
1. Amivalex
2. Duphalac
3. Normase
1. D-lactulose
2. Bifiteral
3. Cephulac
4. Chronulac
5. Constilac
6. Cholac
7. Lactulosa
8. Lactulosum
9. Duphalac
10. 4618-18-2
11. 4-o-beta-d-galactopyranosyl-d-fructose
12. 9xh2p2n8ep
13. 4-o-beta-d-galactopyranosyl-d-fructofuranose
14. Chebi:6359
15. 58166-24-8
16. Isolactose
17. Laevolac
18. 4-o-beta-d-galactopyranosyl-beta-d-fructofuranose
19. Nsc-757082
20. (2s,3r,4s,5r,6r)-2-[(2r,3s,4s,5r)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol
21. Lactulosum [latin]
22. Lactulosa [spanish]
23. Kristalose
24. Lattulosio [italian]
25. Lactulosum [inn-latin]
26. Dsstox_cid_25833
27. Dsstox_rid_81161
28. Dsstox_gsid_45833
29. Lactulosa [inn-spanish]
30. 58166-25-9
31. Lattulosio
32. Actilax
33. Alpha-lactulose
34. Cephulac (tn)
35. (2s,3r,4s,5r,6r)-2-(((2r,3s,4s,5r)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2h-pyran-3,4,5-triol
36. Cas-4618-18-2
37. Sr-05000002084
38. Einecs 225-027-7
39. Unii-9u7d5qh5ae
40. Unii-9xh2p2n8ep
41. Brn 0093773
42. Brn 6278818
43. 4-beta-d-galactosido-(1,4)-d-fructose
44. Delta-lactulose
45. D-fructose, 4-o-beta-d-galactopyranosyl-
46. Cephulac Syrup
47. Lactulose Syrup
48. 4-o-b-d-galactopyranosyl-d-fructose
49. Lactulose Jp17
50. Chronulac (tn)
51. Ncgc00094707-01
52. W9t
53. Beta-d-fructofuranose, 4-o-beta-d-galactopyranosyl-
54. Lactulose [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
55. 4-o-beta-d-galattopiranosil-d-fruttofuranosio [italian]
56. Spectrum_000857
57. Spectrum2_001159
58. Spectrum3_000478
59. Spectrum4_000962
60. Spectrum5_000908
61. .alpha.-lactulose
62. 4-o-beta-d-galattopiranosil-d-fruttofuranosio
63. Schembl18912
64. Bspbio_002216
65. Kbiogr_001303
66. Kbioss_001337
67. 5-17-07-00214 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
68. Fructofuranose, 4-o-beta-d-galactopyranosyl-, D-
69. Divk1c_000064
70. Spectrum1500363
71. Spbio_001117
72. Lactulose (jp17/usp/inn)
73. Alpha-d-fructofuranose, 4-o-beta-d-galactopyranosyl-
74. Chembl296306
75. Dtxsid5045833
76. Hms500d06
77. Kbio1_000064
78. Kbio2_001337
79. Kbio2_003905
80. Kbio2_006473
81. Kbio3_001436
82. Ninds_000064
83. Hms1920j03
84. Hms2094g15
85. Pharmakon1600-01500363
86. Zinc3977952
87. Tox21_111318
88. Bdbm50377984
89. Ccg-39552
90. Mfcd00151469
91. Nsc757082
92. Akos024283994
93. Tox21_111318_1
94. Db00581
95. Nsc 757082
96. Idi1_000064
97. Ncgc00142624-01
98. Ncgc00142624-02
99. Ncgc00142624-03
100. Ncgc00142624-05
101. 2-[(3s,4s,2r,5r)-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)-4,5-dihydroxyoxolan-3-yloxy](2s,4s,3r, 5r,6r)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-2h-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyran-3,4,5-triol
102. 4-o-b-d-galactopyranosyl-d-fructofuranose
103. 4-o-beta-delta-galactopyranosyl-delta-fructose
104. C07064
105. D00352
106. Ab00052029_02
107. Q422689
108. 4-o-beta-delta-galactopyranosyl-delta-fructofuranose
109. Sr-05000002084-1
110. Sr-05000002084-4
111. .alpha.-d-fructofuranose, 4-o-.beta.-d-galactopyranosyl-
112. Wurcs=2.0/2,2,1/[ha122h-2b_2-5][a2112h-1b_1-5]/1-2/a4-b1
113. (2s,3r,4s,5r,6r)-2-{[(2r,3s,4s,5r)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol
| Molecular Weight | 342.30 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H22O11 |
| XLogP3 | -4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 342.11621151 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 342.11621151 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 190 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 395 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 9 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cholac |
| PubMed Health | Lactulose (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent, Laxative, Hyperosmotic |
| Drug Label | Generlac Solution (Lactulose Solution, USP) is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral or rectal administration. Each 15 mL of Generlac Solution contains: 10 g lactulose (and not more than 1.6 g galactose, not more than 1.2 g lactose, not... |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral, rectal |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alra |
| 2 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Constilac |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alra |
| 3 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Constulose |
| PubMed Health | Lactulose (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent, Laxative, Hyperosmotic |
| Drug Label | Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral administration. Each 15 mL of lactulose solution contains: 10 g lactulose (and less than 1.6 g galactose, less than 1.2 g lactose, and 0.1 g or less of fructose).Lactulose is a colonic a... |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actavis Mid Atlantic |
| 4 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Enulose |
| PubMed Health | Lactulose (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent, Laxative, Hyperosmotic |
| Drug Label | Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral or rectal administration. Each15 mL of lactulose solution contains 10 g lactulose (and less than 1.6 g galactose, less than 1.2 g lactose, and 0.1 g or less of fructose). Lactulose solut... |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral, rectal |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actavis Mid Atlantic |
| 5 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Generlac |
| PubMed Health | Lactulose (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent, Laxative, Hyperosmotic |
| Drug Label | Generlac Solution (Lactulose Solution, USP) is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral or rectal administration. Each 15 mL of Generlac Solution contains: 10 g lactulose (and not more than 1.6 g galactose, not more than 1.2 g lactose, not... |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral, rectal |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Morton Grove Pharms |
| 6 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lactulose |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | For solution; Solution |
| Route | Oral; Oral, rectal |
| Strength | 10gm/packet; 10gm/15ml; 20gm/packet |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Ani Pharms; Fresenius Kabi; Pharm Assoc; Morton Grove; Roxane; Cumberland Pharms; Vistapharm; Hi Tech Pharma |
| 7 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cholac |
| PubMed Health | Lactulose (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent, Laxative, Hyperosmotic |
| Drug Label | Generlac Solution (Lactulose Solution, USP) is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral or rectal administration. Each 15 mL of Generlac Solution contains: 10 g lactulose (and not more than 1.6 g galactose, not more than 1.2 g lactose, not... |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral, rectal |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alra |
| 8 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Constilac |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Alra |
| 9 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Constulose |
| PubMed Health | Lactulose (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent, Laxative, Hyperosmotic |
| Drug Label | Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral administration. Each 15 mL of lactulose solution contains: 10 g lactulose (and less than 1.6 g galactose, less than 1.2 g lactose, and 0.1 g or less of fructose).Lactulose is a colonic a... |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actavis Mid Atlantic |
| 10 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Enulose |
| PubMed Health | Lactulose (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent, Laxative, Hyperosmotic |
| Drug Label | Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral or rectal administration. Each15 mL of lactulose solution contains 10 g lactulose (and less than 1.6 g galactose, less than 1.2 g lactose, and 0.1 g or less of fructose). Lactulose solut... |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral, rectal |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actavis Mid Atlantic |
| 11 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Generlac |
| PubMed Health | Lactulose (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Gastrointestinal Agent, Laxative, Hyperosmotic |
| Drug Label | Generlac Solution (Lactulose Solution, USP) is a synthetic disaccharide in solution form for oral or rectal administration. Each 15 mL of Generlac Solution contains: 10 g lactulose (and not more than 1.6 g galactose, not more than 1.2 g lactose, not... |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Oral, rectal |
| Strength | 10gm/15ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Morton Grove Pharms |
| 12 of 12 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lactulose |
| Active Ingredient | Lactulose |
| Dosage Form | For solution; Solution |
| Route | Oral; Oral, rectal |
| Strength | 10gm/packet; 10gm/15ml; 20gm/packet |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Ani Pharms; Fresenius Kabi; Pharm Assoc; Morton Grove; Roxane; Cumberland Pharms; Vistapharm; Hi Tech Pharma |
Lactulose is indicated for use as a laxative in the treatment of chronic constipation in adults and geriatric patients. Additionally, lactulose is also employed as an adjunct to protein restriction and supportive therapy for the prevention and treatment of portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE), including both the hepatic pre-coma and coma variations. In particular, lactulose solution has been effective at managing PSE resulting from surgical portacaval shunts or from chronic hepatic diseases like cirrhosis. Moreover, there have also been studies demonstrating the capacity for lactulose to minimize the formation of gallstones and even some investigations regarding the experimental use of the agent in developing novel anticancer agents owing to its ability to bind galactin carbohydrates involved in various tumor progressions.
FDA Label
Lactulose formulations are most commonly administered via the oral route or the rectal route. Consequently, because the substance experiences minimal absorption by the gut it typically remains localized in the gastrointestinal tract environment and ultimately demonstrates almost all of its pharmacologic effects within the gut. In particular, as lactulose elicits its laxative effects in enhancing stool amounts and softening stool, such biochemical and physiologic activities can cause increased bowel sounds (borborygmi), a feeling of bloatedness, belching, frequent flatus, and diarrhea.
Gastrointestinal Agents
Drugs used for their effects on the gastrointestinal system, as to control gastric acidity, regulate gastrointestinal motility and water flow, and improve digestion. (See all compounds classified as Gastrointestinal Agents.)
A06AD11
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A06 - Drugs for constipation
A06A - Drugs for constipation
A06AD - Osmotically acting laxatives
A06AD11 - Lactulose
Absorption
After administration by the oral route, less than 3% of the given dose of lactulose solution is absorbed by the small intestine. The remaining unabsorbed lactulose reaches the large intestine where it is metabolized - but even then, negligible quantities of unchanged lactulose or its metabolites are absorbed across the colon.
Route of Elimination
The renal excretion of any lactulose that manages to be absorbed into the circulation has been determined to be 3% or less and is generally complete within 24 hours. Any unabsorbed lactulose is largely excreted with stool.
Volume of Distribution
Negligible amounts of lactulose - metabolized or non-metabolized - are absorbed into the body.. Most lactulose that is administered subsequently remains predominantly around the gastrointestinal tract area.
Clearance
Negligible amounts of lactulose - metabolized or non-metabolized - are absorbed into the body.. Regardless, data regarding the clearance of lactulose is not readily available or accessible.
Lactulose is essentially only metabolized in the colon by saccharolytic bacteria that are present there. In particular, the substance is broken down into lactic acid and small amounts of acetic and formic acid. Specific examples of bacteria that normally inhabit the large intestine that are capable of lactulose metabolism include Lactobacilli, Bacteroides, Escherichia coli, and Clostridia.
The data regarding the half-life of lactulose is not readily available or accessible.
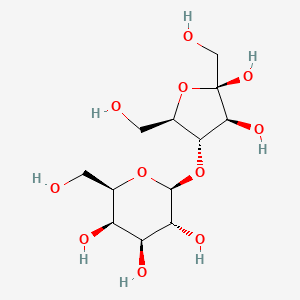
Lactulose is a synthetic disaccharide derivative of lactose that consists of one molecule of galactose and one molecule of fructose. Saccharolytic bacteria present in the large intestine subsequently break the substance down into organic acids like lactic acid and small amounts of formic and acetic acids. Such resultant volatile fatty acid metabolites, in combination with hydrogen and methane that is also generated consequently enhance intraluminal gas formation, peristaltic gut motility, and elicit an osmotic effect that facilitates an increase in the water content of stool as well as associated stool softening. All of these actions ultimately assist in facilitating and increasing the frequency of bowel movements in patients experiencing constipation, although it may take 24 to 48 hours after using the medication for this laxative effect to become evident. At the same time, the formation of such acids via the metabolism of lactulose by colonic bacteria also acidifies the contents of the colon, thereby contributing to the treatment of portal-systemic encephalopathy (PSE). As one of the principal features of PSE involves the accumulation of nitrogenous waste products like ammonia in the systemic circulation, a state in which the colonic contents become more acidic than blood allows ammonia in the circulation to diffuse into the colon.. Furthermore, ammonia that diffuses into the acidic colon is ionized to ammonium ions that are incapable of being absorbed back into the blood. These effects, combined with the laxative action of lactulose facilitates the excretion of excess ammonia. And finally, it is also believed that an acidic colonic environment results in the elimination of urease-producing bacteria that contribute to the formation of ammonia while surviving colonic bacteria use up any trapped ammonia in the colon as a source of nitrogen for protein synthesis.