

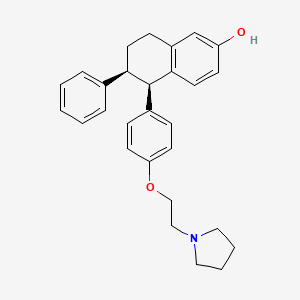

1. (-)-cis-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-phenyl-5-(p-(2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)-2-naphthol
2. Cis-1r-(4'-pyrrolidinoethoxyphenyl)-2s-phenyl-6-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene, Tartrate Salt
3. Cp 336156
4. Cp-336,156
5. Las Estrogen Receptor Modulator
6. Lasofoxifene Hydrochloride
1. 180916-16-9
2. Rac-lasofoxifene
3. Oporia
4. Cp 336156
5. 180915-78-0
6. (5r,6s)-6-phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol
7. Cp-336,156
8. (-)-cis-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-phenyl-5-(p-(2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)-2-naphthol
9. Chembl328190
10. 337g83n988
11. Rel-(5r,6s)-6-phenyl-5-(4-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol
12. Lasofoxifene [inn]
13. (5r,6s)-6-phenyl-5-(4-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol
14. (5r,6s)-6-phenyl-5-{4-[2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol
15. (5r,6s)-6-phenyl-5-(4-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol.
16. 2-naphthalenol, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-phenyl-5-[4-[2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]-, (5r,6s)-
17. Lasofoxifene [inn:ban]
18. Lasofoxifene Hcl
19. Cp-336156
20. Lasofoxifeno
21. Lasofoxifenum
22. Unii-337g83n988
23. 2-naphthalenol, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-phenyl-5-(4-(2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)-, (5r,6s)-
24. C3d
25. Lasofoxifene [mi]
26. (5r,6s)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-phenyl-5-[4-[2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]-2-naphthalenol
27. Schembl26815
28. Lasofoxifene [mart.]
29. Lasofoxifene [who-dd]
30. Gtpl7542
31. Lasofoxifene [ema Epar]
32. Bdbm20606
33. Dtxsid50171037
34. Chebi:135938
35. Bcp03626
36. Hy-a0037
37. Zinc3918428
38. Akos030241621
39. Bcp9000842
40. Db06202
41. Ncgc00487269-02
42. Bcp0726000177
43. Cs-0006740
44. 916l169
45. Q644675
46. J-011550
47. (-)-cis-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-phenyl-5-(p-(2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)-2-naphthol.
48. Cis-6-phenvl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalene-2-ol
49. Cis-6-phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol
50. Cis-6-phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalene-2-ol
51. Cis-6phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalene-2-ol
52. (-)-cis-(5r,6s)-6-phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol
53. 2-naphthalenol, 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-6-phenyl-5-(4-(2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)-, (5r-cis)-
| Molecular Weight | 413.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H31NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 6.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 413.235479232 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 413.235479232 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 32.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 533 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in postmenopausal osteoporosis to reduce the risk of both vertebral and novertebral fractures, as well as address other postmenopausal conditions, including reduction in risk of breast cancer and treatment of vulvar and vaginal atrophy (VVA)
Fablyn is indicated for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fracture. A significant reduction in the incidence of vertebral and non-vertebral fractures but not hip fractures has been demonstrated (see section 5. 1).
When determining the choice of Fablyn or other therapies, including oestrogens, for a postmenopausal woman, consideration should be given to menopausal symptoms, effects on uterine and breast tissues, and cardiovascular risks and benefits (see section 5. 1).
Lasofoxifene exhibits both significant estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity both in vitro and in vivo, targeting any tissues that possess ERs, such as bone, uterus, breast, blood vessels, and liver. Binding assays demonstrated high affinity of the compound for both ER and ER in a tissue-dependent manner. It mimics the effects of estradiol with varying agonist and antagonist effects.
G03
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G03 - Sex hormones and modulators of the genital system
G03X - Other sex hormones and modulators of the genital system
G03XC - Selective estrogen receptor modulators
G03XC03 - Lasofoxifene
Absorption
Peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) were reached in about 6.0 to 7.3 hours. Displays higher oral bioavailability compared to other SERMs with increased resistance to intestinal glucuronidation due to nonpolar tetrahydronaphthalene structure. In a comparative study in the rat, lasofoxifene showed bioavailability of 62%.
Route of Elimination
Primarily fecal excretion and secondarily renal elimination as mainly metabolites, with less than 2% excreted in urine as unchanged parent drug.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution in postmenopausal women is 1350L.
Clearance
The apparent oral clearance (CL/F) of lasofoxifene in postmenopausal women is approximately 6.6 l/hr.
Phase I oxidation via hepatic CYP3A4/CYP3A5 and CYP2D6 accounts for nearly half of total metabolism of lasofoxifene. Phase II conjugation reactions include glucuronidation and sulfation. Its glucuronidation is catalyzed by UGTs that are expressed in both the liver (UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A6, and UGT1A9) and the intestine (UGT1A8 and UGT1A10). Further metabolites of lasofoxifene detected in plasma are the glucuronide of a hydroxylated metabolite, and the methylated catechols.
Lasofoxifene has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(5R,6S)-6-phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl]oxy]oxane-2-carboxylic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Elimination half-life is approximately 6 days.
Lasofoxifene mediates an agonist effect on estrogen receptors expressed on bone to mimic the positive effects of estrogen to reduce the production and lifespan of osteoclasts via altering the NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin system, stimulation of osteoblast (the bone forming cells) activity and additional effects on calcium homeostasis. It acts as an antagonist at uterus and mammary glands by suppressing the estrogen signaling in oncogenic pathways and inhibits the downstream gene transcription. A study also suggests that lasofoxifene may also act as an inverse agonist at CB2 cannabinoid receptor which is expressed in bone to inhibit osteoclast formation and resorptive activity.