

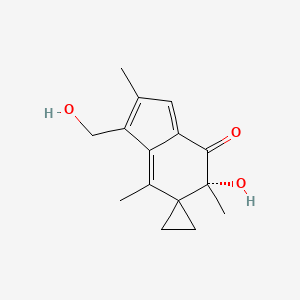

1. 6-(hydroxymethyl)acylfulvene
2. 6-hydroxymethylacylfulvene
3. Hmaf Cpd
4. Mgi 114
5. Mgi-114
6. Mgi.114
1. Hmaf
2. Mgi 114
3. 158440-71-2
4. 6-hydroxymethylacylfulvene
5. (-)-irofulven
6. Mgi-114
7. Nsc 683863
8. (hydroxymethyl)acylfulvene
9. Nsc-683863
10. (5'r)-5'-hydroxy-1'-(hydroxymethyl)-2',5',7'-trimethylspiro[cyclopropane-1,6'-indene]-4'-one
11. 6b799ih05a
12. Lp-100
13. (r)-6'-hydroxy-3'-(hydroxymethyl)-2',4',6'-trimethylspiro(cyclopropane-1,5'-(5h)inden)-7'(6'h)-one
14. 6-(hydroxymethyl)acylfulvene
15. Acylfulvene, 6-(hydroxymethyl)-
16. Irofulven [usan:inn]
17. Unii-6b799ih05a
18. Mgi.114
19. Irofulven [inn]
20. Irofulven [mi]
21. Irofulven (usan/inn)
22. Irofulven [usan]
23. Irofulven [who-dd]
24. Schembl8800
25. Chembl118218
26. Dtxsid50166423
27. Chebi:135002
28. Zinc3916310
29. Bdbm50410835
30. Nsc683863
31. Akos027256650
32. Db05786
33. (r)-6'-hydroxy-3'-(hydroxymethyl)-2',4',6'-trimethylspiro[cyclopropane-1,5'-inden]-7'(6'h)-one
34. Hy-14429
35. Nci60_030149
36. Spiro(cyclopropane-1,5'(5h)-inden)-7'(6'h)-one, 6'-hydroxy-3'-(hydroxymethyl)-2',4',6'-trimethyl-, (r)-
37. Cs-0003353
38. D04614
39. Q6072197
| Molecular Weight | 246.30 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H18O3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 246.125594432 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 246.125594432 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 57.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 558 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in brain cancer, breast cancer, endometrial cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, pediatric indications, prostate cancer, and sarcoma.
Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating
A class of drugs that differs from other alkylating agents used clinically in that they are monofunctional and thus unable to cross-link cellular macromolecules. Among their common properties are a requirement for metabolic activation to intermediates with antitumor efficacy and the presence in their chemical structures of N-methyl groups, that after metabolism, can covalently modify cellular DNA. The precise mechanisms by which each of these drugs acts to kill tumor cells are not completely understood. (From AMA, Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2026) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Alkylating.)
Radiation-Sensitizing Agents
Drugs used to potentiate the effectiveness of radiation therapy in destroying unwanted cells. (See all compounds classified as Radiation-Sensitizing Agents.)
MGI-114(Irofulven) has unique mechanism of action as an anti-tumor agent is due to its ability to be rapidly absorbed by tumor cells. Once inside the cells, the compound binds to DNA and protein targets. This binding interferes with DNA replication and cell division of tumor cells, leading to tumor-specific apoptotic cell death, or cell suicide. During this process, tumor cells tend to automatically shut themselves down when they sense their function is compromised.