


1. Lercadip
2. Lercanidipine Hydrochloride
3. Lerdip
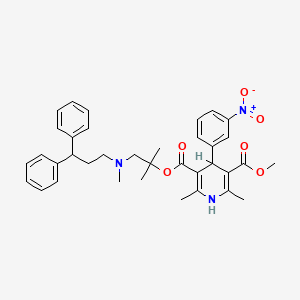
4. Methyl-1,1-dimethyl-2-(n-(3,3-diphenylpropyl)-n-methylamino)ethyl-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
5. Rec 15-2375
6. Rec-15-2375
7. Zanidip
1. 100427-26-7
2. Lercanidipine [inn]
3. Lercanil
4. Lercanidipine (inn)
5. V7xtj4r0bh
6. Masnidipine
7. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 3-[2-[(3,3-diphenylpropyl)methylamino]-1,1-dimethylethyl] 5-methyl Ester
8. 5-o-[1-[3,3-diphenylpropyl(methyl)amino]-2-methylpropan-2-yl] 3-o-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
9. 1-[(3,3-diphenylpropyl)(methyl)amino]-2-methylpropan-2-yl Methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
10. 3-(1-((3,3-diphenylpropyl)(methyl)amino)-2-methylpropan-2-yl) 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
11. 3-{1-[(3,3-diphenylpropyl)(methyl)amino]-2-methylpropan-2-yl} 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
12. Lercanil (tn)
13. Ncgc00167492-01
14. Unii-v7xtj4r0bh
15. Lercanidipine [inn:ban]
16. Lercanadipine
17. 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic Acid O5-[1-[3,3-diphenylpropyl(methyl)amino]-2-methylpropan-2-yl] Ester O3-methyl Ester
18. Lercanidipine [mi]
19. Schembl25268
20. Lercanidipine [who-dd]
21. Chembl250270
22. Schembl6846222
23. Dtxsid2048327
24. Chebi:135930
25. Hms3604g05
26. Bcp21318
27. Hy-b0612
28. Bbl029074
29. S5861
30. Stk639861
31. Akos005571238
32. Db00528
33. Sdccgsbi-0633690.p001
34. Ncgc00167492-02
35. Ncgc00167492-11
36. (+-)-2-((3,3-diphenylpropyl)methylamino)-1,1-dimethylethyl Methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
37. Ac-15409
38. As-75252
39. Ft-0631006
40. C13971
41. D08111
42. 427l267
43. A800200
44. A929939
45. Q410492
46. Sr-01000884000
47. Sr-01000884000-1
48. [2-oxo-3-(3-trifluoromethyl-phenoxy)-propyl]-phosphonic
49. 2-((3,3-diphenylpropyl)methylamino)-1,1-dimethylethyl Methyl (4rs)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
50. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 2-((3,3-diphenylpropyl)methylamino)-1,1-dimethylethyl Methyl Ester
51. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 2-(3,3-diphenylpropyl)methylamino)-1,1-dimethylethyl Methyl Ester
52. O5-[1-[3,3-diphenylpropyl(methyl)amino]-2-methyl-propan-2-yl] O3-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 611.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C36H41N3O6 |
| XLogP3 | 6.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 13 |
| Exact Mass | 611.29953604 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 611.29953604 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 114 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 45 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1090 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of Hypertension, management of angina pectoris and Raynaud's syndrome
Lercanidipine, a dihydropyridine calcium-channel blocker, is used alone or with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, to treat hypertension, chronic stable angina pectoris, and Prinzmetal's variant angina. Lercanidipine is similar to other peripheral vasodilators. Lercanidipine inhibits the influx of extra cellular calcium across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes possibly by deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
C08CA13
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C08 - Calcium channel blockers
C08C - Selective calcium channel blockers with mainly vascular effects
C08CA - Dihydropyridine derivatives
C08CA13 - Lercanidipine
By deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, Lercanidipine inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload.
