


1. Akbeta
2. Apo Levobunolol
3. Apo-levobunolol
4. Apolevobunolol
5. Betagan
6. Levobunolol Hydrochloride
7. Novo Levobunolol
8. Novo-levobunolol
9. Novolevobunolol
10. Pms Levobunolol
11. Pms-levobunolol
12. Pmslevobunolol
13. Ratio Levobunolol
14. Ratio-levobunolol
15. Ultracortenol
16. Vistagan
17. W 7000a
18. W-7000a
19. W7000a
1. 47141-42-4
2. Levobunololum
3. (-)-bunolol
4. Levobunololum [inn-latin]
5. Levobunolol (inn)
6. Levobunolol Hydrochloride
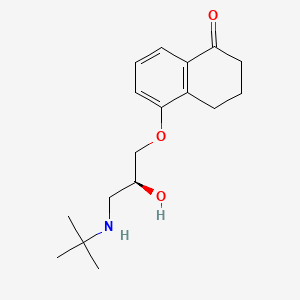
7. (s)-5-(3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2h)-one
8. Bunolol, (s)-
9. Bunolol, (-)-
10. 5-[(2s)-3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]-3,4-dihydro-2h-naphthalen-1-one
11. Chebi:6438
12. G6317aoi7k
13. Levobunolol [inn]
14. Levobunolol [inn:ban]
15. (s)-5-(3-((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-3,4-dihydro-1(2h)-naphthalenone
16. L-bunolol
17. Ccris 4375
18. Ncgc00016801-01
19. Cas-27912-14-7
20. Liquifilm
21. Unii-g6317aoi7k
22. (-)-levobunolol Hydrochloride
23. Beta-site
24. Ak-beta
25. W-6421a
26. Brn 1887243
27. Levobunolol [mi]
28. Prestwick0_000847
29. Prestwick1_000847
30. Prestwick2_000847
31. Prestwick3_000847
32. Levobunolol [vandf]
33. 1(2h)-naphthalenone, 5-(3-((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-3,4-dihydro-, (s)-
34. 5-[(2s)-3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2h)-one
35. Schembl24095
36. Bspbio_000833
37. Gtpl570
38. Levobunolol [who-dd]
39. Spbio_002754
40. Bpbio1_000917
41. Chembl1201237
42. Dtxsid1043833
43. Hy-b1035a
44. Zinc3830339
45. Db01210
46. Ncgc00016801-02
47. Ncgc00016801-03
48. Cas-47141-41-3
49. Cs-0013643
50. C07914
51. D08115
52. Q408556
53. Brd-k31812033-003-03-7
54. (-)-(s)-5-(3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-3,4-dihydro-1(2h)-naphthalenone
55. 5-[(2s)-3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-one
| Molecular Weight | 291.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H25NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 291.18344366 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 291.18344366 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 58.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 350 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Akbeta |
| PubMed Health | Levobunolol (Into the eye) |
| Drug Classes | Antiglaucoma |
| Drug Label | BETAGAN (levobunolol hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, USP) sterile is a noncardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent for ophthalmic use. The solution is colorless to slightly light yellow in appearance with an osmolality range of 250-360 m... |
| Active Ingredient | Levobunolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.5%; 0.25% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Akorn |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Betagan |
| Active Ingredient | Levobunolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.5%; 0.25% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Allergan |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Akbeta |
| PubMed Health | Levobunolol (Into the eye) |
| Drug Classes | Antiglaucoma |
| Drug Label | BETAGAN (levobunolol hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, USP) sterile is a noncardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent for ophthalmic use. The solution is colorless to slightly light yellow in appearance with an osmolality range of 250-360 m... |
| Active Ingredient | Levobunolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.5%; 0.25% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Akorn |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Betagan |
| Active Ingredient | Levobunolol hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.5%; 0.25% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Allergan |
For lowering intraocular pressure (IOP) and may be used in patients with chronic open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
FDA Label
Levobunolol is an ophthalmic beta-blocker, equally effective at β(1)- and β(2)-receptor sites. Levobunolol reduces both elevated and normal IOP in patients with or without glaucoma. In patients with elevated IOP, levobunolol reduces mean IOP by approximately 25-40% from baseline. As the drug is a nonselective &beta-adrenergic blocking agent, it can produce both systemic pulmonary and cardiovascular effects following topical application to the eye. These effects include adverse pulmonary effects (eg. bronchoconstriction, increased airway resistance), and a decrease in blood pressure and heart rate.
Sympatholytics
Drugs that inhibit the actions of the sympathetic nervous system by any mechanism. The most common of these are the ADRENERGIC ANTAGONISTS and drugs that deplete norepinephrine or reduce the release of transmitters from adrenergic postganglionic terminals (see ADRENERGIC AGENTS). Drugs that act in the central nervous system to reduce sympathetic activity (e.g., centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonists, see ADRENERGIC ALPHA-AGONISTS) are included here. (See all compounds classified as Sympatholytics.)
Adrenergic beta-Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate beta-adrenergic receptors thereby blocking the actions of beta-adrenergic agonists. Adrenergic beta-antagonists are used for treatment of hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, glaucoma, migraine headaches, and anxiety. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Antagonists.)
S01ED03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01E - Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics
S01ED - Beta blocking agents
S01ED03 - Levobunolol
Absorption
80%
Hepatic
20 hours
Levobunolol's mechanism of action in reducing IOP is not clearly defined, but is believed to be due to a reduction of the production of aqueous humor via blockage of endogenous catecholamine-stimulated increases in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP) concentrations within the ciliary processes.