


1. 6870-67-3
2. Ccris 5777
3. Hsdb 3500
4. Nsc 89936
5. Brn 0054580
6. Gm32u80h1r
7. Jacobine.
8. Nsc-89936
9. 471-14-7
10. Jacobine [iarc]
11. Jacobine , Hplc Grade
12. Unii-gm32u80h1r
13. 4-27-00-06827 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
14. Chebi:6080
15. Dtxsid501020078
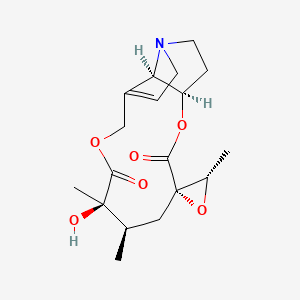
16. 15,20-epoxy-15,20-dihydro-12-hydroxysenecionan-11,16-dione
17. Mfcd00870079
18. (15alpha,20r)15,20-epoxy-15,20-dihydro-12-hydroxysenecionan-11,16-dione
19. 12beta-hydroxy-12alpha,13beta-dimethylsenec-1-enine-15s-spiro-2'-(3'r-methyloxiran)
20. Senecionan-11,16-dione, 15,20-epoxy-15,20-dihydro-12-hydroxy-, (15-alpha,20s)-
21. Senecionan-11,16-dione, 15,20-epoxy-15,20-dihydro-12-hydroxy-, (15alpha,20r)-
22. Hy-124058
23. Cs-0084068
24. Q27107031
25. (15alpha,20r)15,20-epoxy-15,20-dihydro-12-hydroxy-senecionan-11,16-dione
26. (2s,3s,5'r,6'r,9a1'r,14a'r)-6'-hydroxy-3,5',6'-trimethyl-5',6',9',9a1',11',13',14',14a'-octahydro-2'h-spiro[oxirane-2,3'-[1,6]dioxacyclododecino[2,3,4-gh]pyrrolizine]-2',7'(4'h)-dione
27. Senecionan-11,16-dione, 15,20-epoxy-15,20-dihydro-12-hydroxy-, (15.alpha.,20s)-
28. Spiro((1,6)dioxacyclododecino(2,3,4-gh)pyrrolizine-3(2h),2'-oxirane)-2,7(4h)-dione, 5,6,9,11,13,14,14a,14b-octahydro-6-hydroxy-3',5,6-trimethyl-, (2's,3's,5r,6r,14ar,14br)-
| Molecular Weight | 351.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H25NO6 |
| XLogP3 | 0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 351.16818752 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 351.16818752 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 88.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 648 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
The data suggest that consumption of milk from goats fed Senecio jacobaea produces a selective alteration of the activities of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes.
PMID:7302964 Miranda C et al; Toxicol Lett 8(6): 343-7 (1981)
Excretion of pyrrolizidine alkaloids (pa's) in diet of rabbits was not affected by the addition of copper and zinc to the diet. Isolated pa's from Senecio jacobaea were found to be readily transferred across the mucosa of isolated everted sacs of jejunum and ileum in vitro against a concentration gradient. These results suggest that the effects of dietary Senecio jacobaea on alterations in mineral metabolism are not due to changes in GI mineral absorption. In addition, it appears that the resistance of rabbits to dietary Senecio jacobaea intoxication is not caused by low GI absorption of pyrrolizidine alkaloids, but rather by efficient urinary elimination.
PMID:7161214 Swick R et al; J Anim Sci 55 (6): 1417 (1982)
In general, the hepatotoxic pyrrolidine alkaloids are metabolized in rat liver to give hydrolysis products, n-oxides and dehydropyrrolizidine (pyrrolic) deriv. The latter group appears on current evidence to mediate most of toxic reactions of alkaloids. These pyrrolic deriv are produced by mixed-function oxidases of liver cells. Initial product formed from alkaloids that are esters of...retronecine (eg, jacobine...) is very probably the dehydroalkaloid. Dehydroalkaloids are highly reactive alkylating agents which react immediately with cell constituents to give soluble or bound secondary metabolites or which hydrolyze to dehydroaminoalcohol. /pyrrolizidine alkaloids/
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V10 336 (1976)
The effect of prolonged phenobarbital (pb) administration on the toxicity of Senecio jacobaea (sj) was studied in sheep. Results suggested that mixed-function oxidase induction by pb does not increase the susceptibility of sheep to sj intoxication. Sheep possess a high activity of hepatic microsomal epoxide hydrolase which could account for their resistance to sj intoxication.
PMID:6853385 Swick R et al; J Anim Sci 56(4): 887 (1983)
Comparison is made of the alkylating activities of a series of semi-synthetic pyrrole esters and pyrrole derivatives of pyrrolizidine alkaloids under pseudo-first-order reaction conditions. Data for alkylation by jacobine pyrrole (a reactive metabolite of jacobine) fit a simple first-order rate expression for product formation. The large increase in reaction rate for jacobine pyrrole is suggestive of an electronic field effect due to the epoxide ring in proximity to the C-7 ester moiety.
Karchesy J et al; Heterocycles 16(4): 631 (1981)