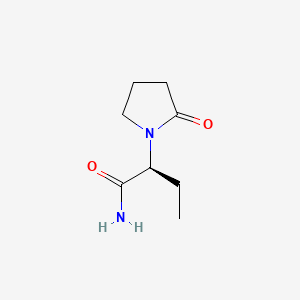

1. Alpha Ethyl 2 Oxo 1 Pyrrolidineacetamide
2. Alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide
3. Etiracetam
4. Etiracetam, (r)-
5. Etiracetam, R Isomer
6. Etiracetam, R-isomer
7. Etiracetam, S Isomer
8. Etiracetam, S-isomer
9. Keppra
10. R-isomer Etiracetam
11. S-isomer Etiracetam
12. Ucb 6474
13. Ucb L059
14. Ucb L060
15. Ucb-6474
16. Ucb-l059
17. Ucb-l060
18. Ucb6474
19. Ucbl060
1. 102767-28-2
2. Keppra
3. (s)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide
4. Keppra Xr
5. (2s)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide
6. Ucb L059
7. Ucb-l 059
8. Matever
9. Ucb-l059
10. Levetiracetame
11. Levetiracetamum
12. Spritam
13. (s)-alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide
14. Sib-s1
15. Elepsia
16. Levetiracetam Sun
17. (-)-(s)-alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide
18. Levetiracetam Teva
19. Ucb-22059
20. Levetiracetam Accord
21. Levetiracetam [inn]
22. Levetiracetam Actavis
23. Levetiracetam Hospira
24. N03ax14
25. Ucb 22059
26. Levetiracetamum [inn-latin]
27. Nsc-760119
28. 1-pyrrolidineacetamide, Alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-, (alphas)-
29. Chebi:6437
30. Levetiracetam In Sodium Chloride
31. Agb-101
32. 44yrr34555
33. Levroxa
34. (s)-(-)-alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide
35. Leviteracetam
36. Levipil
37. Torleva
38. Elepsia Xr
39. (s)-levetiracetam
40. Smr000466303
41. Keppra (tn)
42. Levesam 500
43. Etiracetam Levo-isomer
44. Sr-01000759400
45. Mfcd03265610
46. Unii-44yrr34555
47. E Keppra
48. Hsdb 7528
49. Levetiracetam [usan:usp:inn:ban]
50. E Keppra (tn)
51. Levetiracetam Solution
52. Levetiracetam- Bio-x
53. (s)-2-(2-oxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)butyramide
54. L-059
55. Levetiracetam [mi]
56. Levetiracetam [jan]
57. Chembl1286
58. Levetiracetam [hsdb]
59. Levetiracetam [usan]
60. Levetiracetam [vandf]
61. 1-pyrrolidineacetamide, Alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-, (s)-
62. Mls000759403
63. Mls001424069
64. Mls006010215
65. Bidd:gt0242
66. Levetiracetam [mart.]
67. Schembl118843
68. Levetiracetam Ratiopharm
69. Levetiracetam [usp-rs]
70. Levetiracetam [who-dd]
71. Gtpl6826
72. Levetiracetam (jan/usp/inn)
73. Dtxsid9023207
74. Levetiracetam [ema Epar]
75. Levetiracetam Actavis Group
76. Levetiracetam, >=98% (hplc)
77. Levetiracetam, Analytical Standard
78. Hms2051d07
79. Hms2089l20
80. Hms2235i18
81. Hms3262h11
82. Hms3713p16
83. Hms3884o11
84. Pharmakon1600-01502265
85. Levetiracetam [ep Impurity]
86. Levetiracetam [orange Book]
87. Act02712
88. Albb-027275
89. Bcp11856
90. Hy-b0106
91. Zinc1547851
92. Levetiracetam [ep Monograph]
93. Levetiracetam [usp Impurity]
94. Tox21_500835
95. Bdbm50422542
96. Levetiracetam [usp Monograph]
97. Nsc760119
98. S1356
99. Stl388027
100. Levetiracetam 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
101. Akos015841981
102. Ac-1479
103. Ccg-100928
104. Cs-1854
105. Db01202
106. Ks-1176
107. Lp00835
108. Nc00178
109. Nsc 760119
110. Sdccgsbi-0633760.p001
111. (2s)-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butyramide
112. Ncgc00186028-01
113. Ncgc00186028-13
114. Ncgc00261520-01
115. (s)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butyramide
116. Bl164623
117. (s)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl) Butyramide
118. Am20070676
119. L0234
120. Sw197558-3
121. C07841
122. D00709
123. Ab00639945-06
124. Ab00639945_07
125. Ab00639945_08
126. 767l282
127. A800616
128. (s)-2-(2-oxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-butyramide
129. Q-201292
130. Sr-01000759400-4
131. Sr-01000759400-5
132. (2s)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide;levetiracetam
133. (-)-(s)-.alpha.-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide
134. 1-pyrrolidineacetamide, .alpha.-ethyl-2-oxo-, (.alpha.s)-
135. Levetiracetam, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
136. Levetiracetam, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
137. (-)-(s)-alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide (2s)-2-(2-oxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide
138. Levetiracetam Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
139. Levitiracetam, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 170.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H14N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 170.105527694 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 170.105527694 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 203 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Keppra |
| PubMed Health | Levetiracetam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | KEPPRA is an antiepileptic drug available as 250 mg (blue), 500 mg (yellow), 750 mg (orange), and 1000 mg (white) tablets and as a clear, colorless, grape-flavored liquid (100 mg/mL) for oral administration.The chemical name of levetiracetam, a singl... |
| Active Ingredient | Levetiracetam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; Solution |
| Route | Iv (infusion); Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg; 500mg/5ml (100mg/ml); 100mg/ml; 750mg; 1gm |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ucb |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Keppra xr |
| PubMed Health | Levetiracetam |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | KEPPRA XR is an antiepileptic drug available as 500 mg and 750 mg (white) extended-release tablets for oral administration.The chemical name of levetiracetam, a single enantiomer, is (-)-(S)--ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide, its molecular formu... |
| Active Ingredient | Levetiracetam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg; 750mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ucb |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Levetiracetam |
| PubMed Health | Levetiracetam |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | Levetiracetam is an antiepileptic drug available as 250 mg (blue), 500 mg (yellow) and 750 mg (orange) tablets.The chemical name of levetiracetam, a single enantiomer, is (-)-(S)-acetamide, its molecular formula is C8H14N2O2 and its molecular weight... |
| Active Ingredient | Levetiracetam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Tablet; Injectable; Solution |
| Route | oral; Iv (infusion); Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg/5ml(100mg/ml); 1000mg; 500mg; 500mg/ml (100mg/ml); 500mg/5ml (100mg/ml); 100mg/ml; 750mg; 1gm |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Anchen Pharms; Amneal Pharms; Wockhardt; Silarx; Hospira; Breckenridge Pharm; Actavis Labs Fl; X Gen Pharms; Methapharm; Apotex; Lotus Pharm; Accord Hlthcare; Hetero Labs Ltd Iii; Hikma Farmaceutica; Sun Pharm Inds; Aurobindo |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Keppra |
| PubMed Health | Levetiracetam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | KEPPRA is an antiepileptic drug available as 250 mg (blue), 500 mg (yellow), 750 mg (orange), and 1000 mg (white) tablets and as a clear, colorless, grape-flavored liquid (100 mg/mL) for oral administration.The chemical name of levetiracetam, a singl... |
| Active Ingredient | Levetiracetam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; Solution |
| Route | Iv (infusion); Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg; 500mg/5ml (100mg/ml); 100mg/ml; 750mg; 1gm |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ucb |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Keppra xr |
| PubMed Health | Levetiracetam |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | KEPPRA XR is an antiepileptic drug available as 500 mg and 750 mg (white) extended-release tablets for oral administration.The chemical name of levetiracetam, a single enantiomer, is (-)-(S)--ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide, its molecular formu... |
| Active Ingredient | Levetiracetam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg; 750mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ucb |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Levetiracetam |
| PubMed Health | Levetiracetam |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | Levetiracetam is an antiepileptic drug available as 250 mg (blue), 500 mg (yellow) and 750 mg (orange) tablets.The chemical name of levetiracetam, a single enantiomer, is (-)-(S)-acetamide, its molecular formula is C8H14N2O2 and its molecular weight... |
| Active Ingredient | Levetiracetam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release; Tablet; Injectable; Solution |
| Route | oral; Iv (infusion); Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 500mg/5ml(100mg/ml); 1000mg; 500mg; 500mg/ml (100mg/ml); 500mg/5ml (100mg/ml); 100mg/ml; 750mg; 1gm |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Vintage Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Anchen Pharms; Amneal Pharms; Wockhardt; Silarx; Hospira; Breckenridge Pharm; Actavis Labs Fl; X Gen Pharms; Methapharm; Apotex; Lotus Pharm; Accord Hlthcare; Hetero Labs Ltd Iii; Hikma Farmaceutica; Sun Pharm Inds; Aurobindo |
Levetiracetam is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures in adults and children 4 years of age and older with epilepsy. /included in US product labe/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 1815
Adverse neuropsychiatric effects reported during levetiracetam treatment are classified into 3 categories: somnolence and fatigue, coordination difficulties, and behavioral changes. In controlled studies, 14.8% of patients who received levetiracetam experienced somnolence compared with 8.4% of placebo-treated patients, and about 3% of levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment due to somnolence. About 14.7% of patients who received levetiracetam experienced asthenia compared with 9.1% of placebo-treated patients, and 0.8% of levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment due to asthenia. Coordination difficulties were experienced by 3.4% of levetiracetam patients compared with 1.6% of placebo-treated patients. Somnolence, asthenia, and coordination difficulties occurred most frequently within the first 4 weeks of treatment. Psychotic manifestations and hallucinations were reported rarely in patients receiving levetiracetam in clinical studies. Other behavioral symptoms (e.g., agitation, hostility, anxiety, apathy, emotional lability, depersonalization, depression, aggression, anger, irritability) occurred in 13.3% of levetiracetam-treated patients in clinical studies compared with 6.2% of placebo patients, and 1.7% of levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment because of these events.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2240
Because of the possibility of increased seizure frequency, anticonvulsant drugs, including levetiracetam, should not be discontinued suddenly. Levetiracetam should be withdrawn gradually by reducing the dosage by 1g daily at 2-week intervals.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2240
Adverse effects occurring in 1% or more of patients receiving levetiracetam and more frequently than placebo include somnolence, asthenia, headache, infection, dizziness, pain, pharyngitis, depression, nervousness, rhinitis, anorexia, ataxia, vertigo, amnesia, anxiety, emotional lability, hostility, paresthesia, increased cough, sinusitis, and diplopia and were reported in clinical studies in which levetiracetam was administered in conjunction with other anticonvulsants. Asthenia, somnolence, and dizziness occurred predominantly during the initial 4 weeks of treatment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2240
Minor decreases in total mean erythrocyte count, mean hemoglobin, and mean hematocrit have been reported. Leukopenia, neutropenia, pancytopenia (with myelosuppression in some cases), and thrombocytopenia also have been observed, although a causal relationship to the drug has not been established.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2240
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for LEVETIRACETAM (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Levetiracetam is indicated as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures in epileptic patients who are one month of age and older. Additionally, it is indicated as an adjunct in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy who are 12 years of age and older, and in primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy who are 6 years of age and older. Levetiracetam is also available as an orally dissolvable tablet that is indicated as an adjunct in the treatment of partial onset seizures in patients with epilepsy who are 4 years of age and older and weigh more than 20kg.
Levetiracetam Actavis is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in patients from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Actavis is indicated as adjunctive therapy:
- in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, children and infants from one month of age with epilepsy;
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy;
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Actavis Group is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in patients from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Actavis Group is indicated as adjunctive therapy:
- in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, children and infants from 1 month of age with epilepsy;
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy;
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Hospira is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults and adolescents from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Hospira is indicated as adjunctive therapy
- in the treatment of partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, adolescents and children from 4 years of age with epilepsy.
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy .
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with Idiopathic Generalised Epilepsy .
Levetiracetam Hospira concentrate is an alternative for patients when oral administration is temporarily not feasible.
Levetiracetam ratiopharm is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in patients from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Levetiracetam ratiopharm is indicated as adjunctive therapy:
- in the treatment of partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, children and infants from 1 month of age with epilepsy;
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy;
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Levetiracetam is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in patients from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Levetiracetam is indicated as adjunctive therapy:
- in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, children and infants from one month of age with epilepsy;
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy;
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Teva is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults and adolescents from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Teva is indicated as adjunctive therapy:
- in the treatment of partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, adolescents, children and infants from 1 month of age with epilepsy;
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy;
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Keppra is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in patients from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Keppra is indicated as adjunctive therapy:
- in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, children and infants from one month of age with epilepsy;
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy;
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Matever is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in patients from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Matever is indicated as adjunctive therapy:
- in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults, children and infants from one month of age with epilepsy;
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy;
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Sun is indicated as monotherapy in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in patients from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Sun is indicated as adjunctive therapy:
- in the treatment of partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalisation in adults and children from four years of age with epilepsy;
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy;
- in the treatment of primary generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalised epilepsy.
Levetiracetam Sun concentrate is an alternative for patients when oral administration is temporarily not feasible.
Levetiracetam appears to prevent seizure activity via the selective inhibition of hypersynchronized epileptiform burst firing without affecting normal neuronal transmission, though the exact mechanism through which this occurs is unclear. The therapeutic index of levetiracetam is wide, making it relatively unique amongst other anti-epileptic medications. Anti-epileptic drugs, including levetiracetam, may increase the risk of suicidal ideation or behaviour - patients taking levetiracetam should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depressive symptoms, suicidal ideation, and behavioural abnormalities.
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
Nootropic Agents
Drugs used to specifically facilitate learning or memory, particularly to prevent the cognitive deficits associated with dementias. These drugs act by a variety of mechanisms. (See all compounds classified as Nootropic Agents.)
N03AX14
N03AX14
N03AX14
N03AX14
N03AX14
N03AX14
N03AX14
N03AX14
N03AX14
N03AX14
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AX - Other antiepileptics
N03AX14 - Levetiracetam
Absorption
Levetiracetam is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed following oral administration, with a reported absolute oral bioavailability of essentially 100%. Tmax is approximately 1.3 hours after dosing, and Cmax is 31 g/mL following a single 1000mg dose and 43 g/mL following repeated dosing. Co-administration of levetiracetam with food delays Tmax by approximately 1.5 hours and decreases Cmax by 20%.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 66% of the administered dose of levetiracetam is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug, while only 0.3% of the total dose is excreted via the feces. The primary inactive metabolite of levetiracetam, L057, is also found in the urine as approximately 24% of the administered dose.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of levetiracetam is approximately 0.5 to 0.7 L/kg.
Clearance
The total plasma clearance of levetiracetam is 0.96 mL/min/kg, with renal clearance comprising 0.6 mL/min/kg. The primary inactive metabolite of levetiracetam, L057, has a renal clearance of 4 mL/min/kg. Given the relatively high proportion of drug undergoing renal clearance, overall clearance of levetiracetam is reduced in patients with renal impairment.
Absorption of levetiracetam is rapid, with peak plasma concentrations occurring in about an hour following oral administration in fasted subjects. The oral bioavailability of levetiracetam tablets is 100% and the tablets and oral solution are bioequivalent in rate and extent of absorption. Food does not affect the extent of absorption of levetiracetam but it decreases C max by 20% and delays T max by 1.5 hours.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3315
The pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam are linear over the dose range of 500-5000 mg. Steady state is achieved after 2 days of multiple twice-daily dosing.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3315
Levetiracetam is not significantly protein-bound (<10% bound) and its volume of distribution is close to the volume of intracellular and extracellular water.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3315
Levetiracetam C max and AUC were 20% higher in women (N=11) compared to men (N=12). However, clearances adjusted for body weight were comparable.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3315
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for LEVETIRACETAM (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Levetiracetam is minimally metabolized within the body - the major metabolic pathway appears to be the enzymatic hydrolysis of its acetamide group which produces an inactive carboxylic acid metabolite, L057, which accounts for approximately 24% of the total administered dose. The specific enzyme(s) responsible for this reaction are unclear, but this pathway is known to be independent of hepatic CYP enzymes and has been proposed to be driven primarily by type B esterases in the blood and other tissues. Two minor metabolites involving modifications to the pyrrolidone ring have been identified, one involving hydroxylation of the ring (constituting 1.6% of the total dose) and the other involving opening of the ring structure (constituting 0.9% of the total dose).
Levetiracetam is not extensively metabolized in humans. The major metabolic pathway is the enzymatic hydrolysis of the acetamide group, which produces the carboxylic acid metabolite, ucb L057 (24% of dose) and is not dependent on any liver cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. The major metabolite is inactive in animal seizure models. Two minor metabolites were identified as the product of hydroxylation of the 2-oxo-pyrrolidine ring (2% of dose) and opening of the 2-oxo-pyrrolidine ring in position 5 (1% of dose). There is no enantiomeric interconversion of levetiracetam or its major metabolite.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3315
The plasma half-life of levetiracetam is 6-8 hours and is not affected by dose or repeat administration. Half-life is increased in the elderly (by about 40%) and those with renal impairment.
... The plasma elimination half-life of the unchanged drug varied between 7.4 hr and 7.9 hr. ...
PMID:14530892 Strolin-Benedetti M et al; Eur J Clin Pharmacol 59 (8-9): 621-30 (2003)
Levetiracetam plasma half-life in adults is 7 +/-1 hour and is unaffected by either dose or repeated administration.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3315
The exact mechanism through which levetiracetam exerts its anti-epileptic effects is unclear, but is thought to be unique amongst other anti-epileptic medications. Current knowledge suggests that levetiracetams binding to synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A) is a key driver of its action. SV2A is a membrane-bound protein that is found on synaptic vesicles and is ubiquitous throughout the CNS - it appears to play a role in vesicle exocytosis and in the modulation of synaptic transmission by increasing the available amount of secretory vesicles available for neurotransmission. Stimulation of pre-synaptic SV2A by levetiracetam may inhibit neurotransmitter release, but this action does not appear to affect normal neurotransmission. This has led to the suggestion that levetiracetam exclusively modulates the function of SV2A only under pathophysiological conditions. Levetiracetam and related analogues showed a correlation between affinity for SV2A and anti-epileptic potency, further suggesting that action at this site contributes to the anti-epileptic activity of the drug. Levetiracetam has also been shown to indirectly affect GABAergic neurotransmission (despite having no direct effect on GABAergic or glutamatergic receptors) and modulate ionic currents. Similarly, levetiracetam has been shown in vitro to inhibit N-type calcium channels. How, or even if, these actions are implicated in its anti-epileptic action have yet to be elucidated.
The precise mechanism by which levetiracetam exerts its antiepileptic effect is unknown. The antiepileptic activity of levetiracetam was assessed in a number of animal models of epileptic seizures. Levetiracetam did not inhibit single seizures induced by maximal stimulation with electrical current or different chemoconvulsants and showed only minimal activity in submaximal stimulation and in threshold tests. Protection was observed, however, against secondarily generalized activity from focal seizures induced by pilocarpine and kainic acid, two chemoconvulsants that induce seizures that mimic some features of human complex partial seizures with secondary generalization. Levetiracetam also displayed inhibitory properties in the kindling model in rats, another model of human complex partial seizures, both during kindling development and in the fully kindled state. The predictive value of these animal models for specific types of human epilepsy is uncertain.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3314
In vitro and in vivo recordings of epileptiform activity from the hippocampus have shown that levetiracetam inhibits burst firing without affecting normal neuronal excitability, suggesting that levetiracetam may selectively prevent hypersynchronization of epileptiform burst firing and propagation of seizure activity.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3314
Levetiracetam at concentrations of up to 10 muM did not demonstrate binding affinity for a variety of known receptors, such as those associated with benzodiazepines, GABA (gammaaminobutyric acid), glycine, NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate), re-uptake sites, and second messenger systems. Furthermore, in vitro studies have failed to find an effect of levetiracetam on neuronal voltage-gated sodium or T-type calcium currents and levetiracetam does not appear to directly facilitate GABAergic neurotransmission. However, in vitro studies have demonstrated that levetiractem opposes the activity of negative modulators of GABA- and glycine-gated currents and partially inhibits N-type calcium currents in neuronal cells.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3314
A saturable and stereoselective neuronal binding site in rat brain tissue has been described for levetiracetam. Experimental data indicate that this binding site is the synaptic vesicle protein SV2A, thought to be involved in the regulation of vesicle exocytosis. Although the molecular significance of levetiracetam binding to synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is not understood, levetiracetam and related analogs showed a rank order of affinity for SV2A which correlated with the potency of their antiseizure activity in audiogenic seizure-prone mice. These findings suggest that the interaction of levetiracetam with the SV2A protein may contribute to the antiepileptic mechanism of action of the drug.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 3315
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for LEVETIRACETAM (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.