

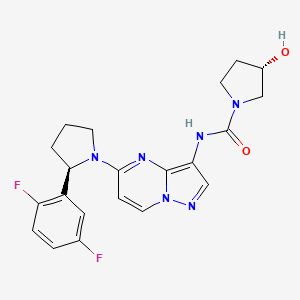

1. (3s)-n-(5-(2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyrazolo(1,5-a)pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
2. Arry-470
3. Arry470
4. Bay-2757556
5. Bay2757556
6. Loxo-101
7. Loxo101
8. N-(5-(2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyrazolo(1,5-a)pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
9. Vitrakvi
1. Loxo-101
2. 1223403-58-4
3. Arry-470
4. (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
5. Vitrakvi
6. Loxo 101
7. Bay2757556
8. Bay-2757556
9. Loxo101
10. Pf9462i9hx
11. (3s)-n-[5-[(2r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
12. 1-pyrrolidinecarboxamide, N-(5-((2r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl)pyrazolo(1,5-a)pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-, (3s)-
13. Arry 470
14. 1-pyrrolidinecarboxamide, N-[5-[(2r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]-3-hydroxy-, (3s)-
15. Larotrectinib [inn]
16. Larotrectinib [mi]
17. Arry-470; Larotrectinib
18. Larotrectinib (usan/inn)
19. Larotrectinib [usan:inn]
20. Larotrectinib [usan]
21. Unii-pf9462i9hx
22. Arry470
23. Larotrectinib [who-dd]
24. Amy264
25. Gtpl8909
26. Schembl2241012
27. Chembl3889654
28. Bdbm136597
29. Dtxsid101020707
30. Bcp16262
31. Ex-a1981
32. Mfcd28902192
33. Nsc785570
34. Nsc801004
35. S5860
36. Larotrectinib (loxo-101 Free Base)
37. Example 14 [us8865698 B2]
38. Zinc118399834
39. Cs-5722
40. Db14723
41. Nsc-785570
42. Nsc-801004
43. Ac-33660
44. As-35231
45. Hy-12866
46. J3.628.138c
47. D11137
48. Us8865698, 14
49. Q27081513
50. Arry-470;arry 470 : Loxo-101; Loxo101; Larotrectinib
51. Arry470;arry-470;arry 470;loxo 101;loxo101;larotrectinib
52. (3s)-n-(5-((2r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin- 1-yl)pyrazolo(1,5-a)pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine- 1-carboxamide
53. (3s)-n-(5-((2r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyrazolo(1,5-a)pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine- 1-carboxamide
54. (s)-n-(5 -((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
55. (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin -1-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
56. (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
57. (s)-n-(5-((r)-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3 Yl)-3-hydroxypyrrolidine-1-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 428.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H22F2N6O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 428.17723029 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 428.17723029 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 659 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Larotrectinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is currently indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with solid tumors that either a) have a neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase (NTRK) gene fusion without a known acquired resistance mutation, b) are metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and c) have no satisfactory alternative treatments or that have progressed following treatment. At the moment, these uses of larotrectinib are only approved under the auspices of an accelerated approval by the US FDA based on overall response rate and duration of response and continuation of support for these indications may be contingent upon the verification and description of continued clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
FDA Label
Vitrakvi as monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of adult and paediatric patients with solid tumours that display a Neurotrophic Tyrosine Receptor Kinase (NTRK) gene fusion,
- who have a disease that is locally advanced, metastatic or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity, and
- who have no satisfactory treatment options.
Treatment of malignant neoplasms of the central nervous system
Treatment of all conditions included in the category of malignant neoplasms (except central nervous system tumours, haematopoietic and lymphoid tissue neoplasms)
At doses that are nine-fold greater than the recommended adult dose, larotrectinib does not elicit any QTc interval prolongation that is clinically relevant.
L01XE53
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX12 - Larotrectinib
Absorption
The mean absolute bioavailability of larotrectinib capsules has been recorded as 34%, from a range spanning 32% to 37%. In adult patients who received larotrectinib capsules 100 mg twice daily, peak plasma levels Cmax were achieved at about one hour after dosing and steady-state was reached within the time span of three days. The mean steady-state of these administered larotrectinib capsules was Cmax 788 ng/mL and the AUC(0-24hr) was 4351 ng*h/mL. Concurrently, in healthy subjects, the AUC of the administered larotrectinib oral solution formulation was similar to that of the capsules and the particular Cmax was 36% greater with the oral solution. The AUC of larotrectinib was similar but the Cmax was reduced by 35% after oral administration of a single 100 mg capsule of larotrectinib to healthy subjects taken with a high-fat meal (approximately 900 calories, 58 grams carbohydrate, 56 grams fat and 43 grams protein) compared to the Cmax and AUC in the fasted state.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration of a single [14C] radiolabeled 100 mg dose of larotrectinib to healthy subjects, 58% (5% unchanged) of the administered radioactivity was recovered in feces and 39% (20% unchanged) was recovered in urine.
Volume of Distribution
The mean volume of distribution Vss of larotrectinib has been documented as being 48L following intravenous administration in healthy subjects.
Clearance
The mean clearance CL/F of larotrectinib has been documented as 98 L/h.
Larotrectinib is metabolized predominantly by the CYP3A4 isoenzymes. Following oral administration of a single [14C] radiolabeled 100 mg dose of larotrectinib to healthy subjects, unchanged larotrectinib constituted 19% and an O-linked glucuronide constituted 26% of the major circulating radioactive drug components in plasma.
The half-life of larotrectinib has been determined to be 2.9 hours.
Tropomysoin Receptor Kinases (TRK) like TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC elicit activities that regulate the natural growth, differentiation, and survival of neurons when they interact with endogenous neutrotrophin ligands. TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC are themselves encoded by the NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3 genes, respectively. It has been discovered that chromosomal rearrangements involving in-frame fusions of these genes with various partners, translocations in the TRK kinase domains, mutations in the TRK ligand-binding site, amplifications of NTRK, or the expression of TRK splice variants can result in constitutively-activated chimeric TRK fusion proteins that can act as oncogenic drivers that promote cell proliferation and survival in tumor cell lines. Subsequently, larotrectinib functions as an inhibitor of TRKs including TRKA, B, and C. In in vitro and in vivo tumor models, larotrectinib demonstrated anti-tumor activity in cells with constitutive activation of TRK proteins resulting from gene fusions, deletion of a protein regulatory domain, or in cells with TRK protein overexpression. Larotrectinib had minimal activity in cell lines with point mutations in the TRKA kinase domain, including the clinically identified acquired resistance mutation, G595R. Point mutations in the TRKC kinase domain with clinically identified acquired resistance to larotrectinib include G623R, G696A, and F617L.