
1. Anhydrous, Levofloxacin
2. Levaquin
3. Levofloxacin Anhydrous
4. Ofloxacin, (s)-isomer
5. Quixin
1. 100986-85-4
2. Levaquin
3. Quixin
4. (-)-ofloxacin
5. Cravit
6. Iquix
7. Ofloxacin S-(-)-form
8. Tavanic
9. Levofloxacine
10. (s)-ofloxacin
11. L-ofloxacin
12. Levofloxacino
13. Levofloxacinum
14. Oftaquix
15. Floxacin
16. Levofloxacin Anhydrous
17. Dr-3355
18. Nofaxin
19. Volequin
20. Fluoroquinolone
21. Levofloxacin Hydrate
22. Mp-376
23. Levofloxacin (inn)
24. Levofloxacin (levaquin)
25. Rwj-25213
26. Levaquin (tn)
27. Elequine
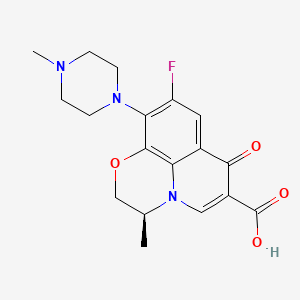
28. (3s)-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
29. (s)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
30. Nsc-758709
31. Rix4e89y14
32. 7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid, 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-, (3s)-
33. Chebi:63598
34. Quinsair
35. Mfcd00865049
36. (s)-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
37. Ofloxacin, (s)-
38. Levofloxacin [inn]
39. (s)-(-)-ofloxacin
40. (3s)-(-)-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
41. Lfx
42. Levofloxacine [inn-french]
43. Levofloxacinum [inn-latin]
44. Levofloxacino [inn-spanish]
45. Dr3355
46. Hr 355
47. Aeroquin
48. Unibiotic
49. Venaxan
50. Levofloxacin [usan:inn:jan]
51. Loxof
52. Levofloxacin (as Hemihydrate)
53. Rwj 25213-097
54. (2s)-7-fluoro-2-methyl-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-10-oxo-4-oxa-1-azatricyclo[7.3.1.0^{5,13}]trideca-5(13),6,8,11-tetraene-11-carboxylic Acid
55. (s)-(-)-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzooxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
56. (s)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
57. Smr000466387
58. Cravit (tn)
59. S-(-)-ofloxacin
60. Ccris 4074
61. (s)-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-3,7-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic Acid
62. Levaquin In Dextrose 5% In Plastic Container
63. Unii-rix4e89y14
64. Levofiexacin
65. Ofloxcacin
66. S-ofloxacin
67. Hsdb 8028
68. Cravit Iv
69. Levofloxacin,(s)
70. Anhydrous Ofloxacin
71. Dr-3355: L-isomer Of Ofloxacin
72. (3s)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
73. Hr-355
74. Mp 376
75. Spectrum_001719
76. Cpd000466387
77. Spectrum2_001676
78. Spectrum3_000995
79. Spectrum4_001123
80. Spectrum5_001438
81. Schembl15397
82. Bspbio_002689
83. Kbiogr_001605
84. Kbioss_002199
85. (-)-(s)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
86. Fluoro-methyl-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-oxo-[?]carboxylic Acid
87. Mls000759524
88. Mls001165709
89. Mls001423977
90. Levofloxacin [who-dd]
91. Spectrum1504260
92. Spbio_001891
93. Dtxsid0041060
94. Gtpl10911
95. Kbio2_002199
96. Kbio2_004767
97. Kbio2_007335
98. Kbio3_001909
99. Ofloxacin S-(-)-form Hemihydrate
100. Hms1922j07
101. Hms2051g04
102. Hms2090o10
103. Hms2093e18
104. Hms2232g06
105. Pharmakon1600-01504260
106. Zinc538273
107. Ex-a1488
108. Hy-b0330
109. Levofloxacin, >=98.0% (hplc)
110. Bdbm50366826
111. Ccg-39093
112. De-108
113. Mmv687798
114. Nsc755604
115. Nsc758709
116. S1940
117. Ofloxacin S-(-)-form [mi]
118. Akos008901361
119. Akos015895104
120. Ac-7593
121. Db01137
122. Nc00094
123. Nsc 758709
124. Nsc-755604
125. Ncgc00178529-01
126. Ncgc00178529-02
127. Ncgc00178529-03
128. Ncgc00178529-06
129. 7h-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid, 2,3-dihydro-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-, (s)-
130. As-31796
131. Lvx
132. Levofloxacin, Analytical Reference Material
133. Sbi-0206768.p001
134. L0193
135. C07660
136. D08120
137. Ab00171657-12
138. Ab00171657-13
139. Ab00171657_14
140. Ab00171657_15
141. 986l854
142. Q424193
143. Sr-05000001999
144. Levofloxacin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
145. Q-201295
146. Sr-05000001999-1
147. Brd-k09471561-001-06-7
148. Tert-butyl?2-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate
149. Z1766089137
150. Levofloxacin Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile, Certified Reference Material
151. (2s)-7-fluoro-2-methyl-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-10-oxo-4-oxa-1-azatricyclo[7.3.1.05,13]trideca-5(13),6,8,11-tetraene-11-carboxylic Acid
152. (2s)-7-fluoro-2-methyl-6-(4-methylpiperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-10-oxo-4-oxa-1-azatricyclo[7.3.1.05,13]trideca-5(13),6,8,11-tetraene-11-carboxylate
153. (s)-9-fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7h-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 361.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H20FN3O4 |
| XLogP3 | -0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 361.14378429 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 361.14378429 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 73.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 634 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Levaquin |
| PubMed Health | Levofloxacin (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | LEVAQUIN is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent for oral and intravenous administration. Chemically, levofloxacin, a chiral fluorinated carboxyquinolone, is the pure (-)-(S)-enantiomer of the racemic drug substance ofloxacin. The chemica... |
| Active Ingredient | Levofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; Solution |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 250mg/10ml; 500mg; eq 500mg/20ml (eq 25mg/ml); eq 750mg/30ml (eq 25mg/ml); 750mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Pharms |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Levofloxacin |
| PubMed Health | Levofloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Levofloxacin is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent for oral and intravenous administration. Chemically, levofloxacin, a chiral fluorinated carboxyquinolone, is the pure (-)-(S)-enantiomer of the racemic drug substance ofloxacin. The chemi... |
| Active Ingredient | sodium chloride; Levofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops; Tablet; Injectable; Solution |
| Route | injection; Ophthalmic; oral; Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 0.5%; 250mg; 250mg/10ml; 500mg; eq 500mg/20ml (eq 25mg/ml); eq 750mg/30ml (eq 25mg/ml); 25mg/ml; 5mg/ml; 750mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Wockhardt; Mylan Pharma; Hospira; Teva; Apotex; Aurobindo Pharma; Torrent Pharms; Lupin; Sandoz; Cipla; Hikma Pharms; Watson Labs; Nexus Pharms; Glenmark Generics; Emcure Pharms; Hi Tech Pharma; Macleods Pharms; Claris Lifesciences; Sagent Pharms; Zydus P |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Quixin |
| PubMed Health | Levofloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | QUIXIN (levofloxacin ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is a sterile topical ophthalmic solution. Levofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial active against a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative ocular pathogens. Levofloxacin is the pure (... |
| Active Ingredient | Levofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Santen |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Levaquin |
| PubMed Health | Levofloxacin (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | LEVAQUIN is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent for oral and intravenous administration. Chemically, levofloxacin, a chiral fluorinated carboxyquinolone, is the pure (-)-(S)-enantiomer of the racemic drug substance ofloxacin. The chemica... |
| Active Ingredient | Levofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Injectable; Solution |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 250mg/10ml; 500mg; eq 500mg/20ml (eq 25mg/ml); eq 750mg/30ml (eq 25mg/ml); 750mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Pharms |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Levofloxacin |
| PubMed Health | Levofloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Levofloxacin is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent for oral and intravenous administration. Chemically, levofloxacin, a chiral fluorinated carboxyquinolone, is the pure (-)-(S)-enantiomer of the racemic drug substance ofloxacin. The chemi... |
| Active Ingredient | sodium chloride; Levofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops; Tablet; Injectable; Solution |
| Route | injection; Ophthalmic; oral; Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 0.5%; 250mg; 250mg/10ml; 500mg; eq 500mg/20ml (eq 25mg/ml); eq 750mg/30ml (eq 25mg/ml); 25mg/ml; 5mg/ml; 750mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Wockhardt; Mylan Pharma; Hospira; Teva; Apotex; Aurobindo Pharma; Torrent Pharms; Lupin; Sandoz; Cipla; Hikma Pharms; Watson Labs; Nexus Pharms; Glenmark Generics; Emcure Pharms; Hi Tech Pharma; Macleods Pharms; Claris Lifesciences; Sagent Pharms; Zydus P |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Quixin |
| PubMed Health | Levofloxacin |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | QUIXIN (levofloxacin ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is a sterile topical ophthalmic solution. Levofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial active against a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative ocular pathogens. Levofloxacin is the pure (... |
| Active Ingredient | Levofloxacin |
| Dosage Form | Solution/drops |
| Route | Ophthalmic |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Santen |
Anti-Bacterial Agents; Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary; Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2012)
Levofloxacin is used for the treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis caused by susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, or Moraxella catarrhalis. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 385
Levofloxacin is used for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia caused by susceptible S. aureus (oxacillin-susceptible strains), S. pneumoniae (including penicillin-resistant strains (penicillin MIC of 2 ug/mL or greater)), H. influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, M. catarrhalis, Chlamydophila pneumoniae (formerly Chlamydia pneumoniae), or Mycoplasma pneumoniae. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 385
Levofloxacin is used for the treatment of mild to moderate complicated urinary tract infections caused by susceptible E. faecalis, Enterobacter cloacae, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis, or Ps. aeruginosa and acute pyelonephritis caused by susceptible E. coli, including cases with concurrent bacteremia. /Included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011, p. 386
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Levofloxacin (23 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Levaquin, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=a1f01e8e-97e9-11de-b91d-553856d89593
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Levaquin may exacerbate muscle weakness in persons with myasthenia gravis. Avoid Levaquin in patients with a known history of myasthenia gravis
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=a1f01e8e-97e9-11de-b91d-553856d89593
Other serious and sometimes fatal events, some due to hypersensitivity, and some due to uncertain etiology, have been reported rarely in patients receiving therapy with fluoroquinolones, including Levaquin. These events may be severe and generally occur following the administration of multiple doses. Clinical manifestations may include one or more of the following: fever, rash, or severe dermatologic reactions (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome); vasculitis; arthralgia; myalgia; serum sickness; allergic pneumonitis; interstitial nephritis; acute renal insufficiency or failure; hepatitis; jaundice; acute hepatic necrosis or failure; anemia, including hemolytic and aplastic; thrombocytopenia, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; leukopenia; agranulocytosis; pancytopenia; and/or other hematologic abnormalities. The drug should be discontinued immediately at the first appearance of skin rash, jaundice, or any other sign of hypersensitivity and supportive measures instituted.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
Post-marketing reports of severe hepatotoxicity (including acute hepatitis and fatal events) have been received for patients treated with Levaquin No evidence of serious drug-associated hepatotoxicity was detected in clinical trials of over 7,000 patients. Severe hepatotoxicity generally occurred within 14 days of initiation of therapy and most cases occurred within 6 days. Most cases of severe hepatotoxicity were not associated with hypersensitivity. The majority of fatal hepatotoxicity reports occurred in patients 65 years of age or older and most were not associated with hypersensitivity. Levaquin should be discontinued immediately if the patient develops signs and symptoms of hepatitis.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Levofloxacin (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In oral and intravenous formulations, levofloxacin is indicated in adults for the treatment of various infections caused by susceptible bacteria, including infections of the upper respiratory tract, lower respiratory tract, skin, skin structures, urinary tract, and prostate. The oral formulation is also indicated in both adults and children 6 months of age and older for the post-exposure management of inhalational anthrax caused by _Bacillus anthracis_ and for the treatment and/or prophylaxis of plague caused by _Yersinia pestis_. In its ophthalmic formulation, levofloxacin is indicated for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis caused by susceptible organisms. An inhalational solution available in Canada is indicated for the management of cystic fibrosis patients aged 18 years or older with chronic pulmonary _Pseudomonas aeruginosa_ infections.
FDA Label
Quinsair is indicated for the management of chronic pulmonary infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in adult patients with cystic fibrosis.
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
Levofloxacin is bactericidal and exerts its antimicrobial effects via inhibition of bacterial DNA replication. It has a relatively long duration of action in comparison with other antibiotics that allows for once or twice daily dosing. Levofloxacin is associated with QTc-interval prolongation and should be used with caution in patients with other risk factors for prolongation (e.g. hypokalemia, concomitant medications). Levofloxacin has demonstrated _in vitro_ activity against a number of aerobic gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and may carry some activity against certain species of anaerobic bacteria and other pathogens such as _Chlamydia_ and _Legionella_. Resistance to levofloxacin may develop, and is generally due to mutations in DNA gyrase or topoisomerase IV, or via alterations to drug efflux. Cross-resistance may occur between levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones, but is unlikely to develop between levofloxacin and other antibiotic classes (e.g. macrolides) due to significant differences in chemical structure and mechanism of action. As antimicrobial susceptibility patterns are geographically distinct, local antibiograms should be consulted to ensure adequate coverage of relevant pathogens prior to use.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary
Substances capable of killing agents causing urinary tract infections or of preventing them from spreading. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents, Urinary.)
Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Drugs and compounds which inhibit or antagonize the biosynthesis or actions of CYTOCHROME P-450 CYP1A2. (See all compounds classified as Cytochrome P-450 CYP1A2 Inhibitors.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
J01MA12
J01MA12
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01M - Quinolone antibacterials
J01MA - Fluoroquinolones
J01MA12 - Levofloxacin
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AE - Fluoroquinolones
S01AE05 - Levofloxacin
Absorption
Absorption of levofloxacin following oral administration is rapid and essentially complete, with an oral bioavailability of approximately 99%. Due to its nearly complete absorption, the intravenous and oral formulations of levofloxacin may be interchangeable. The Tmax is generally attained 1-2 hours following administration and the Cmax is proportional to the given dose - an intravenous dose of 500mg infused over 60 minutes resulted in a Cmax of 6.2 1.0 g/mL whereas a 750mg dose infused over 90 minutes resulted in a Cmax of 11.5 4.0 g/mL. Oral administration with food prolongs the Tmax by approximately 1 hour and slightly decreases the Cmax, but these changes are not likely to be clinically significant. Systemic absorption following oral inhalation is approximately 50% lower than that observed following oral administration.
Route of Elimination
The majority of administered levofloxacin is excreted unchanged in the urine. Following the administration of a single oral dose of levofloxacin, approximately 87% was eliminated unchanged in the urine within 48 hours and less than 4% was eliminated in the feces within 72 hours.
Volume of Distribution
Levofloxacin is widely distributed in the body, with an average volume of distribution following oral administration between 1.09-1.26 L/kg (~89-112 L). Concentrations in many tissues and fluids may exceed those observed in plasma. Levofloxacin is known to penetrate well into skin tissue, fluids (e.g. blisters), lung tissue, and prostatic tissue, amongst others.
Clearance
The average apparent total body clearance of levofloxacin ranges from 8.64-13.56 L/h, and its renal clearance ranges from 5.76-8.52 L/h. The relative similarity of these ranges indicates a small degree of non-renal clearance.
The mean volume of distribution of levofloxacin generally ranges from 74 to 112 L after single and multiple 500 mg or 750 mg doses, indicating widespread distribution into body tissues. Levofloxacin reaches its peak levels in skin tissues and in blister fluid of healthy subjects at approximately 3 hours after dosing. The skin tissue biopsy to plasma AUC ratio is approximately 2 and the blister fluid to plasma AUC ratio is approximately 1 following multiple once-daily oral administration of 750 mg and 500 mg doses of levaquin, respectively, to healthy subjects. Levofloxacin also penetrates well into lung tissues. Lung tissue concentrations were generally 2- to 5-fold higher than plasma concentrations and ranged from approximately 2.4 to 11.3 ug/g over a 24-hour period after a single 500 mg oral dose.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
Levofloxacin pharmacokinetics are linear and predictable after single and multiple oral or IV dosing regimens. Steady-state conditions are reached within 48 hours following a 500 mg or 750 mg once-daily dosage regimen. The mean + or - SD peak and trough plasma concentrations attained following multiple once-daily oral dosage regimens were approximately 5.7 + or - 1.4 and 0.5 + or - 0.2 ug/mL after the 500 mg doses, and 8.6+ or - 1.9 and 1.1 + or - 0.4 ug/mL after the 750 mg doses, respectively. The mean + or - SD peak and trough plasma concentrations attained following multiple once-daily IV regimens were approximately 6.4 + or - 0.8 and 0.6 + or - 0.2 ug/mL after the 500 mg doses, and 12.1+ or - 4.1 and 1.3 + or - 0.71 ug/mL after the 750 mg doses, respectively. Oral administration of a 500 mg dose of levaquin with food prolongs the time to peak concentration by approximately 1 hour and decreases the peak concentration by approximately 14% following tablet and approximately 25% following oral solution administration. Therefore, levaquin tablets can be administered without regard to food. It is recommended that levaquin oral solution be taken 1 hour before or 2 hours after eating.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
Levofloxacin is rapidly and essentially completely absorbed after oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are usually attained one to two hours after oral dosing. The absolute bioavailability of levofloxacin from a 500 mg tablet and a 750 mg tablet of Levaquin are both approximately 99%, demonstrating complete oral absorption of levofloxacin. Following a single intravenous dose of Levaquin to healthy volunteers, the mean + or - SD peak plasma concentration attained was 6.2 + or - 1.0 ug/mL after a 500 mg dose infused over 60 minutes and 11.5+ or - 4.0 ug/mL after a 750 mg dose infused over 90 minutes.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
Levofloxacin is excreted largely as unchanged drug in the urine. The mean terminal plasma elimination half-life of levofloxacin ranges from approximately 6 to 8 hours following single or multiple doses of levofloxacin given orally or intravenously. The mean apparent total body clearance and renal clearance range from approximately 144 to 226 mL/min and 96 to 142 mL/min, respectively. Renal clearance in excess of the glomerular filtration rate suggests that tubular secretion of levofloxacin occurs in addition to its glomerular filtration. Concomitant administration of either cimetidine or probenecid results in approximately 24% and 35% reduction in the levofloxacin renal clearance, respectively, indicating that secretion of levofloxacin occurs in the renal proximal tubule. No levofloxacin crystals were found in any of the urine samples freshly collected from subjects receiving levaquin.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Levofloxacin (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Only 2 metabolites, desmethyl-levofloxacin and levofloxacin-N-oxide, have been identified in humans, neither of which appears to carry any relevant pharmacological activity. Following oral administration, less than 5% of the administered dose was recovered in the urine as these metabolites, indicating very little metabolism of levofloxacin in humans. The specific enzymes responsible for the demethylation and oxidation of levofloxacin have yet to be ascertained.
Levofloxacin is stereochemically stable in plasma and urine and does not invert metabolically to its enantiomer, D-ofloxacin. Levofloxacin undergoes limited metabolism in humans and is primarily excreted as unchanged drug in the urine. Following oral administration, approximately 87% of an administered dose was recovered as unchanged drug in urine within 48 hours, whereas less than 4% of the dose was recovered in feces in 72 hours. Less than 5% of an administered dose was recovered in the urine as the desmethyl and N-oxide metabolites, the only metabolites identified in humans. These metabolites have little relevant pharmacological activity.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
The average terminal elimination half-life of levofloxacin is 6-8 hours.
The mean terminal plasma elimination half-life of levofloxacin ranges from approximately 6 to 8 hours following single or multiple doses of levofloxacin given orally or intravenously.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
The pharmacokinetics of oral levofloxacin and its penetration into inflammatory fluid were studied in 6 healthy male subjects (ages 18-45 yr) who received 500 mg drug every 12 hr for 5 doses or 500 mg every 24 hr for 3 doses in an open crossover design. ... Mean terminal elimination half-lives in plasma were 7.9 and 8 hr for the 2 regimens, respectively, and the same values were seen for inflammatory fluid. ...
Child J et al; Chemother 39 (Dec): 2749-51 (1995)
After single oral administration of (14)C-levofloxacin at a dose of 20 mg kg(-1) under non-fasting conditions, the absorption, distribution and excretion of radioactivity were studied in albino and pigmented rats. ... The uveal tract concentrations reached the maximum value (C(max)) of 26.33 +/- 0.75 ug eq. g(-1) at 24 hr after dosing and declined slowly with a terminal half-life of 468.1 hr (19.5 days).
PMID:15099441 Tanaka M et al; J Pharm Pharmacol 56 (4): 463-9 (2004)
Levofloxacin, like other fluoroquinolone antibiotics, exerts its antimicrobial activity via the inhibition of two key bacterial enzymes: DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Both targets are type II topoisomerases, but have unique functions within the bacterial cell. DNA gyrase is an enzyme found only in bacteria that introduces negative supercoils into DNA during replication - this helps to relieve torsional strain caused by the introduction of positive supercoils during replication, and these negative supercoils are essential for chromosome condensation and the promotion of transcription initiation. It is comprised of four subunits (two A subunits and two B subunits) of which the A subunits appear to be the target of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Bacterial topoisomerase IV, in addition to contributing to the relaxation of positive supercoils, is essential at the terminal stages of DNA replication and functions to unlink newly replicated chromosomes to allow for the completion of cell division. Inhibition of these enzymes by levofloxacin likely occurs via complexation with the topoisomerase enzymes. The end result is a blockade of DNA replication, thus inhibiting cell division and resulting in cell death.
Levofloxacin is the L-isomer of the racemate, ofloxacin, a quinolone antimicrobial agent. The antibacterial activity of ofloxacin resides primarily in the L-isomer. The mechanism of action of levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolone antimicrobials involves inhibition of bacterial topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase (both of which are type II topoisomerases), enzymes required for DNA replication, transcription, repair and recombination.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) tablet, film coated for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) solution for oral use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution, concentrate for intravenous use; LEVAQUIN (levofloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use (October 2011). Available from, as of March 7, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=levofloxacin
Fluoroquinolones prolong the QT interval by blocking voltage-gated potassium channels, especially the rapid component of the delayed rectifier potassium current I(Kr), expressed by HERG (the human ether-a-go-go-related gene). According to the available case reports and clinical studies, moxifloxacin carries the greatest risk of QT prolongation from all available quinolones in clinical practice and it should be used with caution in patients with predisposing factors for Torsades de pointes (TdP).
PMID:22156660 Briasoulis A et al; Cardiology 120 (2): 103-10 (2011)