


1. Aic246
2. Prevymis
1. 917389-32-3
2. Aic246
3. Prevymis
4. Aic-246
5. Aic 246
6. Mk-8228
7. 1h09y5wo1f
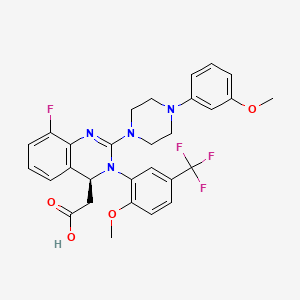
8. 2-[(4s)-8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-[2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4h-quinazolin-4-yl]acetic Acid
9. 2-((4s)-8-fluoro-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4h-quinazolin-4-yl)acetic Acid
10. 4-quinazolineacetic Acid, 8-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl)-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-, (4s)-
11. Letermovir [inn]
12. Letermovir [usan:inn]
13. Unii-1h09y5wo1f
14. Prevymis (tn)
15. (s)-[8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazine-1-yl]-3-(2-methoxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinazoline-4-yl]acetic Acid
16. (s)-{8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazine-1-yl]-3-(2-methoxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinazoline-4-yl}acetic Acid
17. Mk-8828
18. Letermovir(aic246)
19. Letermovir [mi]
20. Letermovir [jan]
21. Letermovir [usan]
22. Letermovir [who-dd]
23. Letermovir (jan/usan/inn)
24. Schembl379403
25. Chembl1241951
26. Letermovir [orange Book]
27. Dtxsid40238683
28. Ex-a1871
29. S8873
30. Zinc100369359
31. Cs-1571
32. Db12070
33. Aic246;aic 246;aic-246
34. Ncgc00378936-01
35. Ncgc00378936-02
36. Ac-35698
37. As-56206
38. Hy-15233
39. J3.556.145e
40. D10801
41. D71052
42. A902281
43. Q15409407
44. (4s)-2-(8-fluoro-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl)acetic Acid
45. (4s)-8-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]-3-[2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-quinazolineacetic Acid
46. (s)-{8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-(2-methoxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-quinazolin-4-yl}acetic Acid
47. (s)-{8-fluoro-2-[4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-(2-methoxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl}acetic Acid
48. (s)-2-(8-fluoro-3-(2-methoxy-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-(4-(3-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-4-yl)acetic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 572.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H28F4N4O4 |
| XLogP3 | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 572.20466804 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 572.20466804 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 931 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For use in prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and disease in adult CMV-seropositive recipients of an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
FDA Label
Prevymis is indicated for prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation and disease in adult CMV-seropositive recipients [R+] of an allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT).
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antiviral agents.
Letermovir inhibits the activity of the DNA terminase complex of CMV thereby preventing the cutting of viral DNA into mature length genomes for packaging into viral particles. Letemovir inhibits the DNA terminase complex with an EC50 of 2.1nM.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors
Chemicals and drugs that inhibit the action of POLY(ADP-RIBOSE)POLYMERASES. (See all compounds classified as Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors.)
J05
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AX - Other antivirals
J05AX18 - Letermovir
Absorption
Letermovir has a bioavailability of 94% in healthy subjects when administered without cyclosporin, 35% in HSCT recipients when administered without cyclosporin, and 85% in HSCT recipients when administered with cyclosporin. Letermovir's Tmax is 45 min to 2.25 h. Time to steady state has been observed to be 9-10 days. Taking Letermovir with food increases Cmax by an average of 129.82% (range of 104.35%-161.50%). No significant effect on AUC has been observed .
Route of Elimination
Letemovir is taken up by the liver through OATP1B1/3 transporters. 93% is excreted in the feces with 70% as the parent drug. <2% is excreted in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The mean steady state volume of distrubution is 45.5L
Clearance
The mean clearance is 11.25 L/h in healthy subjects
Letermovir undergoes a minor degree of metabolism through UGT1A1/1A3.
The mean terminal half-life was observed to be 12 hours following administration of Letemovir 480 mg IV once daily.
CMV relies on a DNA terminase complex consisting of multiple subunits (pUL51, pUL56, and pUL89) for processing of viral DNA. Viral DNA is produced in a single repeating strand which is then cut by the DNA terminase complex into individual viral genomes which can then be packaged into mature viral particles. Letemovir inhibits the activity of this complex to prevent production of mature viral genomes and the production of viable viral particles. The exact nature of Letemovir's binding to this complex is not currently known. Initially, the observation of resistance-causing mutations in pUL56 suggested this subunit was the location of Letemovir binding. However, resistance mutations have now been observed in pUL51, pUL56, and pUL89. It is possible that changes in amino acid sequence in one subunit could result in conformational changes to interacting subunits affecting Letemovir binding or that Letemovir interacts with multiple subunits of the complex but evidence towards either of these distinctions has not yet been seen. pUL89 is known to contain the endonuclease activity of the complex but because all members of the complex are necessary for targeting as well as protection from proteosomal degradation, it is difficult to discern if Letemovir inhibits pUL89's activity directly.
