. Idelalisib is metabolized to its major metabolite, GS-563117, principally by cytochrome P-450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A and aldehyde oxidase; the drug is metabolized only to a minor extent by uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyl transferase (UGT) 1A4.1 GS-563117 is inactive against PI3Kdelta in vitro.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 1175
Idelalisib is metabolized via aldehyde oxidase and CYP3A with additional minor metabolism by UGT1A4.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50
The terminal elimination half-life is 8.2 hours.
The mean terminal half-life of idelalisib is 8.2 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 1175
Idelalisib specifically inhibits P110, the delta isoform of the enzyme phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, also known as PI-3K. The PI-3Ks are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer. In contrast to the other class IA PI3Ks p110 and p110, p110 is principally expressed in leukocytes (white blood cells) and is important for the function of T cells, B cell, mast cells and neutrophils. By inhibiting this enzyme, idelalisib induces apoptosis of malignant cells and inhibits several cell signaling pathways, including B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling and C-X-C chemokine receptors type 5 and type 4 signalling, which are involved in trafficking and homing of B-cells to the lymph nodes and bone marrow. Treatment of lymphoma cells with idelalisib has been shown to result in inhibition of chemotaxis and adhesion, and reduced cell viability.
Idelalisib is an inhibitor of PI3Kdelta kinase, which is expressed in normal and malignant B-cells. Idelalisib induced apoptosis and inhibited proliferation in cell lines derived from malignant B-cells and in primary tumor cells. Idelalisib inhibits several cell signaling pathways, including B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling and the CXCR4 and CXCR5 signaling, which are involved in trafficking and homing of B-cells to the lymph nodes and bone marrow. Treatment of lymphoma cells with idelalisib resulted in inhibition of chemotaxis and adhesion, and reduced cell viability.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Zydelig (Idelalisib) Tablet, Film-coated (Updated: February 8, 2017). Available from, as of March 28, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=efbdafa9-d18c-4e85-b4a2-1e620fc74e50