

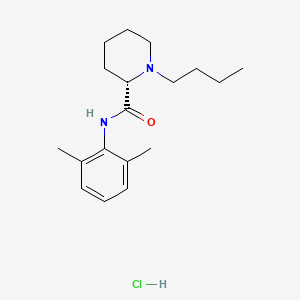

1. Chirocaine
2. Levobupivacaine
1. Levobupivacaine Hcl
2. 27262-48-2
3. Chirocaine
4. Levobupivacaine Hydrochloride [usan]
5. Levobupivacaine (hydrochloride)
6. (s)-1-butyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide Monohydrochloride
7. (s)-1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide Hydrochloride
8. (s)-(-)-bupivacaine Hydrochloride
9. J998rdz51i
10. Chebi:31772
11. Bupivacaine (-)-form Hydrochloride
12. (2s)-1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide Hydrochloride
13. (s)-1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboxamide Monohydrochloride
14. (s)-(-)-bupivacaine Monohydrochloride
15. 27262-48-2 (hcl)
16. Dsstox_cid_26071
17. Dsstox_rid_81319
18. Dsstox_gsid_46071
19. (s)-bupivacaine Hydrochloride
20. Levobupivacaine Free Base
21. Bupicaine Hydrochloride (-)
22. Cas-27262-48-2
23. Ncgc00159482-02
24. Unii-j998rdz51i
25. Popscaine
26. Chirocaine (tn)
27. Levobupivacaine Hydrochloride (anhydrous)
28. Schembl34174
29. (s)-(-)-bupivacaine Hcl
30. (-)-bupivacaine Hydrochloride
31. Levobupivacaine Monohydrochloride
32. Chembl1200749
33. Dtxsid9046071
34. Hy-b0653a
35. 2',6'-pipecoloxylidide, 1-butyl-, Hydrochloride, (-)-
36. Mr-8-a2
37. (s)-(-)-bupivacainehydrochloride
38. Levobupivacaine Hcl [vandf]
39. (-)-(s)-bupivacaine Hydrochloride
40. Act04726
41. Tox21_111706
42. Mfcd01704265
43. S4061
44. Akos016001444
45. Tox21_111706_1
46. Ac-2097
47. Ccg-267755
48. Cs-4301
49. 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, Monohydrochloride, (2s)-
50. Ncgc00178579-04
51. As-15053
52. Levobupivacaine Hydrochloride (jan/usan)
53. Levobupivacaine Hydrochloride [jan]
54. Levobupivacaine Hydrochloride [mart.]
55. Levobupivacaine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
56. Levobupivacaine Hydrochloride, >=98% (hplc)
57. D01287
58. Bupivacaine (-)-form Hydrochloride [mi]
59. (s)-1-butyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide Hydrochloride
60. 262b482
61. Levobupivacaine Hydrochloride [orange Book]
62. Q27114682
63. (2s)-1-butyl-2-[(2,6-dimethylphenyl)carbamoyl]piperidinium Chloride
64. (2s)-1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide;hydrochloride
65. 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-,monohydrochloride, (2s)-
| Molecular Weight | 324.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H29ClN2O |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 324.1968412 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 324.1968412 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 32.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 321 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Anesthetics, Local
Drugs that block nerve conduction when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentrations. They act on any part of the nervous system and on every type of nerve fiber. In contact with a nerve trunk, these anesthetics can cause both sensory and motor paralysis in the innervated area. Their action is completely reversible. (From Gilman AG, et. al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed) Nearly all local anesthetics act by reducing the tendency of voltage-dependent sodium channels to activate. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Local.)