


1. Acid, Iotalamic
2. Acid, Iothalamic
3. Acid, Methalamic
4. Angio Conray
5. Angio-conray
6. Angioconray
7. Conray 420
8. Iodothalamate
9. Iothalamate
10. Iothalamate, Sodium
11. Iothalamic Acid
12. Iothalamic Acid, Calcium (2:1) Salt
13. Iothalamic Acid, Monosilver (1+) Salt
14. Iothalamic Acid, Monosodium Salt
15. Iothalamic Acid, Monosodium Salt, Dimer
16. Lopamidol
17. Methalamic Acid
18. Sodium Iothalamate
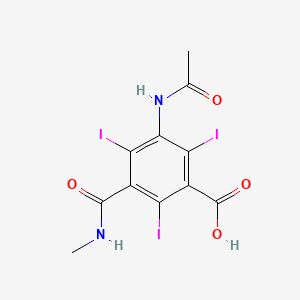
1. Iothalamic Acid
2. 2276-90-6
3. 3-acetamido-2,4,6-triiodo-5-(methylcarbamoyl)benzoic Acid
4. 5-acetamido-2,4,6-triiodo-n-methylisophthalamic Acid
5. Iotalamic Acid [inn]
6. Mi-216
7. Nsc-759891
8. 16chd79mix
9. 3-(acetylamino)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-[(methylamino)carbonyl]benzoic Acid
10. Acidum Jotalamicum
11. Acido Iotalamico
12. Iothalamic Acid [usan]
13. Acide Iotalamique
14. Acidum Iotalamicum
15. Acide Iotalamique [inn-french]
16. Acido Iotalamico [inn-spanish]
17. Acidum Iotalamicum [inn-latin]
18. Einecs 218-897-4
19. Mi 216
20. Unii-16chd79mix
21. Iothalamic Acid [usan:usp]
22. Iothalamic-acid-d3
23. Benzoic Acid, 3-(acetylamino)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-((methylamino)carbonyl)-
24. Iothalamic Acid (usp)
25. Ec 218-897-4
26. Iothalamate [vandf]
27. Schembl38419
28. Iotalamic Acid [jan]
29. Iothalamic Acid [mi]
30. Iotalamic Acid (jp17/inn)
31. Iothalamicacid(200mg)
32. Iotalamic Acid [mart.]
33. Chembl1201300
34. Dtxsid5023164
35. Iotalamic Acid [who-dd]
36. Schembl23630220
37. Chebi:31713
38. Iothalamic Acid [usp-rs]
39. Hms3264d13
40. Pharmakon1600-01503836
41. Bcp13316
42. Hy-b1053
43. Zinc3830961
44. Iotalamic Acid [ep Impurity]
45. Nsc759891
46. Akos025402283
47. Benzoic Acid,3-(acetylamino)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-[(methylamino)carbonyl]-
48. Ac-7611
49. Ccg-213208
50. Cs-4575
51. Db09133
52. Iothalamic Acid [usp Monograph]
53. Nsc 759891
54. Ncgc00183042-01
55. Ft-0740526
56. D01258
57. Ab01563288_01
58. 276i906
59. Sr-01000944232
60. Q-201246
61. Q6064129
62. Sr-01000944232-1
63. 5-acetylamino-2,4,6-triiodo-n-methyl-isophthalamic Acid
64. 1-deoxy-1-(methylamino)-d-glucitol 5-acetamido-2,4,6 Triiodo-n-methylisophthalamate
65. Benzoic Acid, 3-(acetylamino)-2,4,6-triiodo-5-((methylamino)carbonyl
| Molecular Weight | 613.91 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H9I3N2O4 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 613.7696 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 613.7696 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 95.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 421 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Conray is indicated for use in excretory urography, cerebral angiography, peripheral arteriography, venography, arthrography, direct cholangiography, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, contrast enhancement of computed tomographic brain images, cranial computerized angiotomography, intravenous digital subtraction angiography and arterial digital subtraction angiography. Conray may also be used for enhancement of computed tomographic scans performed for detection and evaluation of lesions in the liver, pancreas, kidneys, abdominal aorta, mediastinum, abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
Contrast Media
Substances used to allow enhanced visualization of tissues. (See all compounds classified as Contrast Media.)
V - Various
V08 - Contrast media
V08A - X-ray contrast media, iodinated
V08AA - Watersoluble, nephrotropic, high osmolar x-ray contrast media
V08AA04 - Iotalamic acid
Absorption
Renal accumulation is sufficiently rapid that maximum radiographic density in the calyces and pelves occurs, in most instances, about 3 to 8 minutes after injection. In patients with impaired renal function, diagnostic opacification frequently is achieved only after prolonged periods.
Route of Elimination
Following intravascular injection, Conray is rapidly transported through the circulatory system to the kidneys and is excreted unchanged in the urine by glomerular filtration. The liver and small intestine provide the major alternate route of excretion. In patients with severe renal impairment, the excretion of this contrast medium through the gallbladder and into the small intestine sharply increases.
In patients with normal renal function, the alpha and beta half-lives of Conray were approximately 10 and 90 minutes, respectively.
