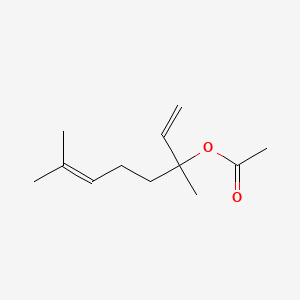

1. Linalyl Acetate, (+-)-isomer
2. Linalyl Acetate, (r)-isomer
3. Linalyl Acetate, (s)-isomer
1. 115-95-7
2. Linalool Acetate
3. 3,7-dimethylocta-1,6-dien-3-yl Acetate
4. Bergamiol
5. Bergamol
6. Linalol Acetate
7. Lynalyl Acetate
8. Licareol Acetate
9. Bergamot Mint Oil
10. Acetic Acid Linalool Ester
11. 1,6-octadien-3-ol, 3,7-dimethyl-, Acetate
12. 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-yl Acetate
13. 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-ol Acetate
14. 1,6-octadien-3-ol, 3,7-dimethyl-, 3-acetate
15. Ex Bois De Rose (synthetic)
16. Fema No. 2636
17. Phanteine
18. Dehydrolinalool, Acetate
19. Nsc 2138
20. 1,5-dimethyl-1-vinyl-4-hexenyl Acetate
21. 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-ctadien-3-ol Acetate
22. 5k47ssq51g
23. Chebi:78333
24. (1)-1,5-dimethyl-1-vinylhex-4-enyl Acetate
25. Nsc-2138
26. 1,5-dimethyl-1-vinylhex-4-en-1-yl Acetate
27. Acetic Acid Linalyl Ester
28. Dsstox_cid_6946
29. Dsstox_rid_78265
30. Dsstox_gsid_26946
31. (+)-1,5-dimethyl-1-vinylhex-4-enyl Acetate
32. Linalyl Acetate (natural)
33. Aetic Acid Linalool Ester
34. Cas-115-95-7
35. Hsdb 644
36. Linalyl Acetate Synthetic
37. Linalyl Acetater
38. Einecs 204-116-4
39. Einecs 254-806-4
40. Mfcd00008907
41. Unii-5k47ssq51g
42. Linaloyl Acetate
43. Ai3-00941
44. Linalyl Acetate Terpenes
45. (-)-s-linalyl Acetate
46. (+/-)-linalyl Acetate
47. Acetic Acid-linalyl Ester
48. (1,5-dimethyl-1-vinyl-hex-4-enyl) Acetate
49. Ec 204-116-4
50. 3,6-octadien-3-ol Acetate
51. 3,6-octadien-3-yl Acetate
52. Schembl58028
53. (.+/-.)-linalyl Acetate
54. Linalyl Acetate [mi]
55. Linalool Acetate, Dl-
56. Linalyl Acetate [fcc]
57. 1, 3,7-dimethyl-, Acetate
58. Linalyl Acetate [fhfi]
59. Linalyl Acetate [hsdb]
60. Linalyl Acetate [inci]
61. Chembl502773
62. Dtxsid7026946
63. Wln: 1y&u3y1u1ov1
64. Fema 2636
65. Linalyl Acetate [usp-rs]
66. Linalyl Acetate(linalool Acetate)
67. Nsc2138
68. Linalyl Acetate, Natural, >=80%
69. Hy-n6948
70. Linalyl Acetate, (+/-)-
71. Linalyl Acetate, Analytical Standard
72. Tox21_201306
73. Tox21_303134
74. Linaloyl Acetate, (+/-)-
75. Akos015901735
76. Linalyl Acetate, >=97%, Fcc, Fg
77. Cs-w010587
78. 3,7-dimethyl-1,6octadien-3-yl Acetate
79. Ncgc00164001-01
80. Ncgc00164001-02
81. Ncgc00257047-01
82. Ncgc00258858-01
83. Ac-20000
84. Bs-49383
85. Ft-0627862
86. L0049
87. 3,7-dimethyl-acetate(3r)-1,6-octadien-3-ol
88. E80781
89. (+)-3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-ol Acetate
90. 1,6-octadien-3-ol, 3, 7-dimethyl-, Acetate
91. 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-yl Acetate 97%
92. 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-yl Acetate, 97%
93. 3,7-dimethyl-3-acetate(3r)-1,6-octadien-3-ol
94. A893739
95. Q188314
96. W-108587
97. Acetic Acid-linalyl Ester 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
| Molecular Weight | 196.29 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H20O2 |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 196.146329876 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 196.146329876 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 26.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 237 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
... Permeation of Salvia desoleana Atzei & Picci essential oil (linalyl acetate, 26.8%) through the porcine buccal mucosa is possible in vitro. /Salvia desoleana Atzei & Picci essential oil (linalyl acetate, 26.8%)/
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development; Screening Information Data Set for LINALYL ACETATE (115-95-7) p.53 (March 2002). Available from, as of July 14, 2008: https://www.chem.unep.ch/irptc/sids/OECDSIDS/sidspub.html
The percutaneous absorption of a massage oil containing lavender oil was studied following application to the skin of a male subject (age 34 yr). Within 5 min after application, traces of linalool and linalyl acetate, the main constituents of lavender oil, could be detected in the blood. After 20 min, maximum concentrations of 100 ng/mL linalyl acetate and 121 ng/mL linalool were reached. Within 90 min most of the lavender oil was eliminated. It was concluded that lavender oil is rapidly absorbed through the skin and is excreted within 90 minutes.
Jager W et al; Journal of Soc Cosmet Chem 43: 49-54 (1992)
Esters are readily hydrolyzed by carboxylesterases or esterases. Linalyl acetate has been demonstrated to be hydrolyzed in vitro in rat blood and liver preparations. It is expected to be readily hydrolyzed in vivo. Acetate is a normal constituent of the body. The metabolism of linalool is known and is primarily through glucuronic acid conjugation and excretion
Api AM et al; Food Chem Toxicol 82 Suppl: S39-48 (2015)
In neutral gastric juice, linalyl acetate is slowly (t1/2=121 min) hydrolyzed to a mixture of linalool and the ring closed isomer alpha-terpineol. In acidic artificial gastric juice, linalyl acetate is rapidly hydrolyzed (t1/2<5 min) to yield linalool, which rapidly rearranges into alpha-terpineol. Linalyl acetate was slowly hydrolyzed (t1/2=153-198 min) in intestinal fluid with or without pancreatin. Linalyl acetate also hydrolyzed in homogenates of rat intestinal mucosal, blood, and liver, but at rates much slower than in acidic gastric juice (rate constant for hydrolysis k=0.01-0.0055/min vs. >5/min). Based on these observations it is concluded that linalyl acetate hydrolyzes in gastric juice to yield linalool which, to some extent, is rapidly ring closed to yield alpha-terpineol.
Letizia CS et al; Food Chem Toxicol 41 (7): 965-76 (2003)
... Hydrolysis occurs more rapidly at the low pH of gastric fluids. The reaction products are linalool and acetic acid (ester hydrolysis). This is supported by the findings of the hydrolysis study ... at pH 4, 7 and 9. Therefore it is expected that linalool is the substance that will enter the systemic circulation after oral uptake of linalyl acetate. Linalool is probably converted to geraniol and its metabolites, 1,5-dimethyl-hexadiene-1,6-dicarboxylic acid and 7-carboxy-5-methylocto-6-enoic acid ...
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development; Screening Information Data Set for LINALYL ACETATE (115-95-7) p.10 (March 2002). Available from, as of July 14, 2008: https://www.chem.unep.ch/irptc/sids/OECDSIDS/sidspub.html
Percutaneous absorption ofthe main components of lavender oil were measured in a male human subject. Blood levels of linalool and linalyl acetate were followed for 90 min after the use of a massage oil which contained lavender oil and peanut oil in a 2:98 ratio. The lavender oil contained 24.79% linalool and 29.59% linalyl acetate. A 1500 mg sample of the lavender oil was gently massaged for 10 min into a 376 sq cm area on the abdomen of a 60 kg male volunteer. Blood samples were drawn from the left cubital vein at 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, 60, 75 and 90 min. After adding heparin to the samples, the plasma was centrifuged and the samples were then stored until they were analyzed. Linalyl acetate was absorbed quickly and trace amounts could be detected in the blood 5 min after finishing the massage. The peak plasma concentration was reached at 19 min with a mean plasma concentration of 121 ng/mL. Most of the linalyl acetate disappeared from the blood in 90 min with a biological half-life of 14.3 min.
Letizia CS et al; Food Chem Toxicol 41 (7): 965-76 (2003)
Linalyl acetate is hydrolysed in gastric and pancreatic fluids with mean half-lives of 5.5 and 52.6 minutes respectively ...
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development; Screening Information Data Set for LINALYL ACETATE (115-95-7) p.10 (March 2002). Available from, as of July 14, 2008: https://www.chem.unep.ch/irptc/sids/OECDSIDS/sidspub.html
In a preliminary experiment, ... lavender essential oil relaxed vascular smooth muscle. Thus, the/se/ ... experiments were designed to investigate the relaxation mechanism of linalyl acetate as the major ingredient of lavender essential oil in rabbit carotid artery specimens. Linalyl acetate produced sustained and progressive relaxation during the contraction caused by phenylephrine. The relaxation effect of linalyl acetate at a concentration near the EC50 was partially but significantly attenuated by nitroarginine as an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, 1H-(1,2,4)oxadiazolo(4,3-a)quinoxaline-1-one as an inhibitor of guanylyl cyclase, or by the denudation of endothelial cells. In specimens without endothelium, the phenylephrine-induced contraction and phosphorylation of myosin light chain (MLC) were significantly attenuated after the pretreatment with linalyl acetate. The relaxation caused by linalyl acetate in the endothelium-denuded specimens was clearly inhibited by calyculin A as an inhibitor of MLC phosphatase, although not by ML-9 as an inhibitor of MLC kinase. Furthermore, suppression of the phenylephrine-induced contraction and MLC phosphorylation with linalyl acetate was canceled by the pretreatment with calyculin A. These results suggest that linalyl acetate relaxes the vascular smooth muscle through partially activation of nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway, and partially MLC dephosphorylation via activating MLC phosphatase.
PMID:16891914 Koto R et al; J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 48 (1): 850-6 (2006)
