


1. Fetzima
2. Levomilnacipran Hydrochloride
1. 96847-54-0
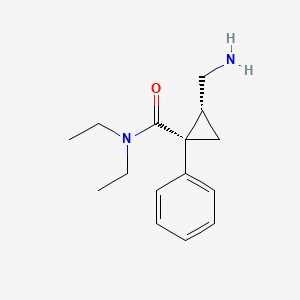
2. (1s,2r)-milnacipran
3. (1s,2r)-2-(aminomethyl)-n,n-diethyl-1-phenylcyclopropane-1-carboxamide
4. F 2695
5. Milnacipran, (1s,2r)-
6. Ugm0326txx
7. Chembl99946
8. F-2695
9. Cyclopropanecarboxamide, 2-(aminomethyl)-n,n-diethyl-1-phenyl-, (1s,2r)-
10. (1s,2r)-2-(aminomethyl)-n,n-diethyl-1-phenylcyclopropanecarboxamide
11. Unii-ugm0326txx
12. Levomilnacipran [usan:inn]
13. Milnacipram
14. (+)-milnacipran
15. Starbld0000863
16. Levomilnacipran (usan/inn)
17. Levomilnacipran [inn]
18. Zinc506
19. Levomilnacipran [usan]
20. Levomilnacipran [vandf]
21. Gtpl7435
22. Schembl1414867
23. Levomilnacipran [who-dd]
24. Chebi:136040
25. Dtxsid701025167
26. Bdbm50032379
27. Db08918
28. F2-695
29. D10072
30. Q6535779
31. (1s,2r)-2-aminomethyl-1-phenyl-cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid Diethylamide
| Molecular Weight | 246.35 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H22N2O |
| XLogP3 | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 246.173213330 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 246.173213330 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 295 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fetzima |
| PubMed Health | Levomilnacipran (By mouth) |
| Active Ingredient | Levomilnacipran hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 40mg base; eq 80mg base; eq 120mg base; eq 20mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Forest Labs |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fetzima |
| PubMed Health | Levomilnacipran (By mouth) |
| Active Ingredient | Levomilnacipran hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 40mg base; eq 80mg base; eq 120mg base; eq 20mg base |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Forest Labs |
Levomilnacipran is a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD).
FDA Label
Treatment of stroke
Levomilnacipran binds with high affinity to human serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE) transporters (Ki = 11 and 91 nM, respectively). It potently inhibits 5-HT and NE reuptake (IC50 = 16 - 19 and 11 nM, respectively). Levomilnacipran does not bind to any other receptors, ion channels, or transporters, including serotonergic (5HT1-7), - and adrenergic, muscarinic, or histaminergic receptors and Ca2+, Na+, K+ or Cl- channels to a significant degree. Levomilnacipran did not inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO). Furthermore, levomilnacipran does not prolong the QTc interval to a clinically relevant extent.
Antidepressive Agents
Mood-stimulating drugs used primarily in the treatment of affective disorders and related conditions. Several MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITORS are useful as antidepressants apparently as a long-term consequence of their modulation of catecholamine levels. The tricyclic compounds useful as antidepressive agents (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, TRICYCLIC) also appear to act through brain catecholamine systems. A third group (ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS, SECOND-GENERATION) is a diverse group of drugs including some that act specifically on serotonergic systems. (See all compounds classified as Antidepressive Agents.)
Serotonin and Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors
Drugs that selectively block or suppress the plasma membrane transport of SEROTONIN and NORADRENALINE into axon terminals and are used as ANTIDEPRESSIVE AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Serotonin and Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors.)
N - Nervous system
N06 - Psychoanaleptics
N06A - Antidepressants
N06AX - Other antidepressants
N06AX28 - Levomilnacipran
Absorption
The relative bioavailability after administration of the extended-release capsule was 92% when compared to oral solution. Food does not affect the concentration of levomilnacipran. After daily dosing of levomilnacipran (extended-release capsule) the mean Cmax is 341 ng/mL, and the mean steady-state AUC value is 5196 ngh/mL. The Tmax is 6 - 8 hours after oral administration. Interconversion of stereoisomers does not occur in humans.
Route of Elimination
Levomilnacipran and its metabolites are eliminated primarily by renal excretion. 58% of the dose is excreted in urine as unchanged levomilnacipran. N-desethyl levomilnacipran is the major metabolite excreted in the urine and accounted for approximately 18% of the dose. Other identifiable metabolites excreted in the urine are levomilnacipran glucuronide (4%), desethyl-levomilnacipran glucuronide (3%), p-hydroxy levomilnacipran glucuronide (1%), and p-hydroxylevomilnacipran (1%). The metabolites are inactive.
Volume of Distribution
387 - 473 L [apparent volume of distribution]
Clearance
21 - 29 L/h [mean apparent total clearance]
Hepatic. Levomilnacipran undergoes desethylation to form desethyl levomilnacipran and hydroxylation to form p-hydroxy-levomilnacipran. Desethylation is facilitated primarily by CYP3A4 and by CYP2C8, 2C19, 2D6, and 2J2 to a lesser extent. Both metabolites undergo further conjugation with glucuronide to form conjugates.
12 hours
The exact mechanism of the antidepressant action of levomilnacipran is unknown but is thought to be related to the potentiation of serotonin and norephinephrine in the central nervous system through inhibition of reuptake at serotonin and norepinephrine transporters.