
1. Caldine
2. Gr 43659x
3. Gr-43659x
4. Lacimen
5. Lacipil
6. Motens
1. 103890-78-4
2. Lacipil
3. Motens
4. Gr-43659x
5. Trans Lacidipine
6. Gr 43659x
7. Lacidipine (lacipil, Motens)
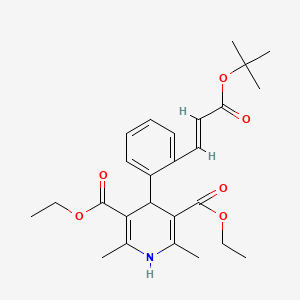
8. Diethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(e)-3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-3-oxoprop-1-enyl]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
9. Gx-1048
10. Sn-305
11. 4-(o-((e)-2-carboxyvinyl)phenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 4-tert-butyl Diethyl Ester
12. Lacimen
13. Dsstox_cid_26429
14. Dsstox_rid_81607
15. Dsstox_gsid_46429
16. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 4-(2-(3-(1,1-dimethylethoxy)-3-oxo-1-propenyl)phenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-, Diethyl Ester, (e)-
17. Diethyl (e)-4-(2-(3-(tert-butoxy)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)phenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
18. 260080034n
19. Lacidipinum [latin]
20. Lacidipino [spanish]
21. Lacidipino
22. Lacidipinum
23. Lacirex
24. (e)-diethyl 4-(2-(3-(tert-butoxy)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)phenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
25. Smr000466342
26. Cas-103890-78-4
27. Sr-05000001445
28. Gr 43659 X
29. Viapres
30. Molap
31. Lacidipine [usan:inn:ban]
32. Lacidipine,(s)
33. Ncgc00164545-01
34. (e)-diethyl 4-(2-(3-tert-butoxy-3-oxoprop-1-enyl)phenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
35. Lacidipine- Bio-x
36. Motens (tn)
37. Unii-260080034n
38. Lacidipine [mi]
39. Lacidipine [inn]
40. Lacidipine [jan]
41. Lacidipine (usan/inn)
42. Lacidipine [usan]
43. Lacidipine [vandf]
44. Lacidipine [mart.]
45. Lacidipine [who-dd]
46. Lacipil, Motens, Lacidipine
47. Schembl49277
48. Schembl49278
49. Mls000759454
50. Mls001424282
51. Chembl460291
52. Chembl1728809
53. Dtxsid1046429
54. Schembl13287288
55. Chebi:94480
56. Gtpl11740
57. Chebi:135737
58. Hms2052f03
59. Hms2089k22
60. Hms3713d20
61. Hms3884i18
62. (non-isotopelabelled)lacidipine-d9
63. Bcp02933
64. Gr43659x
65. Hy-b0347
66. Tox21_112174
67. Gx1048
68. S1994
69. Stl454986
70. Akos005066844
71. Tox21_112174_1
72. Zinc100015470
73. Bcp9000831
74. Ccg-101153
75. Ccg-220579
76. Db09236
77. Gx 1048
78. Hs-0086
79. Nc00403
80. Ncgc00263529-01
81. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-(3-(1,1-dimethylethoxy)-3-oxo-1-propenyl)phenyl)-, Diethyl Ester, (e)-
82. Ac-11008
83. Ac-33195
84. Bl164603
85. Cpd000466342
86. Bcp0726000285
87. L0276
88. Sw219840-1
89. C71162
90. D04657
91. Ab00698350-05
92. Ab01275445-01
93. Ab01275445_02
94. Gx-1048,gr-43659x,sn-305
95. 890l784
96. A800840
97. J-001058
98. Q1163827
99. Sr-05000001445-1
100. Sr-05000001445-2
101. Brd-k05851096-001-01-9
102. 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(e)-3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-3-oxoprop-1-enyl]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic Acid Diethyl Ester
103. Diethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-[2-[(e)-3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-3-oxidanylidene-prop-1-enyl]phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
104. Diethyl 4-{2-[(1e)-3-tert-butoxy-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl]phenyl}-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 455.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H33NO6 |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 455.23078777 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 455.23078777 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 90.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 805 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for the treatment of hypertension either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, including -adrenoceptor antagonists, diuretics, and ACE-inhibitors.
acidipine is a specific and potent calcium antagonist with a predominant selectivity for calcium channels in the vascular smooth muscle. Its main action is to dilate predominantly peripheral and coronary arteries, reducing peripheral vascular resistance and lowering blood pressure. Following the oral administration of 4 mg lacidipine to volunteer subjects, a minimal prolongation of QTc interval has been observed (mean QTcF increase between 3.44 and 9.60 ms in young and elderly volunteers).
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C08 - Calcium channel blockers
C08C - Selective calcium channel blockers with mainly vascular effects
C08CA - Dihydropyridine derivatives
C08CA09 - Lacidipine
Absorption
Since it is a highly lipophilic compound, lacidpine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration with the peak plasma concentrations reached between 30 and 150 minutes of dosing. The peak plasma concentrations display large interindividual variability, with the values ranging from 1.6 to 5.7 g/L following single-dose oral administration of lacidipine 4mg in healthy young volunteers. Absolute bioavailability is less than 10% due to extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 70% of the administered dose is eliminated as metabolites in the faeces and the remainder as metabolites in the urine.
Lacidipine undergoes complete CYP3A4-mediated hepatic metabolism, with no parent drug detected in the urine or faeces. The 2 main metabolites have no pharmacological activity.
The average terminal half-life of lacidipine ranges from between 13 and 19 hours at steady state.
By blocking the voltage-dependent L-type calcium channels, it prevents the transmembrane calcium influx. Normally, calcium ions serve as intracellular messengers or activators in exictable cells including vascular smooth muscles. The influx of calcium ultimately causes the excitation and depolarization of the tissues. Lacidipine inhibits the contractile function in the vascular smooth muscle and reduce blood pressure. Due to its high membrane partition coefficient, some studies suggest that lacidipine may reach the receptor via a two-step process; it first binds and accumulates in the membrane lipid bilayer and then diffuses within the membrane to the calcium channel receptor. It is proposed that lacidipine preferentially blocks the inactivated state of the calcium channel. Through its antioxidant properties shared amongst other dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, lacidipine demonstrates an additional clinical benefit. Its antiatherosclerotic effects are mediated by suppressing the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and subsequent inflammatory actions by chemokines, cytokines and adhesion molecules, thus reducing atherosclerotic lesion formation. Lacidipine may also suppress cell proliferation and migration in smooth muscle cells and suppress the expression of matrix metalloproteinases, which affects the stability of atheromatous plaques.