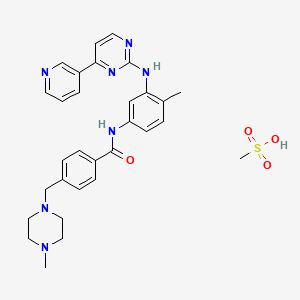

1. Alpha-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-3'-((4-(3-pyridyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)-p-tolu-p-toluidide
2. Cgp 57148
3. Cgp-57148
4. Cgp57148
5. Cgp57148b
6. Gleevec
7. Glivec
8. Imatinib
9. Imatinib Methanesulfonate
10. Mesylate, Imatinib
11. Methanesulfonate, Imatinib
12. St 1571
13. St1571
14. Sti 571
15. Sti-571
16. Sti571
1. 220127-57-1
2. Gleevec
3. Glivec
4. Imatinib Mesilate
5. Sti-571
6. Imatinib Methanesulfonate
7. Imatinib Mesylate (sti571)
8. Imatinib (mesylate)
9. Imatinib Accord
10. Imatinib Medac
11. Cgp-57148b
12. Imatinib Monomesylate
13. Nsc-716051
14. Sti 571
15. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide Monomethanesulfonate
16. Qti-571
17. St-1571 Mesylate
18. Cgp 57148b
19. Imatinib (as Mesilate)
20. 220127-57-1 (mesylate)
21. Imatinib Methane Sulfonate
22. Imatinib Mesylate [usan]
23. Qti571
24. N-(4-methyl-3-((4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamide Methanesulfonate
25. Chebi:31690
26. 8a1o1m485b
27. Mfcd04307699
28. Imatinib Mesilate (jan)
29. Imatinib Mesylate (usan)
30. Dsstox_cid_20502
31. Dsstox_rid_79501
32. Dsstox_gsid_40502
33. Imatinib Methansulfonate
34. N-(4-methyl-3-(4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-ylamino)phenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamide Methanesulfonate
35. Imatinib Mesilate [jan]
36. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]benzamide Methanesulfonate
37. Benzamide, 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-, Methanesulfonate (1:1)
38. Cas-220127-57-1
39. Cgp-57148
40. Ncgc00159456-02
41. Gleevec (imatinib Mesylate)
42. Gleevac
43. Shantinib
44. Imatinibmesylate
45. Imatinib, Methanesulfonate Salt
46. Hsdb 7142
47. Gleevec (tn)
48. Imatinib(free Base)
49. Glivec (tn)
50. Schembl8217
51. Imatinib Monomethanesulfonate
52. Chembl1642
53. Benzamide,monomethanesulfonate
54. Imatinib Methanesulfonate Salt
55. Mls001401456
56. Unii-8a1o1m485b
57. Dtxsid9040502
58. Imatinib Mesylate [hsdb]
59. Ex-a954
60. Imatinib Mesylate [vandf]
61. Imatinib Mesilate [mart.]
62. Bcpp000204
63. Ggp-57148b
64. Hms2052b09
65. Hms2233d16
66. Hms3265e01
67. Hms3265e02
68. Hms3265f01
69. Hms3265f02
70. Hms3372o12
71. Hms3394b09
72. Hms3654c07
73. Imatinib Mesilate [who-dd]
74. Act05102
75. Bcp01255
76. Tox21_111684
77. Ac-525
78. Nsc716051
79. S1026
80. Imatinib Methanesulfonate [mi]
81. Akos015852497
82. Tox21_111684_1
83. Bcp9000776
84. Ccg-101175
85. Imatinib Mesylate [orange Book]
86. Ks-1236
87. Nc00425
88. Nsc 716051
89. Imatinib Mesilate [ep Monograph]
90. Ncgc00159456-11
91. 111ge005
92. Benzamide, 4-((4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl)-n-(4-methyl-3-((4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)phenyl)-, Monomethanesulfonate
93. Bi164678
94. Hy-50946
95. Methanesulfonic Acid; 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl]benzamide
96. Methanesulfonic Acid;4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl]benzamide
97. Smr000469175
98. Sy013513
99. Am20080900
100. Ft-0601612
101. I0936
102. Sw197805-4
103. Ec-000.2338
104. D01441
105. Imatinib Mesylate (cgp-57148b, Sti-571)
106. 127i571
107. A815828
108. A846640
109. J-523068
110. Q-201232
111. Q27114666
112. Imatinib Mesylate,gleevec,glivec,cgp-57148b,sti-571
113. 4-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-n-[4-methyl-3-(4-pyridin- 3-yl)-pyrimidin-2-ylamino)-phenyl]-benzamidemethanesulfonic Acid Salt
114. 4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-ylmethyl)-n-[4-methyl-3-(4-pyridin-3-yl-pyrimidin-2-ylamino)phenyl]benzamide Methanesulfonic Acid Salt
115. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-methyl]-n-{4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]-amino]-phenyl}-benzamide Monomethanesulphonate
116. 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]-phenyl]benzamide Methanesulfonate
117. 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-(4-methyl-3-{[4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}phenyl)benzamide Methanesulfonate
118. 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-{4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl}benzamide Methanesulfonate
119. Benzamide, 4-((4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl)-n-(4-methyl-3-((4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)aminophenyl)-, Methanesulfonate Salt
120. Benzamide, 4-((4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl)-n-(4-methyl-3-((4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl)aminophenyl)-, Methanesulphonate Salt
121. Hydron;methanesulfonate;4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl]benzamide
122. Methanesulfonic Acid; 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-n-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]benzamide
123. N-(4-methyl-3-((4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)-4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)benzamidemethanesulfonate
| Molecular Weight | 589.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C30H35N7O4S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 589.24712380 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 589.24712380 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 149 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 42 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 799 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gleevec |
| PubMed Health | Imatinib (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Immunological Agent |
| Drug Label | Imatinib is a small molecule kinase inhibitor. Gleevec film-coated tablets contain imatinib mesylate equivalent to 100mg or 400 mg of imatinib free base. Imatinib mesylate is designated chemically as 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3... |
| Active Ingredient | Imatinib mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 100mg base; eq 400mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Imatinib mesylate |
| Drug Label | Imatinib is a small molecule kinase inhibitor. Gleevec film-coated tablets contain imatinib mesylate equivalent to 100mg or 400 mg of imatinib free base. Imatinib mesylate is designated chemically as 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3... |
| Active Ingredient | Imatinib mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | 400mg; 100mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Sun Pharm Inds |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Gleevec |
| PubMed Health | Imatinib (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Immunological Agent |
| Drug Label | Imatinib is a small molecule kinase inhibitor. Gleevec film-coated tablets contain imatinib mesylate equivalent to 100mg or 400 mg of imatinib free base. Imatinib mesylate is designated chemically as 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3... |
| Active Ingredient | Imatinib mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 100mg base; eq 400mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Imatinib mesylate |
| Drug Label | Imatinib is a small molecule kinase inhibitor. Gleevec film-coated tablets contain imatinib mesylate equivalent to 100mg or 400 mg of imatinib free base. Imatinib mesylate is designated chemically as 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3... |
| Active Ingredient | Imatinib mesylate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | 400mg; 100mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Sun Pharm Inds |
Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec), ... /an/ inhibitor of abl, kit, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) tyrosine kinases, has been reported to be effective in the treatment of hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and a rare eosinophilia-associated chronic myeloid disorder (eos-CMD) characterized by the t(5;12)(q33;p13) cytogenetic abnormality. In the current study, we sought to confirm the preliminary observations in HES as well as evaluate the therapeutic value of imatinib in eos-CMD that is not associated with t(5;12)(q33;p13). Five patients with HES (all men, median age = 46 years) and 2 with eos-CMD (both men, aged 45 and 58 years) were treated with imatinib at a starting dose of 100 to 400 mg/day. Cytogenetic studies showed no evidence of either the bcr-abl translocation or t(5;12)(q33;p13) in any patient. Screening of exons encoding the intracellular catalytic domains and extracellular ligand binding domains of PDGFR beta (exons 2-23) and c-kit (exons 1-21) in six patients demonstrated mostly previously known polymorphisms. At a median follow-up of 17 weeks (range, 10-33 weeks), 2 patients with HES and 1 with eos-CMD have achieved complete clinical remission and 1 additional patient with HES has achieved a partial remission. In contrast to previous observations, all four responding patients had elevated serum interleukin-5 levels.
PMID:12506022 Pardanani AD et al; Blood 101 (9): 3391-7 (2003)
/A study was conducted to include/ 28 patients with accelerated phase chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) ... . Diagnosis of accelerated phase CML was based on karyotypic evolution (n = 9) and hematologic criteria (n = 18). All patients were begun on 600 mg/day of imatinib mesylate. Dose reductions to 400 mg/day and then 300 mg/day were prescribed for an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of <0.5/microl or a platelet count of <20,000/microl. Twenty-seven of the 28 patients continued treatment for a median of 34 weeks. Eleven patients developed thrombocytopenia following an average of 8.4 +/- 1.4 weeks of therapy. The onset of thrombocytopenia was associated with disease progression in one patient and a decline in bone marrow megakaryocytes in the other 10. Nine patients recovered to a platelet count of >20,000/microl after an average of 19.7 +/- 1.8 weeks. Patients who developed thrombocytopenia had a longer duration of disease (9.39 vs. 4.35 years; P < 0.01) and were more likely to be diagnosed with accelerated phase CML by hematologic criteria. Hematologic responses in patients with and without thrombocytopenia were comparable; however, 31.3% of patients without thrombocytopenia had a complete cytogenetic response compared to none of those with thrombocytopenia. Grade III-IV thrombocytopenia is common in accelerated phase CML and may be a marker for the inability to achieve cytogenetic response using single agent imatinib mesylate.
PMID:12410573 van Deventer HW et al; Am J Hematol 71 (3): 184-90 (2002)
Imatinib is indicated for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). /NOT included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1520
Imatinib is indicated for the treatment of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (MCL) in blast crisis; accelerated phase, or in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy. (NOTE: Effectiveness is based on overall hematologic and cytogenetic response rates. There are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit, such as improvement in disease-related symptoms or increased survival.) /Included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1520
Imatinib mesylate (STI571, Gleevec, Glivec, a selective inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase causative of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), represents the paradigm of how a better understanding of the pathogenetic mechanisms of a neoplastic disease can lead to the development of a targeted molecular therapy. Phase II clinical trials have shown marked therapeutic activity of imatinib in all evolutive phases of CML, but notably in the chronic phase, where it induces complete hematological responses in almost 100% of patients resistant or intolerant to interferon, with a major cytogenetic response rate of 60%, including 41% complete cytogenetic responses. The preliminary results of an ongoing phase III multicenter randomized study comparing imatinib with interferon plus cytarabine as first-line treatment for CML favor imatinib in terms of efficacy and safety. If confirmed with longer follow-up,these results would establish imatinib as the choice therapy for the majority of CML patients, with allogeneic transplantation being restricted as initial therapy only to younger patients with a family donor.
PMID:12582448 Hernandez-Boluda JC, Cervantes F; Drugs Today 38 (9): 601-13 (2002)
Imatinib mesylate blocks bcr/abl kinase activity effectively, and thus is a promising drug in Philadelphia chromosome positive leukemias. While under imatinib treatment high hematological and cytogenetic response rates could be observed, usually only mild non-hematological side-effects like skin rash, edema, and muscular cramps occur. ... Two severe cases of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to imatinib /are reported/. In both patients the generalized pustular eruptions could be observed 12 wk after initiation of imatinib treatment. Numerous microbiological investigations excluded an infectious etiology, and histopathology of cutaneous lesions was consistent with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. ... Withdrawal of imatinib led to a restitution at integrum of the integument. ...
Schwarz M et al; Eur J Hematol 69 (4): 254-6 (2002)
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (STI571, Gleevec) has recently been applied in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. /A/ ... case of pityriasis rosea occurring as a reaction to Gleevec in a woman with blast crisis of this disorder /is detailed/.
PMID:12218236 Konstantopoulos K et al; Dermatology 205 (2): 172-3 (2002)
Imatinib or STI 571 is ... a member of a new class of drugs known as signal transduction inhibitors. These compounds specifically inhibit the proliferation of v-abl- and bcr-abl-expressing cells and have recently been approved as treatment for chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML). ... An erosive oral lichenoid eruption confined to the buccal mucosa and dorsum of the tongue which appeared 12 weeks after commencement of imatinib in a 72-year-old woman with CML /is presented/. The histology was consistent with a lichenoid drug eruption. The lesions resolved upon withdrawal of the drug.
PMID:12218235 Lim DS, Muir J; Dermatology 205 (2): 169-71 (2002)
Adverse effects occurring in 10% or more of patients include nausea, vomiting, edema, muscle cramps, diarrhea, GI or CNS hemorrhage, musculoskeletal pain, rash, headache, fatigue, arthralgia, dyspepsia, myalgia, weight increase, pyrexia, abdominal pain, cough, dyspnea, anorexia, constipation, nasopharyngitis, night sweats, pruritus, epistaxis, hypokalemia, petechiae, pneumonia, and weakness.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1027
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for IMATINIB MESYLATE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Glivec is indicated for the treatment of
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia-chromosome (bcr-abl)-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone-marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment;
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis;
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia-chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy;
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy;
- adult patients with myelodysplastic / myeloproliferative diseases (MDS / MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements;
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and / or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFRa rearrangement.
The effect of Glivec on the outcome of bone-marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Glivec is indicated for:
- the treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117)-positive unresectable and / or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST);
- the adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment;
- the treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and / or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of Glivec is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS / MPD, on haematological response rates in HES / CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and / or metastatic GIST and DFSP and on recurrence-free survival in adjuvant GIST. The experience with Glivec in patients with MDS / MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited (see section 5. 1). Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib medac is indicated for the treatment of:
- paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment;
- paediatric patients with Ph+CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase;
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+CML in blast crisis;
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ALL) integrated with chemotherapy;
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ALL as monotherapy;
- adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements;
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement;
- adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
The effect of imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic DFSP.
The experience with imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited. Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib Accord is indicated for the treatment of
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment.
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy.
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy.
- adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement.
- adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
- the treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST).
- the adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment
The effect of imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic DFSP. The experience with imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited (see section 5. 1). Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Imatinib Teva B. V. is indicated for the treatment of:
- Paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment.
- Paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
- Adult patients with Ph+ CML in blast crisis.
- Adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy.
- Adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy.
- Adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
- Adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement.
The effect of imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Imatinib Teva B. V. is indicated for:
- The treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST).
- The adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment.
- The treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic GIST and DFSP and on recurrence-free survival in adjuvant GIST. The experience with imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited. There are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, Hypereosinophilic syndrome and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia with FIP1L1-platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha gene re-arrangement, Kit (CD 117)-positive gastrointestinal stromal tumours, Myelodysplastic / myeloproliferative diseases associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor gene re-arrangements, Philadelphia chromosome (BCR-ABL translocation)-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, Philadelphia chromosome (BCR-ABL translocation)-positive chronic myeloid leukaemia
Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Imatinib Koanaa is indicated for the treatment of
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome (bcr-abl) positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) for whom bone marrow transplantation is not considered as the first line of treatment.
- adult and paediatric patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, or in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
- adult and paediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Ph+ ALL) integrated with chemotherapy.
- adult patients with relapsed or refractory Ph+ ALL as monotherapy.
- adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
- adult patients with advanced hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukaemia (CEL) with FIP1L1-PDGFR rearrangement.
The effect of Imatinib on the outcome of bone marrow transplantation has not been determined.
Imatinib Koanaa is indicated for
- the treatment of adult patients with Kit (CD 117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST).
- the adjuvant treatment of adult patients who are at significant risk of relapse following resection of Kit (CD117)-positive GIST. Patients who have a low or very low risk of recurrence should not receive adjuvant treatment.
- the treatment of adult patients with unresectable dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) and adult patients with recurrent and/or metastatic DFSP who are not eligible for surgery.
In adult and paediatric patients, the effectiveness of Imatinib is based on overall haematological and cytogenetic response rates and progression-free survival in CML, on haematological and cytogenetic response rates in Ph+ ALL, MDS/MPD, on haematological response rates in HES/CEL and on objective response rates in adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic GIST and DFSP and on recurrence-free survival in adjuvant GIST. The experience with Imatinib in patients with MDS/MPD associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangements is very limited (see section 5. 1). Except in newly diagnosed chronic phase CML, there are no controlled trials demonstrating a clinical benefit or increased survival for these diseases.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Agents that inhibit PROTEIN KINASES. (See all compounds classified as Protein Kinase Inhibitors.)
L01EA01
L01XE01
L01EA01
L01XE01
L01EA01
Imatinib is well absorbed after oral administration with Cmax achieved within 2-4 hours post-dose. Mean absolute bioavailability for the capsule formulation is 98%. Following oral administration in healthy volunteers, the elimination half-lives of imitanib and its major active metabolite, the N-desmethyl derivative, were approximately 18 and 40 hours, respectively. Mean imatinib AUC increased proportionally with increasing dose in the range 25 mg-1000 mg. There was no signficant change in the pharmacokinetics of imatinib on repeated dosing, and accumulation is 1.5-2.5 fold at steady state when Gleevec is dosed once daily. At clinically relevant concentrations of imatinib, binding to plasma proteins in in vitro experiments is approximately 95%, mostly to albumin and (alpha)1-acid glycoprotein.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference on line version as of July 24, 2003
Fecal /elimination/ - 68% within 7 days (20% of dose unchanged); Renal /elimination/ - 13% within 7 days (5% of dose unchanged).
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1520
Typically, clearance of imitanib in a 50-year-old patient weighing 50 kg is expected to be 8 L/hr, while for a 50-year-old patient weighing 100 kg the clearance will increase to 14 L/hr. However, the inter-patient variability of 40% in clearance does not warrant initial dose adjustment based on body weight and/or age but indicates the need for close monitoring for treatment related toxicity.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference on line version as of July 24, 2003
In lactating female rats administered 100 mg/kg ... imatinib and/or its metabolites were extensively excreted in milk. It is estimated that approximately 1.% of a maternal dose is excreted into milk, which is equivalent to a dose to the infant of 30% the maternal dose per unit body weight.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference on line version as of July 24, 2003
CYP3A4 is the major enzyme responsible for metabolism of imatinib. Other cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19, play a minor role in its metabolism. The main circulating active metabolite in humans is the N-demethylated piperazine derivative, formed predominantly by CYP3A4. It shows in vitro potency similar to imatinib. The plasma AUC for this metabolite is about 15% of the AUC for imatinib.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference on line version as of July 24, 2003
Elimination - Approximately 18 and 40 hours, for imatinib and its primary metabolite, respectively.
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1520
Imatinib mesylate is a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase, the constitutive abnormal tyrosine kinase created by the Philadelphia chromosome abnormality in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in Bcr-Abl positive cell lines as as well as fresh leukemic cells from Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia. In colony formation assays using ex vivo peripheral blood and bone marrow samples, imatinib shows inhibition of Bcr-Abl positive colonies from CML patients.In vivo, it inhibits tumor growth of Bcr-Abl transfected murine myeloid cells as well as Bcr-Abl positive leukemia lines derived from CML patients in blast crisis.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference on line version as of July 24, 2003
Imatinib is also an inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinases for platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and stem cell factor (SCF), c-kit, and inhibits PDGF=and SCF-mediated cellular events, In vitro, imatinib inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) cells, which express an activating c-kit mutation.
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference on line version as of July 24, 2003