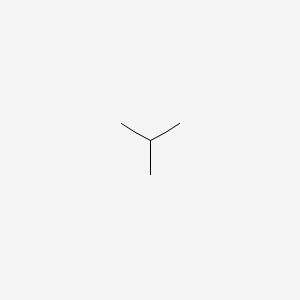
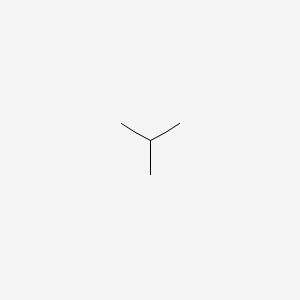
1. Butanes
2. Isobutanes
1. 2-methylpropane
2. 75-28-5
3. Propane, 2-methyl-
4. Trimethylmethane
5. 1,1-dimethylethane
6. R 600a
7. Iso-butane
8. A 31 (hydrocarbon)
9. Isobutane [nf]
10. R-600a
11. Bxr49tp611
12. Chebi:30363
13. Isobutane (nf)
14. Caswell No. 503a
15. Hsdb 608
16. Einecs 200-857-2
17. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 097101
18. Dimethylethane
19. Unii-bxr49tp611
20. Methylpropane
21. Tert-butane
22. I-butane
23. Meb
24. H-tbu
25. Isobutane [fcc]
26. Isobutane [ii]
27. Iso-c4h10
28. 2-methylpropane, 99%
29. Isobutane [hsdb]
30. Isobutane [inci]
31. Isobutane [vandf]
32. 2-methylpropane, Puriss.
33. Isobutane [mart.]
34. Ec 200-857-2
35. Isobutane [who-dd]
36. E943b
37. (ch3)2ch-ch3
38. 2-methylpropane, 99.995%
39. Chembl2106398
40. Dtxsid1026401
41. Zinc8214586
42. Mfcd00008926
43. Akos015917447
44. Zinc256652644
45. Un 1969
46. I0090
47. D04623
48. Q407225
49. (1r,5s,9r)-tert-butyl 9-hydroxy-3-oxa-7-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane-7-carboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 58.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H10 |
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 58.078250319 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 58.078250319 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 4.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
A study was conducted to establish whether volatile hydrocarbons, such as propane, n-butane and iso-butane, are metabolized in mice or not. In mice having inhaled these gases, isopropanol and acetone were yielded from propane, sec-butanol and methyl ethyl ketone from n-butane, and tert-butanol from iso-butane as the respective metabolites. In addition, liver microsomes were found to contain the enzymic system participating in these metabolisms. In vitro reactions with liver microsomes produced isopropanol from propane, sec-butanol from n-butane, and tert-butanol from iso-butane. It was assumed that hydrocarbons were first converted to (omega-1)-alcohols by microsomal enzyme system and then to corresponding ketones by alcohol dehydrogenase.
Tsukamoto S et al; J Toxicol Sci 10 (4): 323-32 (1985)
Isobutane is oxidatively metabolized by rat liver microsomes to its parent alcohol.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V4 18