
1. Orungal
2. R 51211
3. R-51211
4. R51211
5. Sporanox
1. Sporanox
2. 84625-61-6
3. Oriconazole
4. Itrizole (tn)
5. Sporanox (tn)
6. Itcz
7. Itrizole
8. Itraconazol
9. Orungal
10. Sporonox
11. Itraconazole (sporanox)
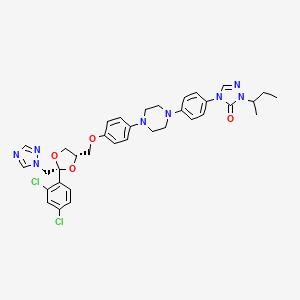
12. 2-butan-2-yl-4-[4-[4-[4-[[(2r,4s)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
13. 873066-43-4
14. R-51211
15. Itraconazol [spanish]
16. Itraconazolum [latin]
17. Triasporin
18. Candistat
19. Canditral
20. Itralek
21. Sempera
22. Sporamelt
23. Traconal
24. Chembl22587
25. Itrac
26. Cis-itraconazole
27. Chebi:6076
28. Spherazole Cr
29. Spherazole Ir
30. R51211
31. Nsc-759239
32. Itz
33. Dsstox_cid_3180
34. Dsstox_rid_76908
35. (2r,4s)-itraconazole (mixture Of Diastereomers)
36. Dsstox_gsid_23180
37. Fungitraxx
38. Cladosal 100
39. 2-(butan-2-yl)-4-{4-[4-(4-{[(2r,4s)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy}phenyl)piperazin-1-yl]phenyl}-2,4-dihydro-3h-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
40. 4-[4-[4-[4-[[(2r,4s)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-2-sec-butyl-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
41. Cas-84625-61-6
42. 304nug5gf4
43. Intraconazole
44. Itraconazolo
45. Sporanox(tm)
46. Ncgc00018268-03
47. 3h-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, 4-(4-(4-(4-((2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methoxy)phenyl)-1-piperazinyl)phenyl)-2,4-dihydro-2-(1-methylpropyl)-
48. 4-(4-{4-[4-({[(2r,4s)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methyl}oxy)phenyl]piperazin-1-yl}phenyl)-2-(1-methylpropyl)-2,4-dihydro-3h-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
49. 84604-65-9
50. Itraconazole & Nyotran
51. R 51,211
52. Itraconazole [mi]
53. Itraconazole [inn]
54. Itraconazole [jan]
55. Itraconazole [inci]
56. Itraconazole [usan]
57. Itraconazole (jp17/usp)
58. Itraconazole [vandf]
59. Schembl23934
60. Itraconazole [mart.]
61. Mls006011958
62. Itraconazole [usp-rs]
63. Itraconazole [who-dd]
64. Amy922
65. Dtxsid3023180
66. Gtpl11426
67. Itraconazole [green Book]
68. Itraconazole [ep Impurity]
69. Itraconazole [orange Book]
70. Pharmakon1600-01505756
71. Itraconazole [ep Monograph]
72. 4-(4-(4-(4-((2-((1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methoxy)phenyl)piperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-2-(sec-butyl)-2,4-dihydro-3h-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
73. Itraconazole [usp Monograph]
74. Tox21_110854
75. Ac-542
76. Bdbm50127138
77. Nsc759239
78. S2476
79. Akos015842738
80. Akos015961385
81. Tox21_110854_1
82. Ccg-270391
83. Db01167
84. Ks-1268
85. Ncgc00274068-01
86. Ncgc00274068-02
87. Ncgc00274068-07
88. 1-(butan-2-yl)-4-{4-[4-(4-{[(2r,4s)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy}phenyl)piperazin-1-yl]phenyl}-4,5-dihydro-1h-1,2,4-triazol-5-one
89. 4-(4-(4-(4-(((2r,4s)-2-((1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methoxy)phenyl)piperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-2-(sec-butyl)-2,4-dihydro-3h-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
90. Hy-17514
91. Smr001827898
92. Itraconazole & Nyotran(liposomal Nystatin)
93. Sbi-0206914.p001
94. Itraconazole (ema Epar: Veterinary)
95. Sw219756-1
96. Itraconazole 2.0 Mg/ml In Dimethyl Sulfoxide
97. D00350
98. Suba-itraconazole Component Itraconazole
99. Ab01274818-01
100. Ab01274818_02
101. Ab01274818_03
102. A933954
103. Itraconazole Component Of Suba-itraconazole
104. Q411229
105. Brd-a23067620-001-01-7
106. (+/-)-1-sec-butyl-4-(p-(4-(p-(((2r*,4s*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)methoxy)phenyl)-1-piperazinyl)phenyl)-.delta.(sup 2)-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
107. 3h-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, 4-[4-[4-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-pipera-zinyl]phenyl]-2,4-dihydro-2-(1-methylpropyl)
108. 4-[4-[4-[4-[[(2r,4s)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1h-1,2,4-triazole-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolane-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazino]phenyl]-2-(1-methylpropyl)-4h-1,2,4-triazole-3(2h)-one
| Molecular Weight | 705.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C35H38Cl2N8O4 |
| XLogP3 | 5.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 704.2393071 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 704.2393071 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 101 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 49 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1120 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Itraconazole |
| PubMed Health | Itraconazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | SPORANOX is the brand name for itraconazole, a synthetic triazole antifungal agent. Itraconazole is a 1:1:1:1 racemic mixture of four diastereomers (two enantiomeric pairs), each possessing three chiral centers. It may be represented by the followi... |
| Active Ingredient | Itraconazole |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 100mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Sandoz |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Sporanox |
| PubMed Health | Itraconazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | SPORANOX is the brand name for itraconazole, a synthetic triazole antifungal agent. Itraconazole is a 1:1:1:1 racemic mixture of four diastereomers (two enantiomeric pairs), each possessing three chiral centers. It may be represented by the followi... |
| Active Ingredient | Itraconazole |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Solution |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 10mg/ml; 100mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Pharms; Janssen Pharma |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Itraconazole |
| PubMed Health | Itraconazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | SPORANOX is the brand name for itraconazole, a synthetic triazole antifungal agent. Itraconazole is a 1:1:1:1 racemic mixture of four diastereomers (two enantiomeric pairs), each possessing three chiral centers. It may be represented by the followi... |
| Active Ingredient | Itraconazole |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 100mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Sandoz |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Sporanox |
| PubMed Health | Itraconazole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antifungal |
| Drug Label | SPORANOX is the brand name for itraconazole, a synthetic triazole antifungal agent. Itraconazole is a 1:1:1:1 racemic mixture of four diastereomers (two enantiomeric pairs), each possessing three chiral centers. It may be represented by the followi... |
| Active Ingredient | Itraconazole |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Solution |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 10mg/ml; 100mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Pharms; Janssen Pharma |
Antifungal Agents; Antiprotozoal Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Itraconazole capsules are indicated for the treatment of the following fungal infections in immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised patients: Blastomycosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary; Histoplasmosis, including chronic cavitary pulmonary disease and disseminated, non-meningeal histoplasmosis and Aspergillosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary, in patients who are intolerant of or who are refractory to amphotericin B therapy. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (February 2010). Available from, as of September 27, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=16279
Itraconazole capsules are also indicated for the treatment of the following fungal infections in non-immunocompromised patients: Onychomycosis of the toenail, with or without fingernail involvement, due to dermatophytes (tinea unguium) and Onychomycosis of the fingernail due to dermatophytes (tinea unguium). /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (February 2010). Available from, as of September 27, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=16279
/BOXED WARNING/ Congestive Heart Failure, Cardiac Effects: Itraconazole capsules should not be administered for the treatment of onychomycosis in patients with evidence of ventricular dysfunction such as congestive heart failure (CHF) or a history of CHF. If signs or symptoms of congestive heart failure occur during administration of itraconazole capsules, discontinue administration. When itraconazole was administered intravenously to dogs and healthy human volunteers, negative inotropic effects were seen.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (Updated: June 2014). Available from, as of April 24, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=d343050e-00bb-440c-a24b-7cd18c97e184
/BOXED WARNING/ Drug Interactions: Coadministration of the following drugs are contraindicated with itraconazole capsules: methadone, disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, quinidine, ergot alkaloids (such as dihydroergotamine, ergometrine (ergonovine), ergotamine, methylergometrine (methylergonovine)), irinotecan, lurasidone, oral midazolam, pimozide, triazolam, felodipine, nisoldipine, ranolazine, eplerenone, cisapride, lovastatin, simvastatin and, in subjects with renal or hepatic impairment, colchicine. Coadministration with itraconazole can cause elevated plasma concentrations of these drugs and may increase or prolong both the pharmacologic effects and/or adverse reactions to these drugs. For example, increased plasma concentrations of some of these drugs can lead to QT prolongation and ventricular tachyarrhythmias including occurrences of torsades de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (Updated: June 2014). Available from, as of April 24, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=d343050e-00bb-440c-a24b-7cd18c97e184
Itraconazole is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or any ingredient in the formulation. Although information concerning cross-sensitivity between itraconazole and other triazole or imidazole antifungal agents is not available, the manufacturer states that itraconazole should be used with caution in individuals hypersensitive to other azoles.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 531
Adverse GI effects have been reported in about 1-11% of patients receiving IV or oral itraconazole for the treatment of systemic fungal infections or oropharyngeal or esophageal candidiasis or for empiric anti-fungal therapy. These adverse GI effects usually are transient and respond to symptomatic treatment without alteration of itraconazole therapy; however, reduction of dosage or discontinuance of the drug occasionally may be required.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2010. Bethesda, MD. (2010), p. 530
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Itraconazole (27 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of the following fungal infections in immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised patients: pulmonary and extrapulmonary blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, aspergillosis, and onychomycosis.
FDA Label
For the treatment of aspergillosis and candidiasis in companion birds
Itraconazole is an imidazole/triazole type antifungal agent. Itraconazole is a highly selective inhibitor of fungal cytochrome P-450 sterol C-14 α-demethylation via the inhibition of the enzyme cytochrome P450 14α-demethylase. This enzyme converts lanosterol to ergosterol, and is required in fungal cell wall synthesis. The subsequent loss of normal sterols correlates with the accumulation of 14 α-methyl sterols in fungi and may be partly responsible for the fungistatic activity of fluconazole. Mammalian cell demethylation is much less sensitive to fluconazole inhibition. Itraconazole exhibits in vitro activity against Cryptococcus neoformans and Candida spp. Fungistatic activity has also been demonstrated in normal and immunocompromised animal models for systemic and intracranial fungal infections due to Cryptococcus neoformans and for systemic infections due to Candida albicans.
14-alpha Demethylase Inhibitors
Compounds that specifically inhibit STEROL 14-DEMETHYLASE. A variety of azole-derived ANTIFUNGAL AGENTS act through this mechanism. (See all compounds classified as 14-alpha Demethylase Inhibitors.)
Antifungal Agents
Substances that destroy fungi by suppressing their ability to grow or reproduce. They differ from FUNGICIDES, INDUSTRIAL because they defend against fungi present in human or animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antifungal Agents.)
Cytochrome P-450 CYP3A Inhibitors
Drugs and compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of CYTOCHROME P-450 CYP3A. (See all compounds classified as Cytochrome P-450 CYP3A Inhibitors.)
QJ02AC02
J02AC02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J02 - Antimycotics for systemic use
J02A - Antimycotics for systemic use
J02AC - Triazole and tetrazole derivatives
J02AC02 - Itraconazole
Absorption
The absolute oral bioavailability of itraconazole is 55%, and is maximal when taken with a full meal.
Route of Elimination
Itraconazole is metabolized predominately by the cytochrome P450 3A4 isoenzyme system (CYP3A4) in the liver, resulting in the formation of several metabolites, including hydroxyitraconazole, the major metabolite. Fecal excretion of the parent drug varies between 3-18% of the dose. Renal excretion of the parent drug is less than 0.03% of the dose. About 40% of the dose is excreted as inactive metabolites in the urine. No single excreted metabolite represents more than 5% of a dose.
Volume of Distribution
796 185 L
Clearance
381 +/- 95 mL/minute [IV administration]
The pharmacokinetics of itraconazole after intravenous administration and its absolute oral bioavailability from an oral solution were studied in a randomized crossover study in 6 healthy male volunteers. The observed absolute oral bioavailability of itraconazole was 55%.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (February 2010). Available from, as of September 27, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=16279
The oral bioavailability of itraconazole is maximal when itraconazole capsules are taken with a full meal. The pharmacokinetics of itraconazole were studied in 6 healthy male volunteers who received, in a crossover design, single 100 mg doses of itraconazole as a polyethylene glycol capsule, with or without a full meal. The same 6 volunteers also received 50 mg or 200 mg with a full meal in a crossover design. In this study, only itraconazole plasma concentrations were measured. The respective pharmacokinetic parameters for itraconazole are presented in the table /provided/.
Table: Oral Bioavailability of Itraconazole (Itraconazole capsules): [Table#7591]
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (February 2010). Available from, as of September 27, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=16279
[Table#7591]
Steady-state concentrations were reached within 15 days following oral doses of 50 mg to 400 mg daily. Values given in the table below are data at steady-state from a pharmacokinetics study in which 27 healthy male volunteers took 200 mg itraconazole capsules b.i.d. (with a full meal) for 15 days [Table#7592]
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (February 2010). Available from, as of September 27, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=16279
[Table#7592]
Thirty healthy men received single 200 mg doses of itraconazole capsules under fasted conditions either 1) with water; 2) with water, after ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. for 3 days; or 3) with cola, after ranitidine 150 mg b.i.d. for 3 days. When itraconazole capsules were administered after ranitidine pretreatment, itraconazole was absorbed to a lesser extent than when itraconazole capsules were administered alone, with decreases in AUC0-24 and Cmax of 39% +/- 37% and 42% +/- 39%, respectively. When itraconazole capsules were administered with cola after ranitidine pretreatment, itraconazole absorption was comparable to that observed when itraconazole capsules were administered alone.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (February 2010). Available from, as of September 27, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=16279
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Itraconazole (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Itraconazole is extensively metabolized by the liver into a large number of metabolites, including hydroxyitraconazole, the major metabolite. The main metabolic pathways are oxidative scission of the dioxolane ring, aliphatic oxidation at the 1-methylpropyl substituent, N-dealkylation of this 1-methylpropyl substituent, oxidative degradation of the piperazine ring and triazolone scission.
Itraconazole is metabolized predominantly by the cytochrome P450 3A4 isoenzyme system (CYP3A4), resulting in the formation of several metabolites, including hydroxyitraconazole, the major metabolite. Results of a pharmacokinetics study suggest that itraconazole may undergo saturable metabolism with multiple dosing.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (February 2010). Available from, as of September 27, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=16279
Itraconazole (ITZ) is metabolized in vitro to three inhibitory metabolites: hydroxy-itraconazole (OH-ITZ), keto-itraconazole (keto-ITZ), and N-desalkyl-itraconazole (ND-ITZ). The goal of this study was to determine the contribution of these metabolites to drug-drug interactions caused by ITZ. Six healthy volunteers received 100 mg ITZ orally for 7 days, and pharmacokinetic analysis was conducted at days 1 and 7 of the study. The extent of CYP3A4 inhibition by ITZ and its metabolites was predicted using this data. ITZ, OH-ITZ, keto-ITZ, and ND-ITZ were detected in plasma samples of all volunteers. A 3.9-fold decrease in the hepatic intrinsic clearance of a CYP3A4 substrate was predicted using the average unbound steady-state concentrations (C(ss,ave,u)) and liver microsomal inhibition constants for ITZ, OH-ITZ, keto-ITZ, and ND-ITZ. Accounting for circulating metabolites of ITZ significantly improved the in vitro to in vivo extrapolation of CYP3A4 inhibition compared to a consideration of ITZ exposure alone.
PMID:17495874 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3488349 Templeton IE et al; Clin Pharmacol Ther 83 (1): 77-85 (2008)
21 hours
Itraconazole interacts with 14-α demethylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme necessary to convert lanosterol to ergosterol. As ergosterol is an essential component of the fungal cell membrane, inhibition of its synthesis results in increased cellular permeability causing leakage of cellular contents. Itraconazole may also inhibit endogenous respiration, interact with membrane phospholipids, inhibit the transformation of yeasts to mycelial forms, inhibit purine uptake, and impair triglyceride and/or phospholipid biosynthesis.
In vitro studies have demonstrated that itraconazole inhibits the cytochrome P450-dependent synthesis of ergosterol, which is a vital component of fungal cell membranes.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Itraconazole (itraconazole) capsule (February 2010). Available from, as of September 27, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=16279