

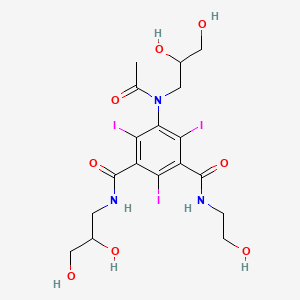

1. 5-(n-2,3-dihydroxypropylacetamido)-2,4,6-triiodo-n-(2-hydroxyethyl)-n'-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)isophthalamide
2. Oxilan
1. 107793-72-6
2. Oxilan
3. Ioxitol
4. Oxilan-300
5. Nsc-760056
6. A4yj7j11tg
7. 5-[acetyl(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino]-3-n-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-1-n-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzene-1,3-dicarboxamide
8. N-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5-(n-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)acetamido)-n'-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide
9. Ncgc00182070-02
10. Dsstox_cid_28643
11. Dsstox_rid_82913
12. Dsstox_gsid_48717
13. Ioxilane
14. Ioxilanum
15. 1,3-benzenedicarboxamide, 5-(acetyl(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino)-n-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-n'-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-
16. Cas-107793-72-6
17. Oxilan-350
18. Ioxilane [inn-french]
19. Ioxilanum [inn-latin]
20. Unii-a4yj7j11tg
21. Ioxilan [usan:usp:inn]
22. Imagenil
23. Loxilan
24. Ccris 6727
25. 1,3-benzenedicarboxamide, 5-(acetyl(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino)-n1-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-n3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-
26. 1,3-benzenedicarboxamide, 5-[acetyl(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino]-n1-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-n3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-
27. Ioxilan(400 Mg)
28. Ioxilan [vandf]
29. Loxilan [vandf]
30. Ioxilan [usan]
31. Ioxilan [inn]
32. Ioxilan [jan]
33. Ioxilan [mi]
34. Oxilan-300 (tn)
35. Ioxilan [mart.]
36. Ioxilan [usp-rs]
37. Ioxilan [who-dd]
38. Ioxilan (jan/usp/inn)
39. Schembl25634
40. Ioxilan [orange Book]
41. Ioxilan (400 Mg)
42. Ioxilan [usp Impurity]
43. Ioxilan [usp Monograph]
44. Chembl1201075
45. Dtxsid0048717
46. Chebi:135884
47. Hms3264d15
48. Moli000985
49. Pharmakon1600-01503838
50. Tox21_113127
51. Nsc760056
52. Akos016014026
53. Tox21_113127_1
54. Ccg-213210
55. Db09135
56. Nsc 760056
57. Ncgc00182070-03
58. Hy-109513
59. Cs-0031230
60. Ft-0627286
61. D02161
62. Ab01563289_01
63. Sr-01000883963
64. J-002011
65. Q6064819
66. Sr-01000883963-1
67. 3-(3-methyl-4-oxo-thiazolidin-2-ylideneamino)-benzoicacid
68. 5-(n-2,3-dihydroxypropylacetamido)-2,4,6-triiodo-n-(2-hydroxyethyl)-n -(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-isophthalamide
69. 5-[acetyl(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)amino]-n-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-n'-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide
70. N-(2,3-dihdroxypropyl)-n -(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-[n-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)acetamido]-2,4,6-triiodoiosphthalamide
71. N-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-n'-(2- Hydroxyethyl)-5-[n-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) Acetamido]-2,4,6-triiodoisophthal-amide
| Molecular Weight | 791.1 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H24I3N3O8 |
| XLogP3 | -2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 790.8698 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 790.8698 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 180 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 647 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Oxilan-300 |
| Active Ingredient | Ioxilan |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 62% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Guerbet |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Oxilan-350 |
| Active Ingredient | Ioxilan |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 73% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Guerbet |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Oxilan-300 |
| Active Ingredient | Ioxilan |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 62% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Guerbet |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Oxilan-350 |
| Active Ingredient | Ioxilan |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 73% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Guerbet |
When administered intra-arterially, Ioxilan is indicated for the following diagnostic tests: cerebral arteriography (300 mgI/mL), coronary arteriography and left ventriculography (350 mgI/mL), visceral angiography(350 mgI/mL), aortography(350 mgI/mL), and peripheral arteriography(350 mgI/mL). When administered intravenously, Ioxilan is indicated for excretory urography and contrast enhanced computed tomographic (CECT) imaging of the head and body (300 and 350 mgI/mL).
FDA Label
As with other iodinated contrast agents the degree of contrast enhancement is directly related to the iodine content in the administered dose.
Contrast Media
Substances used to allow enhanced visualization of tissues. (See all compounds classified as Contrast Media.)
V - Various
V08 - Contrast media
V08A - X-ray contrast media, iodinated
V08AB - Watersoluble, nephrotropic, low osmolar x-ray contrast media
V08AB12 - Ioxilan
Absorption
Peak iodine plasma levels occur immediately following rapid intravenous injection. Iodine plasma levels fall rapidly within 5 to 10 minutes. This can be accounted for by the dilution in the vascular and extravascular fluid compartments.
Route of Elimination
The average amount of ioxilan excreted unchanged in urine at 24 hours represents 93.7% of the dose in young healthy subjects (21-27 years) after intravenous administration. This finding suggests that, compared to the renal excretion, biliary and/or gastrointestinal excretion are not important.
Volume of Distribution
Ioxilan is distributed mainly in the blood as suggested by the apparent volume of distribution (central compartment), 7.2 1.0 L in women and 10.0 2.4 L in men
Clearance
The total clearance values were 95.4 11.1 mLmin-1 and 101.0 14.7 mLmin-1 and the renal clearance values were 89.4 13.3 mLmin-1 and 94.9 16.6 mLmin-1 for women and men, respectively.
There is no evidence for metabolism.
An initial fast distribution phase with a half-life of 13.1 4.2 minutes (women) or 23.5 15.3 minutes (men) was followed by an elimination phase with a half-life of 102.0 16.9 minutes (women) and 137 35.4 minutes (men).
Intravascular injection results in opacification of vessels in the path of flow of the contrast medium, permitting radiographic visualization of the internal structures of the human body until significant hemodilution occurs.