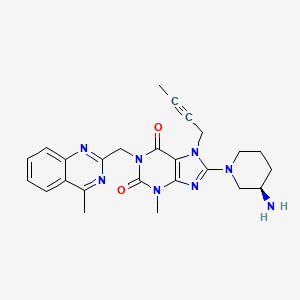

1. (r)-8-(3-amino-piperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione
2. 1356, Bi
3. 1h-purine-2,6-dione, 8-((3r)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl)-7-(2-butynyl)-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-1-((4-methyl-2-quinazolinyl)methyl)-
4. Bi 1356
5. Bi-1356
6. Bi1356
7. Tradjenta
8. Trajenta
1. 668270-12-0
2. Tradjenta
3. Bi 1356
4. Bi-1356
5. Ondero
6. Linagliptin (bi-1356)
7. Trajenta
8. Trazenta
9. Bi-1356-bs
10. Bs 1356 Bs
11. Ione
12. 3x29zej4r2
13. Chembl237500
14. (r)-8-(3-amino-piperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione
15. Bi-1356bs
16. Chebi:68610
17. Bi 1356 Bs
18. Bs-1356-bs
19. (r)-8-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-(but-2-ynyl)-3-methyl-1-((4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl)-1h-purine-2,6(3h,7h)-dione
20. (r)-8-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-(4-methylquinazolin-2-ylmethyl)-3,7-dihydro-purine-2,6-dione
21. 8-[(3r)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-but-2-yn-1-yl-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
22. 8-[(3r)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]purine-2,6-dione
23. 8-[(3r)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-(but-2-yn-1-yl)-3- Methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
24. 8-[(3r)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-(but-2-yn-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
25. C25h28n8o2
26. Unii-3x29zej4r2
27. Linaglitpin
28. Linagliptin [usan:inn:jan]
29. Hsdb 8204
30. Tradjenta (tn)
31. 8-((3r)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-(but-2-yn-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-((4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl)-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
32. 8-[(3r)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl]-7-(2-butynyl)-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-1-[(4-methyl-2-quinazolinyl)methyl]-1h-purine-2,6-dione
33. Linagliptin [mi]
34. Linagliptin [inn]
35. Linagliptin [jan]
36. Linagliptin [usan]
37. Linagliptin [vandf]
38. Linagliptin [mart.]
39. Linagliptin [who-dd]
40. Mls006010217
41. Schembl160188
42. Linagliptin (jan/usan/inn)
43. Gtpl6318
44. Amy8953
45. Ex-a076
46. Linagliptin [orange Book]
47. Bcpp000185
48. Dtxsid201021653
49. Bcp02462
50. Zinc3820029
51. Bdbm50228403
52. Glyxambi Component Linagliptin
53. Mfcd14635356
54. S3031
55. Akos015951179
56. Akos015995251
57. Ac-8761
58. Bcp9000854
59. Ccg-269463
60. Cs-0637
61. Db08882
62. Linagliptin Component Of Glyxambi
63. Trijardy Xr Component Linagliptin
64. Ncgc00346655-01
65. Ncgc00346655-02
66. 1h-purine-2,6-dione, 8-((3r)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl)-7-(2-butynyl)-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-1-((4-methyl-2-quinazolinyl)methyl)-
67. As-35080
68. Bl164627
69. Hy-10284
70. Jentadueto Component Of Linagliptin
71. Linagliptin Component Of Jentadueto
72. Smr004701306
73. Linagliptin Component Of Trijardy Xr
74. Sw219813-1
75. D09566
76. Ab01563307_01
77. Ab01563307_03
78. 270l120
79. Q909745
80. J-519354
81. (r)-8-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-(but-2-yn-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-((4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl)-1h-purine-2,6(3h,7h)-dione
82. (r)-8-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-(but-2-yn-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-((4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl)-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-dione
83. 1-[(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3-methyl-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-8-(3-(r)-aminopiperidin-1-yl)xanthine
84. 1-[(4-methyl-quinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3-methyl-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-8-(3-(r)aminopiperidin-1-yl)xanthine
85. 1-[(4-methyl-quinazolin-2yl) Methyl]-3-methyl-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-8-[3-(r) Amino-piperidin-1-yl]-xanthine
86. 1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)-methyl]-3-methyl-7-(2-butin-1-yl)-8-(3-(r)-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-xanthine
87. 1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3-methyl-7-(2-butin-1-yl)-8-(3-(r)-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-xanthine
88. 1233245-11-8
89. 1h-purine-2,6-dione, 8-((3r)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl)-7-(2-butynyl)-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-1-((4-methyl-2- Quinazolinyl)methyl)-
90. 8-[(3r)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-but-2-yn-1-yl-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-d
91. 8-[(3r)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-but-2-yn-1-yl-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]-3,7-dihydro-1h-purine-2,6-d Ione
92. Linagliptin; (r)-8-(3-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7-(but-2-yn-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-((4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl)-1h-purine-2,6(3h,7h)-dione
| Molecular Weight | 472.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H28N8O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 472.23352217 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 472.23352217 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 114 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 885 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tradjenta |
| PubMed Health | Linagliptin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | TRADJENTA (linagliptin) tablets contain, as the active ingredient, an orally-active inhibitor of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme. Linagliptin is described chemically as 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 8-[(3R)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl]-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-3,... |
| Active Ingredient | Linagliptin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Boehringer Ingelheim |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tradjenta |
| PubMed Health | Linagliptin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Hypoglycemic |
| Drug Label | TRADJENTA (linagliptin) tablets contain, as the active ingredient, an orally-active inhibitor of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme. Linagliptin is described chemically as 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 8-[(3R)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl]-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-3,... |
| Active Ingredient | Linagliptin |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Boehringer Ingelheim |
Hypoglycemic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Linagliptin. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of July 18, 2014: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Tradjenta tablets are indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (Linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of July 18, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: RISK OF LACTIC ACIDOSIS. Lactic acidosis is a rare, but serious, complication that can occur due to metformin accumulation. The risk increases with conditions such as renal impairment, sepsis, dehydration, excess alcohol intake, hepatic impairment, and acute congestive heart failure. The onset is often subtle, accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, increasing somnolence, and nonspecific abdominal distress. Laboratory abnormalities include low pH, increased anion gap, and elevated blood lactate. If acidosis is suspected, Jentadueto should be discontinued and the patient hospitalized immediately. /Linagliptin and metformin hydrochloride combination product/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Jentadueto (Linagliptin and Metformin Hydrochloride) Tablets (Revised: May 2014). Available from, as of July 18, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=f6dd9b86-0d18-95d4-2bc7-05591bfdd597
FDA is evaluating unpublished new findings by a group of academic researchers that suggest an increased risk of pancreatitis and pre-cancerous cellular changes called pancreatic duct metaplasia in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with a class of drugs called incretin mimetics. These findings were based on examination of a small number of pancreatic tissue specimens taken from patients after they died from unspecified causes. FDA has asked the researchers to provide the methodology used to collect and study these specimens and to provide the tissue samples so the Agency can further investigate potential pancreatic toxicity associated with the incretin mimetics. Drugs in the incretin mimetic class include exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon), liraglutide (Victoza), sitagliptin (Januvia, Janumet, Janumet XR, Juvisync), saxagliptin (Onglyza, Kombiglyze XR), alogliptin (Nesina, Kazano, Oseni), and linagliptin (Tradjenta, Jentadueto). These drugs work by mimicking the incretin hormones that the body usually produces naturally to stimulate the release of insulin in response to a meal. They are used along with diet and exercise to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes. FDA has not reached any new conclusions about safety risks with incretin mimetic drugs. This early communication is intended only to inform the public and health care professionals that the Agency intends to obtain and evaluate this new information. ... FDA will communicate its final conclusions and recommendations when its review is complete or when the Agency has additional information to report. The Warnings and Precautions section of drug labels and patient Medication Guides for incretin mimetics contain warnings about the risk of acute pancreatitis. FDA has not previously communicated about the potential risk of pre-cancerous findings of the pancreas with incretin mimetics. FDA has not concluded these drugs may cause or contribute to the development of pancreatic cancer. At this time, patients should continue to take their medicine as directed until they talk to their health care professional, and health care professionals should continue to follow the prescribing recommendations in the drug labels. ...
US FDA; Safety Alerts for Human Medicial Products: Incretin Mimetic Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes: Early Communication - Reports of Possible Increased Risk of Pancreatitis and Pre-cancerous Findings of the Pancreas (Posted March 14, 1013). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm343805.htm
There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, in patients taking Tradjenta. Take careful notice of potential signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue Tradjenta and initiate appropriate management. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using Tradjenta.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with Tradjenta. These reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions. Onset of these reactions occurred within the first 3 months after initiation of treatment with Tradjenta, with some reports occurring after the first dose. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, discontinue Tradjenta, assess for other potential causes for the event, and institute alternative treatment for diabetes. Angioedema has also been reported with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema to another DPP-4 inhibitor because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to angioedema with Tradjenta.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Linagliptin (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Linagliptin is indicated for the treatment of type II diabetes in addition to diet and exercise. It should not be used to treat type I diabetes or in diabetic ketoacidosis. An extended-release combination product containing empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin was approved by the FDA in January 2020 for the improvement of glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus when used adjunctively with diet and exercise.
FDA Label
Trajenta is indicated in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus to improve glycaemic control in adults:
as
* monotherapy:
- in patients inadequately controlled by diet and exercise alone and for whom metformin is inappropriate due to intolerance, or contraindicated due to renal impairment.
as
* combination therapy:
- in combination with metformin when diet and exercise plus metformin alone do not provide adequate glycaemic control.
- in combination with a sulphonylurea and metformin when diet and exercise plus dual therapy with these medicinal products do not provide adequate glycaemic control.
- in combination with insulin with or without metformin, when this regimen alone, with diet and exercise, does not provide adequate glycaemic control.
A 5mg oral dose of linagliptin results in >80% inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) for 24 hours. Inhibition of DPP-4 increases the concentration of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), leading to decreased glycosylated hemoglobin and fasting plasma glucose.
Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors
Compounds that suppress the degradation of INCRETINS by blocking the action of DIPEPTIDYL-PEPTIDASE IV. This helps to correct the defective INSULIN and GLUCAGON secretion characteristic of TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS by stimulating insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release. (See all compounds classified as Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors.)
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
Incretins
Peptides which stimulate INSULIN release from the PANCREATIC BETA CELLS following oral nutrient ingestion, or postprandially. (See all compounds classified as Incretins.)
A10BH05
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BH - Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (dpp-4) inhibitors
A10BH05 - Linagliptin
Absorption
Oral bioavailability of linagliptin is 30%.
Route of Elimination
84.7% of linagliptin is eliminated in the feces and 5.4% is eliminated in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
A single intravenous dose of 5mg results in a volume of distribution of 1110L. However an intravenous infusion of 0.5-10mg results in a volume of distribution of 380-1540L.
Clearance
Total clearance of linagliptin is 374mL/min.
Available animal data have shown excretion of linagliptin in milk at a milk-to-plasma ratio of 4:1.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
After oral administration of a single 5-mg dose to healthy subjects, peak plasma concentrations of linagliptin occurred at approximately 1.5 hours post dose (Tmax); the mean plasma area under the curve (AUC) was 139 nmol*h/L and maximum concentration (Cmax) was 8.9 nmol/L.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
The absolute bioavailability of linagliptin is approximately 30%. High-fat meal reduced Cmax by 15% and increased AUC by 4%; this effect is not clinically relevant. Tradjenta may be administered with or without food.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
Following administration of an oral (14C)-linagliptin dose to healthy subjects, approximately 85% of the administered radioactivity was eliminated via the enterohepatic system (80%) or urine (5%) within 4 days of dosing. Renal clearance at steady state was approximately 70 mL/min.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Linagliptin (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
An oral dose of linagliptin is excreted primarily in the feces. 90% of an oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine and feces. The predominant metabolite in the plasma is CD1790 and the predominant metabolite recovered after excretion was M489(1). Other metabolites are produced through oxidation, oxidative degradation, N-acetylation, glucuronidation, and cysteine adduct formation. Other metabolites have been identified through mass spectrometry though no structures were determined. Metabolism of linagliptin is mediated by cytochrome P450 3A4, aldo-keto reductases, and carbonyl reductases.
Following oral administration, the majority (about 90%) of linagliptin is excreted unchanged, indicating that metabolism represents a minor elimination pathway. A small fraction of absorbed linagliptin is metabolized to a pharmacologically inactive metabolite, which shows a steady-state exposure of 13.3% relative to linagliptin.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
The terminal half life of linagliptin is 155 hours.
The effective half-life for accumulation of linagliptin, as determined from oral administration of multiple doses of linagliptin 5 mg, is approximately 12 hours.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
Plasma concentrations of linagliptin decline in at least a biphasic manner with a long terminal half-life (>100 hours), related to the saturable binding of linagliptin to DPP-4.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of August 1, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f
Linagliptin is a competitive, reversible DPP-4 inhibitor. Inhibition of this enzyme slows the breakdown of GLP-1 and glucose-dependant insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). GLP-1 and GIP stimulate the release of insulin from beta cells in the pancreas while inhibiting release of glucagon from pancreatic beta cells. These effects together reduce the breakdown of glycogen in the liver and increase insulin release in response to glucose.
Linagliptin is an inhibitor of DPP-4, an enzyme that degrades the incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Thus, linagliptin increases the concentrations of active incretin hormones, stimulating the release of insulin in a glucose-dependent manner and decreasing the levels of glucagon in the circulation. Both incretin hormones are involved in the physiological regulation of glucose homeostasis. Incretin hormones are secreted at a low basal level throughout the day and levels rise immediately after meal intake. GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin biosynthesis and secretion from pancreatic beta-cells in the presence of normal and elevated blood glucose levels. Furthermore, GLP-1 also reduces glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha-cells, resulting in a reduction in hepatic glucose output.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Tradjenta (Linagliptin) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: June 2014). Available from, as of July 31, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=c797ea5c-cab7-494b-9044-27eba0cfe40f