

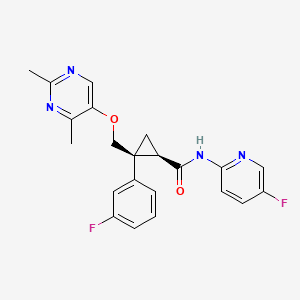

1. (1r,2s)-2-(((2,4-dimethyl-5-pyrimidinyl)oxy)methyl)-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoro-2-pyridinyl)cyclopropanecarboxamide
2. Cyclopropanecarboxamide, 2-(((2,4-dimethyl-5-pyrimidinyl)oxy)methyl)-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoro-2-pyridinyl)-, (1r,2s)-
3. Dayvigo
1. 1369764-02-2
2. Dayvigo
3. E-2006
4. E2006
5. 0k5743g68x
6. (1r,2s)-2-[(2,4-dimethylpyrimidin-5-yl)oxymethyl]-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoropyridin-2-yl)cyclopropane-1-carboxamide
7. (1r,2s)-2-(((2,4-dimethylpyrimidin-5-yl)oxy)methyl)-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoropyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide
8. Cyclopropanecarboxamide, 2-(((2,4-dimethyl-5-pyrimidinyl)oxy)methyl)-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoro-2-pyridinyl)-, (1r,2s)-
9. (1~{r},2~{s})-2-[(2,4-dimethylpyrimidin-5-yl)oxymethyl]-~{n}-(5-fluoranylpyridin-2-yl)-2-(3-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1-carboxamide
10. E 2006
11. Lemborexant [usan:inn]
12. Unii-0k5743g68x
13. (1r,2s)-2-(((2,4-dimethyl-5-pyrimidinyl)oxy)methyl)-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoro-2-pyridinyl)cyclopropanecarboxamide
14. (1r,2s)-2-((2,4-dimethylpyrimidin-5-yl)oxymethyl)-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoropyridin-2-yl)cyclopropane-1-carboxamide
15. (1r,2s)-2-[[(2,4-dimethyl-5-pyrimidinyl)oxy]methyl]-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoro-2-pyridinyl)cyclopropanecarboxamide
16. Cyclopropanecarboxamide, 2-[[(2,4-dimethyl-5-pyrimidinyl)oxy]methyl]-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoro-2-pyridinyl)-, (1r,2s)-
17. Dayvigo (tn)
18. Lemborexant [inn]
19. Lemborexant(e2006)
20. Lemborexant [mi]
21. Lemborexant; E-2006
22. Lemborexant [jan]
23. Lemborexant [usan]
24. Lemborexant [who-dd]
25. Lemborexant (jan/usan/inn)
26. Gtpl9302
27. Schembl2116558
28. Chembl3545367
29. Lemborexant [orange Book]
30. Dtxsid401027940
31. Amy27888
32. Ex-a2337
33. Bdbm50093793
34. Zinc118073503
35. Db11951
36. Compound 34 [pmid: 25953512]
37. Ncgc00488783-01
38. Ac-30918
39. Hy-16725
40. J3.610.985h
41. D11022
42. E-2006e-2006
43. A886588
44. Q20707990
45. (1r,2s)-2-{[(2,4-dimethylpyrimidin-5-yl)oxy]methyl}-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-n-(5-fluoropyridin-2-yl)cyclopropane-1-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 410.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H20F2N4O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 410.15543222 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 410.15543222 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 612 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Lemborexant is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with insomnia characterized by difficulties with sleep onset and/or sleep maintenance.
FDA Label
Lemborexant promotes sleep by antagonizing the actions of wake-promoting chemicals in the brain. Episodes of complex sleep behaviors (e.g. eating food, having sex, making phone calls) have been reported in patients using lemborexant - these events may occur in hypnotic-naive and hyponotic-experienced patients, and patients are unlikely to remember these events. Patients exhibiting complex sleep behaviors should discontinue lemborexant immediately. Lemborexant may carry some risk of abuse, and should be used with caution in patients with a history of alcohol or drug addiction. Its controlled substance schedule is currently under review by the Drug Enforcement Administration.
Orexin Receptor Antagonists
Substances that bind to and inhibit the action of OREXIN RECEPTORS. Drugs in this class have been used as SLEEP AIDS, PHARMACEUTICAL. (See all compounds classified as Orexin Receptor Antagonists.)
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05C - Hypnotics and sedatives
N05CM - Other hypnotics and sedatives
N05CM21 - Lemborexant
Absorption
Animal models of lemborexant disposition have demonstrated rapid absorption following oral administration. The Tmax of lemborexant is approximately 1-3 hours, or 3-5 hours following administration of a high-fat, high-calorie meal. Cmax and AUC0-24h increase at a rate slightly less than proportionate to the given dose. Following administration of a high-fat, high-calorie meal, Cmax is decreased by 23% and AUC0-inf is increased by 18%. AUC, Cmax, and terminal half-life are increased in the presence of moderate hepatic impairment, and AUC (but not half-life) is increased in the presence of mild hepatic impairment.
Route of Elimination
Following oral administration, 57.4% of the dose is found in the feces and 29.1% in the urine. Less than 1% of the dose recovered in the urine exists as unchanged parent drug, suggesting extensive metabolism.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of lemborexant is 1970 L, indicating extensive tissue distribution.
Given that less than 1% of an administered dose is recovered unchanged in the urine, it is likely that lemborexant is extensively metabolized - this has been confirmed in rat and monkey models, but its metabolism in humans has not been fully characterized. Prescribing information states that it is predominantly metabolized by CYP3A4, with a smaller contribution by CYP3A5. The major circulating metabolite is lemborexant's M10 metabolite, which is pharmacologically active and binds to orexin receptors with a similar affinity to the parent drug. The M10 metabolite has the potential to induce CYP3A and CYP2B6 enzymes, weakly inhibit CYP3A enzymes, and is a substrate of P-gp transporters.
The half-life for lemborexant at doses of 5mg and 10mg is 17 and 19 hours, respectively.
The orexin neuropeptide signaling system is involved in many physiologic functions, including sleep/wake control. Orexin-A and orexin-B activate post-synaptic G-protein coupled orexin-1 receptors (OX1R) and orexin-2 receptors (OX2R), which are found on neurons in the hypothalamus that project to numerous wake-controlling nuclei. Each receptor carries slightly different activity - activation of OX1R appears to suppress the onset of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, whereas activation of OX2R appears to suppress non-REM sleep. Lemborexant is an competitive antagonist of OX1R and OX2R. By blocking the binding of wake-promoting orexin-A and -B at these receptors, lemborexant suppresses the wake-drive, thereby promoting sleep.

