


1. Diiodohydroxyquin
2. Diiodohydroxyquinoline
3. Diiodoquin
4. Diodoquin
5. Diodoxyquinoline
6. Diquinol
7. Entero Diyod
8. Entero-diyod
9. Enterodiyod
10. Entodiba
11. Sebaquin
12. Yodoxin
1. 83-73-8
2. Diiodohydroxyquinoline
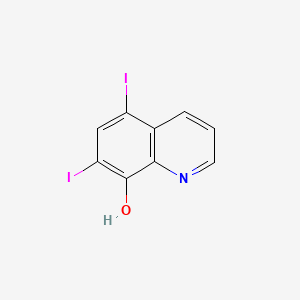
3. 5,7-diiodoquinolin-8-ol
4. 5,7-diiodo-8-hydroxyquinoline
5. 5,7-diiodo-8-quinolinol
6. Diiodoquin
7. Diodoquin
8. Yodoxin
9. Diiodohydroxyquin
10. Lanodoxin
11. Searlequin
12. Zoaquin
13. Ioquin
14. Quinadome
15. Sebaquin
16. 8-quinolinol, 5,7-diiodo-
17. Diodohydroxyquin
18. Dijodoxichinoline
19. Enterodiamoebin
20. Diamoebin
21. Dinoleine
22. Diodoquine
23. Diodoxylin
24. Direxiode
25. Disoquin
26. Embequin
27. Enterosept
28. Floraquin
29. Fluoraquin
30. Moebiquin
31. Dyodin
32. Di-quinol
33. Stanquinate
34. Rafamebin
35. 5,7-diiodo-oxine
36. Ioquin Suspension
37. Dijodoxichinolinum
38. 8-hydroxy-5,7-diiodoquinoline
39. 5,7-diodo-8-quinolinol
40. Diodoxyquinoleine
41. Diiodoidrossichinolina
42. Panaquin
43. Diiodohidroxiquinoleina
44. Diiodohydroxyquinoleine
45. Diiodohydroxyquinolinum
46. Ss 578
47. Enterodiamoebine
48. Nsc 8704
49. Nsc-8704
50. 5,7-diiod-8-chinolinol [iupac]
51. Diiodohydroxyquinoline [inn]
52. Mls000069404
53. Chebi:5950
54. 63w7ie88k8
55. Mmv002817
56. Ss-578
57. Ncgc00018098-04
58. Smr000059090
59. Dsstox_cid_3155
60. Dsstox_rid_76894
61. Diiodohydroxyquinoline (inn)
62. Dsstox_gsid_23155
63. Iodoquinol [usan]
64. Caswell No. 354
65. Iodoquinol;5,7-diiodo-8-hydroxyquinoline;5,7-diiodo-8-quinolinol
66. Cas-83-73-8
67. Diiodoidrossichinolina [dcit]
68. Hsdb 3224
69. Sr-01000002969
70. Diiodohydroxyquinolinum [inn-latin]
71. Iodoquinol [usan:usp]
72. Diiodohydroxyquinoleine [inn-french]
73. Einecs 201-497-9
74. 5,7-diiod-8-chinolinol
75. Diiodohidroxiquinoleina [inn-spanish]
76. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 024003
77. Brn 0153639
78. Searlewuin
79. Meobiquin
80. Unii-63w7ie88k8
81. Ai3-16443
82. 5,7-diiodooxine
83. Component Of Vytone
84. Iodoquinol (usp)
85. Yodoxin (tn)
86. Mfcd00006789
87. Spectrum_000943
88. Iodoquinol [mi]
89. 8-quinolinol,7-diiodo-
90. Spectrum2_001041
91. Spectrum3_000470
92. Spectrum4_000020
93. Spectrum5_000872
94. Iodoquinol [hsdb]
95. 4,7-diiodo-8-quinolinol
96. Bmse000836
97. Ec 201-497-9
98. Cid_3728
99. Schembl3460
100. Iodoquinol [usp-rs]
101. Bspbio_002180
102. Cbdive_011080
103. Kbiogr_000399
104. Kbioss_001423
105. Ksc-8-193
106. Chembl86754
107. Divk1c_000119
108. Spectrum1500353
109. Spbio_000962
110. Di-iodohydroxy Quinoline
111. Dtxsid6023155
112. 5,7-bis(iodanyl)quinolin-8-ol
113. Bdbm66035
114. Hms500f21
115. Kbio1_000119
116. Kbio2_001423
117. Kbio2_003991
118. Kbio2_006559
119. Kbio3_001400
120. Uxzfqzandvdgmm-uhfffaoysa-
121. Iodoquinol [usp Impurity]
122. Nsc8704
123. Ninds_000119
124. Wln: T66 Bnj Gi Ii Jq
125. Hms1920h05
126. Hms2091n15
127. Hms2230g24
128. Hms3369c20
129. Iodoquinol [usp Monograph]
130. Kuc105860n
131. Pharmakon1600-01500353
132. Hy-b1400
133. Zinc3830942
134. Tox21_110823
135. Ccg-40132
136. Nsc757077
137. S4565
138. Stk070581
139. Diiodohydroxyquinoline [mart.]
140. Akos000120804
141. Tox21_110823_1
142. 5,7-diiodo-8-hydroxyquinoline, 97%
143. Cs-4910
144. Db09115
145. Diiodohydroxyquinoline [who-dd]
146. Iodoquinol (5,7-diiodoquinolin-8-ol)
147. Nsc-757077
148. Idi1_000119
149. Ncgc00018098-01
150. Ncgc00018098-02
151. Ncgc00018098-03
152. Ncgc00018098-05
153. Ncgc00018098-07
154. Ncgc00018098-08
155. Ncgc00021685-03
156. Ncgc00021685-04
157. Ds-17759
158. Sbi-0051417.p003
159. Db-056739
160. Am20061527
161. D1736
162. Ft-0619847
163. C07636
164. D00581
165. F12461
166. Ab00052024_12
167. An-329/13210059
168. Q5276473
169. Sr-01000002969-2
170. Sr-01000002969-5
171. Brd-k75855670-001-06-8
172. F3034-0058
173. Iodoquinol, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 396.95 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H5I2NO |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 396.84606 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 396.84606 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 33.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 191 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Amebicides; Anti-Infective Agents, Local
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
...MAY BE USED IN LOCAL & SYSTEMIC TREATMENT OF TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS VAGINITIS & INFECTIONS CAUSED BY TRICHOMONAS HOMINIS (INTESTINALIS). IT IS USED IN TOPICAL TREATMENT OF CERTAIN FUNGAL CUTANEOUS INFECTIONS & IN ECZEMA IN WHICH FUNGAL INFECTION IS COMPLICATION.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1159
...HAVE BEEN USED FOR TREATMENT OF VARIOUS DERMATOLOGICAL DISORDERS, & LARGE DOSES HAVE BEEN EMPLOYED ORALLY IN TREATMENT OF ACRODERMATITIS ENTEROPATHICA, RARE, POTENTIALLY FATAL PEDIATRIC CONDITION.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1074
...EFFECTIVE FOR INTESTINAL AMEBIASIS &...FOR TREATMENT OF ASYMPTOMATIC PASSERS OF CYSTS. ...USEFUL FOR AMBULATORY & MASS TREATMENT. THEY ARE INEXPENSIVE. ...OF VALUE IN CASES OF LAMBLIASIS RESISTANT TO QUINACRINE THERAPY, IN BALANTIDIAL DYSENTERY, & IN INTESTINAL INFECTIONS DUE TO DIENTAMEBA FRAGILIS. /8-HYDROXYQUINOLINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1074
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DIIODOHYDROXYQUIN (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
WHILE...EFFECTIVE IN CYST-PASSING PT, THEY ARE MUCH LESS EFFECTIVE IN TREATMENT OF ACUTE AMEBIC DYSENTERY.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1073
USE OF THESE AGENTS TO TREAT "TRAVELER'S DIARRHEA" & CHRONIC NONSPECIFIC DIARRHEA IN CHILDREN /PRC: OR ADULTS/ CANNOT BE CONDONED, SINCE SUCH CONDITIONS ARE SELF-LIMITED & ANY POSSIBLE THERAPEUTIC BENEFIT DOES NOT JUSTIFY RISK OF SERIOUS NEUROTOXICITY. /8-HYDROXYQUINOLINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1074
THESE DRUGS ARE CONTRAINDICATED IN PT WITH HEPATIC DAMAGE OR IODINE INTOLERANCE. ...THESE AGENTS INTERFERE WITH CERTAIN THYROID FUNCTION TESTS FOR MO BECAUSE OF THEIR CONTENT OF IODINE. /8-HYDROXYQUINOLINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1074
...IT NOW APPEARS THAT GI-NEUROLOGIC SYNDROME OF OBSCURE ETIOLOGY, COMMON IN REGIONS WHERE DIIODOHYDROXYQUIN IS USED, IS CAUSED BY DRUG... FOR THIS REASON, JAPAN WITHDREW SUCH DRUGS FROM MARKET.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1159
VET: COMMERCIAL PREPN MAY CAUSE YELLOW-BROWN STAINING OF WHITE HAIR. USE MAY ALTER SERUM PROTEIN-BOUND IODINE TEST.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 177
4(?). 4= VERY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 50-500 MG/KG, BETWEEN 1 TEASPOON & 1 OZ FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). ...ITS TOXICITY IS UNPREDICTABLE.
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-234
Used in the treatment of amoebiasis.
Amebicides
Agents which are destructive to amebae, especially the parasitic species causing AMEBIASIS in man and animal. (See all compounds classified as Amebicides.)
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G01 - Gynecological antiinfectives and antiseptics
G01A - Antiinfectives and antiseptics, excl. combinations with corticosteroids
G01AC - Quinoline derivatives
G01AC01 - Diiodohydroxyquinoline
AFTER ORAL ADMIN, VARIABLE BUT SIGNIFICANT PORTION OF INGESTED DOSE IS ABSORBED. ... DIIODOHYDROXYQUIN WAS LEAST WELL ABSORBED--ONLY 1/3 AS MUCH AS IODOCHLORHYDROXYQUIN. BULK OF THESE DRUGS IS PASSED IN FECES.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1073
Unknown.
...IT IS NOT KNOWN IF THEY ARE EFFECTIVE IN INTESTINAL AMEBIASIS SOLELY BY VIRTUE OF THEIR PRESENCE IN LUMEN OF BOWEL OR ALSO IN PART BY THEIR PRESENCE IN CIRCULATION. /8-HYDROXYQUINOLINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1073
...8-HYDROXYQUINOLINES ARE DIRECTLY AMEBICIDAL. THEY ARE ACTIVE AGAINST BOTH MOTILE & CYSTIC FORMS, BUT THEIR EFFICACY IN ELIMINATING CYSTS IS PROBABLY BASED ON THEIR ABILITY TO DESTROY TROPHOZOITES. THEY ACT ONLY ON AMEBAE IN INTESTINAL TRACT & ARE INEFFECTIVE IN AMEBIC ABSCESS & HEPATITIS. /8-HYDROXYQUINOLINES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1073