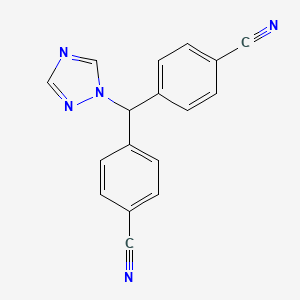

1. 4,4'-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl-methylene)-bis(benzonitrile)
2. Cgs 20267
3. Cgs-20267
4. Cgs20267
5. Fmara
6. Femara
1. 112809-51-5
2. Femara
3. 4,4'-((1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methylene)dibenzonitrile
4. Letrozol
5. Cgs 20267
6. Cgs-20267
7. 4-[(4-cyanophenyl)-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl]benzonitrile
8. 4,4'-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)dibenzonitrile
9. Letrazole
10. Benzonitrile, 4,4'-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)bis-
11. Femera
12. 4,4'-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethanediyl)dibenzonitrile
13. 4,4'-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)bisbenzonitrile
14. Nsc-759652
15. Chembl1444
16. 4-[(4-cyanophenyl)(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl]benzonitrile
17. 4,4'-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)bis-benzonitrile
18. 7lkk855w8i
19. Chebi:6413
20. 4,4'-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene) Bis-benzonitrile
21. Ncgc00016973-01
22. Letoval
23. Cas-112809-51-5
24. Dsstox_cid_3202
25. Dsstox_rid_76924
26. Dsstox_gsid_23202
27. Smr000466343
28. Femara (tn)
29. Hsdb 7461
30. Sr-01000759382
31. Letrozole (jan/usp/inn)
32. Unii-7lkk855w8i
33. Ccris 8822
34. 1-[bis(4-cyanophenyl)methyl]-1,2,4-triazole
35. Fem-345
36. Femara, Letrozole
37. Letrozole [usan:usp:inn:ban]
38. Letrozole- Bio-x
39. Cgs20267
40. Mfcd00866241
41. Letrozole [inn]
42. Letrozole [jan]
43. Letrozole [mi]
44. Letrozole [hsdb]
45. Letrozole [usan]
46. Prestwick0_001025
47. Prestwick1_001025
48. Prestwick2_001025
49. Prestwick3_001025
50. Femara (tn) (novartis)
51. Letrozole [mart.]
52. Letrozole [usp-rs]
53. Letrozole [who-dd]
54. Schembl4331
55. 1-[bis-(4-cyanophenyl)methyl]-1,2,4-triazole
56. Bidd:pxr0130
57. Bspbio_001209
58. Mls000759455
59. Mls001424038
60. Mls002584991
61. Mls006010040
62. Bidd:gt0015
63. Spbio_003070
64. Bpbio1_001331
65. Gtpl5209
66. Letrozole [ep Impurity]
67. Letrozole [orange Book]
68. Dtxsid4023202
69. Letrozole [ep Monograph]
70. Letrozole, >=98% (hplc)
71. Bdbm13061
72. Ex-a965
73. Letrozole [usp Monograph]
74. Hms1571m11
75. Hms2051e08
76. Hms2089l22
77. Hms2098m11
78. Hms2233c23
79. Hms3369e11
80. Hms3393e08
81. Hms3651k05
82. Hms3715m11
83. Pharmakon1600-01502354
84. Amy32541
85. Bcp23354
86. Zinc3778874
87. Tox21_110719
88. Tox21_303572
89. Nsc719345
90. Nsc759652
91. S1235
92. Stl451047
93. Akos005145822
94. Ab07525
95. Ac-1193
96. Bcp9000848
97. Ccg-100849
98. Cs-1776
99. Db01006
100. Ks-1269
101. Nc00099
102. Nsc 759652
103. Nsc-719345
104. Ncgc00016973-02
105. Ncgc00016973-03
106. Ncgc00016973-06
107. Ncgc00257460-01
108. Bl164620
109. Hy-14248
110. Bcp0726000213
111. 1-bis(4-cyanophenyl)methyl-1,2,4-triazole
112. 4,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)dibenzonitrile
113. Ab00514009
114. L0248
115. Sw197294-4
116. A25380
117. C08163
118. D00964
119. Ab00514009-05
120. Ab00514009-07
121. Ab00514009-08
122. Ab00514009-09
123. Ab00514009_10
124. Ab00514009_11
125. 809l515
126. Kisqali Femara Co-pack Component Letrozole
127. Q194974
128. W-60273
129. 4,4'-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)dibenzonitrile
130. Letrozole Component Of Kisqali Femara Co-pack
131. Q-201291
132. Sr-01000759382-4
133. Sr-01000759382-5
134. Brd-k88789588-001-03-2
135. 4,4 -(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethanediyl)dibenzonitrile
136. 4,4'-(1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)-bisbenzonitrile
137. F2173-0288
138. Z1741968261
139. 4,4'-((1h-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-methylene)dibenzonitrile
140. Letrozole, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
141. Letrozole, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
142. 4-[1-(4-cyanophenyl)-1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl]benzonitrile
143. Letrozole, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 285.30 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H11N5 |
| XLogP3 | 2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 285.10144537 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 285.10144537 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 78.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 420 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Femara |
| PubMed Health | Letrozole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | Femara tablets for oral administration contains 2.5 mg of letrozole, a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (inhibitor of estrogen synthesis). It is chemically described as 4,4'-(1H-1,2,4-Triazol-1-ylmethylene)dibenzonitrile, and its structural formula i |
| Active Ingredient | Letrozole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Letrozole |
| PubMed Health | Letrozole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | Letrozole tablets USP for oral administration contain 2.5 mg of letrozole, a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (inhibitor of estrogen synthesis). It is chemically described as 4,4'-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)dibenzonitrile, and its structural for |
| Active Ingredient | Letrozole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Fresenius Kabi Oncol; Apotex; Accord Hlthcare; Jiangsu Hengrui Med; Indicus Pharma; Natco Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Roxane; Teva Pharms; Kudco Ireland; Zydus Pharms Usa; Dr Reddys Labs; Mylan; Impax Labs |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Femara |
| PubMed Health | Letrozole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | Femara tablets for oral administration contains 2.5 mg of letrozole, a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (inhibitor of estrogen synthesis). It is chemically described as 4,4'-(1H-1,2,4-Triazol-1-ylmethylene)dibenzonitrile, and its structural formula i |
| Active Ingredient | Letrozole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Novartis Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Letrozole |
| PubMed Health | Letrozole (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent |
| Drug Label | Letrozole tablets USP for oral administration contain 2.5 mg of letrozole, a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (inhibitor of estrogen synthesis). It is chemically described as 4,4'-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethylene)dibenzonitrile, and its structural for |
| Active Ingredient | Letrozole |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Fresenius Kabi Oncol; Apotex; Accord Hlthcare; Jiangsu Hengrui Med; Indicus Pharma; Natco Pharma; Sun Pharm Inds; Roxane; Teva Pharms; Kudco Ireland; Zydus Pharms Usa; Dr Reddys Labs; Mylan; Impax Labs |
Antineoplastic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 974
Letrozole is indicated for first-line treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor positive or hormone receptor unknown locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Letrozole is also indicated for treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following antiestrogen therapy. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1902
A 37-year-old premenopausal woman with relapsed breast cancer (BC) in the right supraclavicular nodes, after failed treatment with the combination luteinizing hormone releasing hormone-a (LHRHa; triptorelin) plus tamoxifen, was started on triptorelin 3.75 mg every 28 days plus letrozole 2.5 mg daily. Approximately 6 months after starting this therapy, she complained of a daily scalp hair loss while combing and progressively developed a diffuse non-scarring alopecia on her crown. There were no signs of virilization ... She was not taking any other drug. Hematological parameters were normal. Blood examination ruled out pituitary or thyroid problems. There were no other possible causes that could induce alopecia, such as lupus erythematosus, HIV infection, secondary syphilis, or deficiencies of protein, iron, biotin or zinc.
PMID:14581280 Carlini P et al; Ann Oncol 14 (11): 1689-90 (2003)
In patients receiving letrozole as first-line therapy, bone pain, back pain, and limb pain occurred in 22, 18, and 10% of patients, respectively. In patients receiving letrozole as second-line therapy, adverse musculoskeletal effects (including musculoskeletal pain, skeletal pain, back pain, arm pain, and leg pain) were reported in 21% and fracture was reported in less than 5% of patients. Arthralgia was reported in 16% of patients receiving letrozole as first-line therapy and in 8% of patients receiving the drug as second-line therapy. Hypercalcemia occurred in less than 5% of patients receiving letrozole as second-line therapy.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1114
Adverse musculoskeletal effects have been reported in patients receiving letrozole as adjuvant therapy for early-stage breast cancer in clinical trials. In a double-blind, randomized trial in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer who had received approximately 5 years of tamoxifen adjuvant therapy following primary treatment for early breast cancer, extended adjuvant therapy with letrozole was associated with an increased incidence of arthritis, arthralgia, and myalgia, and a trend toward higher rates of newly diagnosed osteoporosis and bone fracture compared with placebo therapy.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1114
All women receiving adjuvant therapy with letrozole should be advised to adopt lifestyle changes (eg, weight-bearing exercise, abstinence from smoking, moderation in alcohol consumption) and dietary supplementation with calcium and vitamin D to reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1114
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for LETROZOLE (26 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Letrozole is indicated to treat postmenopausal women with hormone receptor (HR) positive early breast cancer, postmenopausal women with early breast cancer who have periviously been treated with tamoxifen, and postmenopausal women with HR+ or unknown advanced breast cancer. Letrozole, given with ribociclib, is indicated to treat pre, peri, and postmenopausal women with HR+ and human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2) negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
FDA Label
Letrozole is an aromatase inhibitor used in the treatment of breast cancer. Aromatase inhibitors work by inhibiting the action of the enzyme aromatase, which converts androgens into estrogens by a process called aromatization. As breast tissue is stimulated by estrogens, decreasing their production is a way of suppressing recurrence of the breast tumor tissue. Letrozole is a third generation type II aromatase inhibitor used to treat estrogen dependant breast cancers. It has a long duration of action as it has a half life of over 42 hours in breast cancer patients. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis, QT prolongation, elevated transaminase levels, neutropenia, and embryo-fetal toxicity.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Aromatase Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit AROMATASE in order to reduce production of estrogenic steroid hormones. (See all compounds classified as Aromatase Inhibitors.)
L02BG04
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L02 - Endocrine therapy
L02B - Hormone antagonists and related agents
L02BG - Aromatase inhibitors
L02BG04 - Letrozole
Absorption
Letrozole is 99.9% orally bioavailable. A 2.5mg oral dose reaches a Cmax of 104nmol/L with a Tmax of 8.10h, and an AUC of 7387nmol\*h/L.
Route of Elimination
Letrozole is 90% eliminated in the urine. 75% of the dose is recovered as a glucuronide metabolite, 9% is in the form of the ketone and carbinol metabolites, and 6% is recovered in urine as unchanged letrozole.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of letrozole is 1.87L/kg.
Clearance
The average clearance after a single dose of letrozole was 1.52L/h and at steady state was 1.20L/h.
Letrozole is rapidly and completely absorbed from the GI tract following oral administration. Steady-state plasma concentrations of the drug are reached in 2-6 weeks in patients receiving letrozole 2.5 mg daily. Letrozole exhibits slightly nonlinear pharmacokinetics with repeated administration of 2.5 mg daily, with steady-state plasma concentrations 1.5-2 times higher than predicted based on plasma concentrations measured after a single dose. However, continuous accumulation of letrozole does not occur, and steady-state concentrations are maintained over extended periods of daily drug administration. Food does not affect the oral absorption of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1116
Letrozole has a large volume of distribution of approximately 1.9 L/kg. Letrozole is weakly bound to plasma proteins.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1116
Following oral administration of radiolabeled letrozole, 90% of the administered dose was excreted in the urine. Of the radiolabeled drug recovered in urine, at least 75% was the glucuronide of the carbinol metabolite, about 9% consisted of 2 unidentified metabolites, and 6% was unchanged drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1116
It is not known whether letrozole is distributed into human breast milk.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 1902
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for LETROZOLE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Letrozole is metabolized by CYP2A6 to a ketone analog metabolite, which is further metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP2A6 to 4,4'-(hydroxymethylene)dibenzonitrile. 4,4'-(hydroxymethylene)dibenzonitrile is glucuronidated by UGT2B7.
The primary elimination pathway of letrozole consists of slow metabolism in the liver to a pharmacologically inactive carbinol metabolite (4,4'-methanol-bisbenzonitrile) followed by renal excretion of the glucuronide conjugate of this metabolite. Formation of the carbinol metabolite is mediated by cytochrome P-450 (CYP) isoenzymes 3A4 and 2A6, and formation of the ketone analog of the carbinol metabolite is mediated by isoenzyme 2A6.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1116
The terminal elimination half life of letrozole is approximately 42h in healthy volunteers, but longer in breast cancer patients.
Letrozole has a terminal elimination half-life of about 2 days.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 1116
Letrozole is a non-steroidal type II aromatase inhibitor. It blocks the active site, and therefore the electron transfer chain of CYP19A1. This competitive inhibition prevents the conversion of androgens to estrogen. This action leads to a reduction in uterine weight and elevated leuteinizing hormone. In postmenopausal women, the action of aromatase is responsible for the majority of estrogen production. With reduced availability of estrogen, estrogen-dependant tumors regress. Third generation aromatase inhibitors do not significantly affect cortisol, aldosterone, and thyroxine levels.
Letrozole is a nonsteroidal competitive inhibitor of the aromatase enzyme system; it inhibits the conversion of androgens to estrogens. In adult nontumor- and tumor-bearing female animals, letrozole is as effective as ovariectomy in reducing uterine weight, elevating serum LH, and causing the regression of estrogen-dependent tumors. In contrast to ovariectomy, treatment with letrozole does not lead to an increase in serum FSH. Letrozole selectively inhibits gonadal steroidogenesis but has no significant effect on adrenal mineralocorticoid or glucocorticoid synthesis. Letrozole inhibits the aromatase enzyme by competitively binding to the heme of the cytochrome P450 subunit of the enzyme, resulting in a reduction of estrogen biosynthesis in all tissues. Treatment of women with letrozole significantly lowers serum estrone, estradiol and estrone sulfate and has not been shown to significantly affect adrenal corticosteroid synthesis, aldosterone synthesis, or synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 2210