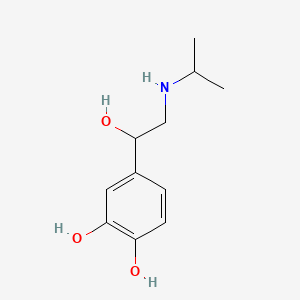

1. 4-(1-hydroxy-2-((1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)-1,2-benzenediol
2. Euspiran
3. Hydrochloride, Isoproterenol
4. Isadrin
5. Isadrine
6. Isoprenaline
7. Isopropyl Noradrenaline
8. Isopropylarterenol
9. Isopropylnoradrenaline
10. Isopropylnorepinephrine
11. Isoproterenol Hydrochloride
12. Isoproterenol Sulfate
13. Isuprel
14. Izadrin
15. Noradrenaline, Isopropyl
16. Norisodrine
17. Novodrin
18. Sulfate, Isoproterenol
1. Isoprenaline
2. Novodrin
3. Isopropydrin
4. Asmalar
5. 7683-59-2
6. Bellasthman
7. Isoprenalin
8. Norisodrine
9. Aludrine
10. Asiprenol
11. Assiprenol
12. Respifral
13. Neodrenal
14. Proternol
15. Neo-epinine
16. Isopropylarterenol
17. Saventrine
18. Aludrin
19. Isadrine
20. Isonorin
21. Isorenin
22. N-isopropylnoradrenaline
23. Isonorene
24. Isopropyladrenaline
25. Lomupren
26. N-isopropylnorepinephrine
27. Isopropylnorepinephrine
28. Vapo-n-iso
29. Isupren
30. Isopropylnoradrenaline
31. Isopropyl Noradrenaline
32. Racemic Isoprenaline
33. Dl-isadrine
34. Racemic Isoproterenol
35. (+-)-isoproterenol
36. Epinephrine Isopropyl Homolog
37. Isoprenalinum
38. Aleudrin
39. Aleudrine
40. (+-)-isoprenaline
41. Dl-isoproterenol
42. Isoprenalina
43. 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(propan-2-ylamino)ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol
44. Dihydroxyphenylethanolisopropylamine
45. Win 5162
46. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(isopropylamino)ethanol
47. Ici 46399
48. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-isopropylaminoethanol
49. Alpha-(isopropylaminomethyl)protocatechuyl Alcohol
50. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-[1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl]-
51. 149-53-1
52. N-isopropyl-beta-dihydroxyphenyl-beta-hydroxyethylamine
53. Isoprenaline (inn)
54. Isoprenaline [inn]
55. 4-(1-hydroxy-2-((1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)-1,2-benzenediol
56. 1,2-benzenediol, 4-(1-hydroxy-2-((1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)-
57. Nsc-9975
58. Nsc-33791
59. Chembl434
60. 4-(1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl)benzene-1,2-diol
61. 3,4-dihydroxy-alpha-((isopropylamino)methyl)benzyl Alcohol
62. Isoproterenolum
63. Chebi:64317
64. Isopropylaminomethyl(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)carbinol
65. L628tt009w
66. 7683-59-2 (free)
67. Nsc33791
68. 3,4-dihydroxy-alpha-[(isopropylamino)methyl]benzyl Alcohol
69. Ncgc00015558-06
70. 3,4-dihydroxy-.alpha.-(isopropylaminomethyl)-benzyl Alcohol
71. A-21
72. Isoproterenol [jan]
73. Protocatechuyl Alcohol,-
74. Dsstox_cid_3175
75. Dl(+-)-isoproterenol
76. L-isoproterenol; Levisoprenaline; Proternol L
77. Dsstox_rid_76904
78. Dsstox_gsid_23175
79. Isoprenalinum [inn-latin]
80. .alpha.-(isopropylaminomoethyl)protocatechuyl Alcohol
81. Isoprenalina [inn-spanish]
82. Isoproterenol Chloride
83. Wln: Qr Bq Dyq1my1&1
84. 3,4-dihydroxy-.alpha.-[(isopropylamino)methyl]benzyl Alcohol
85. 4-{1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl}benzene-1,2-diol
86. 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl]-1,2-benzenediol
87. Cas-7683-59-2
88. Isoprop
89. Ccris 3081
90. Nsc 9975
91. 1, 4-[1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl]-
92. Einecs 231-687-7
93. Nsc 33791
94. Isopropylaminomethyl-3,4-dihydroxyphenyl Carbinol
95. 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol
96. Brn 2213857
97. Benzyl Alcohol,4-dihydroxy-.alpha.-[(isopropylamino)methyl]-
98. Isoproterenol-l
99. Isoproterenol;
100. Unii-l628tt009w
101. 3,4-dihydroxy-.alpha.-((isopropylamino)methyl)benzyl Alcohol
102. Isoproterenol (-)
103. Isoproterenol,(+)
104. Protocatechuyl Alcohol, Alpha-(isopropylaminomethyl)-
105. Isoproteronol
106. Isoproterenol Dl-form
107. Isuprel (salt/mix)
108. Izadrin (salt/mix)
109. Euspiran (salt/mix)
110. (+/-)-isoprenaline
111. (+/-)-isoproterenol
112. Spectrum_000949
113. Prestwick0_001097
114. Prestwick1_001097
115. Prestwick2_001097
116. Spectrum2_001061
117. Spectrum3_000474
118. Spectrum4_000024
119. Spectrum5_000880
120. (.+/-.)-isoprenaline
121. Isoproterenol [mi]
122. (.+/-.)-isoproterenol
123. Schembl4165
124. Dl(.+/-.)-isoproterenol
125. Lopac0_000711
126. Oprea1_009434
127. Bspbio_002208
128. Gtpl536
129. Isoprenaline [mart.]
130. Isoproterenol [vandf]
131. Kbiogr_000427
132. Kbioss_001429
133. 3-13-00-02387 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
134. Divk1c_000894
135. Isoprenaline [who-dd]
136. Spbio_001042
137. Spbio_003057
138. Sgcut00015
139. 4-(1-hydroxy-2(isopropylamino)ethyl)-benzene 1,2-diol
140. Dtxsid4023175
141. Bdbm25392
142. Kbio1_000894
143. Kbio2_001429
144. Kbio2_003997
145. Kbio2_006565
146. Kbio3_001428
147. Nsc9975
148. Ninds_000894
149. 4-{1-hydroxy-2-[(propan-2-yl)amino]ethyl}benzene-1,2-diol
150. Hms2089a12
151. Hms3742a11
152. Isoproterenol Dl-form [mi]
153. Bcp09043
154. Benzyl Alcohol, 3,4-dihydroxy-alpha-((isopropylamino)methyl)-
155. To_000062
156. (a+/-)-isoproterenol Hydrochloride
157. Tox21_110172
158. Pdsp1_001425
159. Pdsp2_001409
160. Stl558077
161. Akos015913894
162. Tox21_110172_1
163. Ccg-204727
164. Ccg-204796
165. Db01064
166. Sdccgsbi-0050620.p003
167. Sdccgsbi-0050689.p005
168. Idi1_000894
169. Ncgc00015558-04
170. Ncgc00015558-05
171. Ncgc00015558-07
172. Ncgc00015558-08
173. Ncgc00015558-09
174. Ncgc00015558-10
175. Ncgc00015558-11
176. Ncgc00015558-12
177. Ncgc00015558-14
178. Ncgc00015558-25
179. Ncgc00016665-02
180. Ncgc00025274-03
181. Ncgc00025274-04
182. Ncgc00162220-01
183. Sbi-0050689.p004
184. Hy-108353
185. Cs-0028436
186. Ft-0724367
187. C07056
188. D08090
189. Ab00053487-09
190. Ab00053487-10
191. Ab00053487_11
192. Ab00053487_12
193. 683i592
194. Ag-219/03618046
195. L000936
196. Q415550
197. .alpha.-(isopropylaminomethyl)protocatechuyl Alcohol
198. Protocatechuyl Alcohol,.alpha.-(isopropylamino-methyl),-
199. 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl]-1,2-benzenediol #
200. N-isopropyl-.beta.-dihydroxyphenyl-.beta.-hydroxyethylamine
201. 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(isopropylamino)ethyl]pyrocatechol;hydrochloride
202. 4-{1-hydroxy-2-[(propan-2-yl)amino]ethyl}benzene-1,2-diol, 2
203. Benzyl Alcohol, 3,4-dihydroxy-.alpha.-((isopropylamino)methyl)-
204. 114-45-4
205. Iso
1. Isoproterenol Sulfate
2. Isoprenaline Sulfate
3. Isoprenaline Sulphate
4. Isopropylarterenol Sulfate
5. Schembl41841
| Molecular Weight | 211.26 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H17NO3 |
| XLogP3 | -0.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 211.12084340 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 211.12084340 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 72.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 187 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Isuprel |
| PubMed Health | Isoproterenol (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Bronchodilator, Vasopressor |
| Drug Label | Isoproterenol hydrochloride is 3,4-Dihydroxy--[(isopropylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol hydrochloride, a synthetic sympathomimetic amine that is structurally related to epinephrine but acts almost exclusively on beta receptors. The molecular formula... |
| Active Ingredient | Isoproterenol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 0.2mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Isuprel |
| PubMed Health | Isoproterenol (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Bronchodilator, Vasopressor |
| Drug Label | Isoproterenol hydrochloride is 3,4-Dihydroxy--[(isopropylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol hydrochloride, a synthetic sympathomimetic amine that is structurally related to epinephrine but acts almost exclusively on beta receptors. The molecular formula... |
| Active Ingredient | Isoproterenol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 0.2mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
Isoprenaline is indicated to treat mild or transient episodes of heart block not requiring electric shock or pacemakers, serious episodes of heart block and Adams-Stokes attacks not caused by ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, and bronchospasm during anesthesia. Isoprenaline is also indicated for cases of cardiac arrest until preferable treatments like electric shock and pacemakers are available. Isoprenaline is also indicated as an adjunct therapy to fluid and electrolyte replacement therapy in hypovolemic shock, septic shock, hypoperfusion, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock.
FDA Label
Isoprenaline is a non-selective beta adrenergic receptor agonist used in a number of indications for the heart, as well as bronchospasm in anesthesia. Isoprenaline has a short duration of action as it is rapidly cleared, and a wide therapeutic index. Patients should be counselled regarding the risks of isoprenaline in the treatment of cardiogenic shock following myocardial infarction, paradoxical worsening of heart block, or precipitation of Adams-Stokes attacks.
Adrenergic beta-Agonists
Drugs that selectively bind to and activate beta-adrenergic receptors. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Agonists.)
Bronchodilator Agents
Agents that cause an increase in the expansion of a bronchus or bronchial tubes. (See all compounds classified as Bronchodilator Agents.)
Sympathomimetics
Drugs that mimic the effects of stimulating postganglionic adrenergic sympathetic nerves. Included here are drugs that directly stimulate adrenergic receptors and drugs that act indirectly by provoking the release of adrenergic transmitters. (See all compounds classified as Sympathomimetics.)
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
C01CA02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C01 - Cardiac therapy
C01C - Cardiac stimulants excl. cardiac glycosides
C01CA - Adrenergic and dopaminergic agents
C01CA02 - Isoprenaline
R - Respiratory system
R03 - Drugs for obstructive airway diseases
R03A - Adrenergics, inhalants
R03AB - Non-selective beta-adrenoreceptor agonists
R03AB02 - Isoprenaline
R - Respiratory system
R03 - Drugs for obstructive airway diseases
R03C - Adrenergics for systemic use
R03CB - Non-selective beta-adrenoreceptor agonists
R03CB01 - Isoprenaline
Absorption
Data regarding absorption kinetics of isoprenaline are not readily available.
Route of Elimination
Isoprenaline is 12.2-27.0% recovered in the feces and 59.1-106.8% recovered in the urine after 48 hours. The majority of the recovered dose in the urine is conjugated isoprenaline, with 6.5-16.2% free isoprenaline, and 2.6-11.4% 3-O-methylisoprenaline and conjugates.
Volume of Distribution
In pediatric patients, the volume of distribution was 216 57 mL/kg.
Clearance
In pediatric patients, the clearance of isoprenaline was 42.5 5.0 mL/kg/min.
Isoprenaline is predominantly metabolized to glucuronide conjugates. Isoprenaline can also be O-methylated by catechol O-methyltransferase to the metabolite 3-O-methylisoprenaline, which can also be further glucuronidated.
The half life of intravenous isoprenaline is 2.5-5 minutes. Oral isoprenaline has a half life of 40 minutes.
Isoprenaline is a non-selective beta adrenergic receptor agonist. Agonism of beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors causes the alpha subunit of G-protein coupled receptors to exchange GMP for GTP, activating them, and allowing the alpha subunit to dissociate from the beta and gamma subunits. Dissociation of the alpha subunit activates adenylate cyclase, converting ATP to cyclic AMP. Cyclic AMP activates protein kinase A (PKA), which phosphorylates cardiac L-type calcium channels such as Cav1.2. These channels depolarize cells by inward active transport of calcium ions. Agonism of beta-1 adrenergic receptors lead to increased strength of contractility, conduction of nerve impulses, speed of relaxation, and rate in the heart. Agonism of beta-2 adrenergic receptors leads to glycogenolysis in the liver, glucagon release from the pancreas, and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. In the alveoli, agonism of beta-2 adrenergic receptors, activates similar pathways to the heart, however the end result is regulation of sodium channels, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), and sodium potassium ATPase. PKA phosphorylates scaffolding proteins and sodium channels, increasing the number of sodium channels on the apical side of alveolar cells and increasing active transport of sodium ions into cells. Agonism of beta-2 adrenergic receptors can also increase chloride ion transport across CFTR. Together, these actions lead to passive transport of water out of the alveoli, and the clearance of alveolar fluid.