

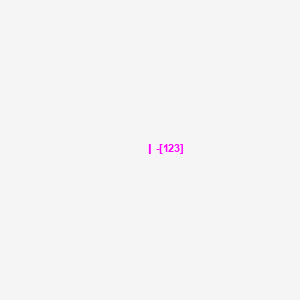
1. Iodine-123(1-)
2. Iodide (123i(1-))
3. Iodide I-123
4. 69239-56-1
5. 98qpv8670c
6. I-123
7. Iodide-123
8. Unii-98qpv8670c
9. Iodine 123
10. Iodide I-123 Ion
11. Iodide Ion I 123
12. Iodide, I-123
13. Iodide Ion (123 I)
14. Dtxsid40988959
15. Db09420
16. 123i-
17. Q3801335
| Molecular Weight | 122.90559 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | I- |
| XLogP3 | 0.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 122.90559 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 122.90559 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 1 |
| Formal Charge | -1 |
| Complexity | 0 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 1 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Administration of Sodium Iodide I 123 Capsules is indicated as a diagnostic procedure to be used in evaluating thyroid function and/or morphology.
FDA Label
Iodine-123 decays by electron capture with a physical half-life of 13.2 hours
Sodium Iodide I-123 is a radioactive isotope of iodine used in nuclear medicine for the diagnostic study of thyroid disease. Following oral administration, I-123 is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract and is taken up by the thyroid gland. After incorporation, a gamma camera is used to detect the decay by electron capture to tellurium-123. Iodine is commonly used in thyroid function diagnostic tests as this gland normally absorbs iodine through the diet for formation of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and its prohormone, thyroxine (T4).
