


1. 114311-32-9
2. Pulsar
3. Raptor
4. Imazamox [iso]
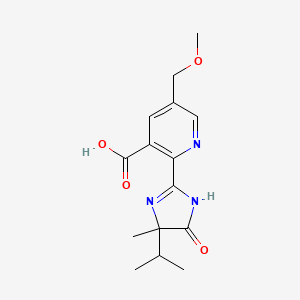
5. 3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid, 2-[4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1h-imidazol-2-yl]-5-(methoxymethyl)-
6. Mfcd03427427
7. 5-(methoxymethyl)-2-(4-methyl-5-oxo-4-propan-2-yl-1h-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
8. Ug6793on5f
9. Dtxsid3034664
10. Chebi:83742
11. 2-(4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid
12. 2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-5-(methoxymethyl)pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
13. 2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-5-(methoxymethyl)nicotinic Acid
14. 2-(5-isopropyl-5-methyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-5-(methoxymethyl)nicotinic Acid
15. 2-[4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1h-imidazol-2-yl]-5-(methoxymethyl)-3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid
16. 3-pyridinecarboxylic Acid, 2-(4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)-5-oxo-1h-imidazol-2-yl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-
17. Raptor (herbicide)
18. (+-)-imazamox
19. Cl29926;(+/-)-imazamox
20. Hsdb 7013
21. Unii-ug6793on5f
22. Ac 299263
23. Cl 299263
24. Einecs Annex I Index 613-208-00-7
25. Imazamox (standard)
26. Imazamox 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
27. Imazamox [mi]
28. Raptor [hsdb]
29. Sweeper 70dg
30. 5-methoxymethyl-2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl)nicotinic Acid
31. Cl29926;()-imazamox
32. Schembl18640
33. (+/-)-imazamox
34. Chembl1881028
35. Dtxcid1014664
36. Schembl22939437
37. Glxc-25871
38. Tox21_301007
39. Akos015895776
40. Akos040741871
41. Cs-5783
42. Hy-100427r
43. Ncgc00163955-01
44. Ncgc00163955-02
45. Ncgc00163955-03
46. Ncgc00254909-01
47. As-13848
48. Ac-299263
49. Cl-299263
50. Db-041210
51. Hy-100427
52. Cas-114311-32-9
53. Imazamox, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
54. Ns00000438
55. C18598
56. F21405
57. J-003080
58. Q17166948
59. 2-[4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl]-5-methoxymethylnicotinic Acid
60. 5-methoxymethyl-2-(4-isopropyl-4-methyl-5-oxo-2-imidazolin-2-yl) Nicotinic Acid
61. 5-(methoxymethyl)-2-[4-methyl-5-oxo-4-(propan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1h-imidazol-2-yl]pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 305.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H19N3O4 |
| XLogP3 | 0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | Da |
| Monoisotopic Mass | Da |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 101 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 491 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Herbicides
Pesticides used to destroy unwanted vegetation, especially various types of weeds, grasses (POACEAE), and woody plants. Some plants develop HERBICIDE RESISTANCE. (See all compounds classified as Herbicides.)
Plant absorption: Absorption occurs through both the foliage and roots.
US EPA; Pesticide Fact Sheet. Imazamox. Conditional Registration. August 22, 2000. Washington, DC: USEPA, Off Prev Pest Tox Sub (7501C).
Rapidly excreted primarily in the urine following iv admin /to rats/, and in the urine and feces following oral admin, mainly as unchanged parent.
US EPA; Pesticide Fact Sheet. Imazamox. Conditional Registration. August 22, 2000. Washington, DC: USEPA, Off Prev Pest Tox Sub (7501C).
Forty-four Sprague Dawley rats (5/sex/group) were dosed with (14)C-/imazamox/ by a single intravenous (iv) dose at 10 mg/kg or a single oral gavage dose according to the following regiments: (1) 10 mg/kg body weight; (2) 14-day preconditioning with 10 mg/kg non-radiolabelled /imazamox/, followed by 10 mg/kg (14)C-/imazamox/; or (3) 1000 mg/kg body weight. The elimination patterns indicated that the radioactive residue were rapidly cleared from the body (ca. 95%) excreted in urine and recovered within 12 hours after dosing for all dose groups. Approximately, 74-75% of the radioactivity was absorbed via oral administration at 10 mg/kg dose and 74.4-74.5% excreted in urine and 18.7- 24.0% in feces. Much higher proportion of the dose was excreted in feces following oral dose (18.7- 24.0%) compared to iv injection (1.9-2.7%), most likely due to incomplete absorption. Three components accounted for ca. 99% of the total urinary radioactivity (98.2%, parent; 0.6%, 5- hydroxymethyl-nicotinic acid metabolite; and 0.4%, 5-carboxy-nicotinic acid metabolite) and ca. 89% of the extractable radioactivity in the feces (76.4%, parent; 9.6%, 5-hydroxymethyl-nicotinic acid metabolite; and 2.5%, 5-carboxy-nicotinic acid metabolite). The radioactive residues in the tissues were low (< 0.007%), and no (14)C-residues were detected in the expired air.
California Environmental Protection Agency/Department of Pesticide Regulation; Summary of Toxicology Data for Imazamox (October, 2000)
In rats, imazamox was rapidly absorbed, and the oral absorption was approximately 75% of the administered dose. Urine was the major route of excretion (>74%).
Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues; Pesticide Residues in Food-214, Part II p. 231 (2014)
Imazamox is a racemic mixture. No information on chiral conversion in the mammalian metabolism or toxicity of specific enantiomer is available. However, information available in the fate and behaviour and residues section indicated that chiral conversion does not occur and exposure would be only to the racemic mixture.
EFSA Journal 14 (4): 4432 (2016)
Forty-four Sprague Dawley rats (5/sex/group) were dosed with (14)C-/imazamox/ ...Three components accounted for ca. 99% of the total urinary radioactivity (98.2%, parent; 0.6%, 5- hydroxymethyl-nicotinic acid metabolite; and 0.4%, 5-carboxy-nicotinic acid metabolite) and ca. 89% of the extractable radioactivity in the feces (76.4%, parent; 9.6%, 5-hydroxymethyl-nicotinic acid metabolite; and 2.5%, 5-carboxy-nicotinic acid metabolite). The radioactive residues in the tissues were low (<0.007%), and no (14)C-residues were detected in the expired air.
California Environmental Protection Agency/Department of Pesticide Regulation; Summary of Toxicology Data for Imazamox (October, 2000)
(14)C-(15)N-labelled/unlabelled imazamox mix was incubated with dog, rabbit, rat, mouse or human liver microsomes in the presence of a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-generating system. With 90% recovered radioactivity and above, only the parent molecule was detected in all test systems by high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis in fresh samples after the incubation. Under the conditions of the study, imazamox was not metabolized by liver microsomes of dogs, rabbits, rats, mice or humans. No unique human metabolite was detected. Under the conditions of the study, the positive control, testosterone, was metabolized by the microsome samples originating from different species.
Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues; Pesticide Residues in Food-214, Part II p. 231 (2014)
In rats, imazamox was rapidly absorbed, and the oral absorption was approximately 75% of the administered dose. Urine was the major route of excretion (>74%). Most of the elimination occurred within the first 24 hours after dosing, as unchanged parent compound. Smaller amounts of the test substance were excreted through faeces (>19% in animals receiving 10 mg/kg bw and approximately 10-20% in animals receiving 1000 mg/kg bw). Only trace amounts of tissue residue were detected. Imazamox appears not to be metabolized. Trace levels of imazamox-related compounds detected in the urine and faeces were attributed to the presence of impurities in the dosing solution, not to rat metabolism.
Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues; Pesticide Residues in Food-214, Part II p. 231 (2014)