


1. Litarex
2. Monolithium Citrate
1. 919-16-4
2. Trilithium Citrate
3. Litarex
4. Citric Acid Trilithium Salt
5. Lithium Citrate Anhydrous
6. Lithium (citrate)
7. Citric Acid, Trilithium Salt
8. Lithium Citrate (anhydrous)
9. Lithium Citrate Tribasic Tetrahydrate
10. 1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic Acid, 2-hydroxy-, Trilithium Salt
11. Anhydrous Lithium Citrate
12. Demalit; Litarex; Lithonate S
13. 6680-58-6
14. Demalit
15. Chebi:64735
16. Lithium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
17. Trilithium;2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
18. 1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic Acid, 2-hydroxy-, Lithium Salt (1:3)
19. Einecs 213-045-8
20. Citric Acid, Lithium Salt
21. Trilithium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
22. Einecs 233-819-9
23. Anh. Lithium Citrate
24. Unii-3655633623
25. Lithium Citrate (anh.)
26. Citric Acid,lithium Salt
27. Lithium Citrate [mi]
28. Spectrum1504269
29. Chembl1201170
30. Dtxsid70883185
31. Hms1923k13
32. Hms2093g04
33. Lithium Citrate Tribasic 4-hydrate
34. 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic Acid Lithium Salt (1:3)
35. Akos015839591
36. Akos015902460
37. Ccg-213298
38. Db14507
39. Ncgc00095267-01
40. Ncgc00095267-02
41. 1313437-84-1
42. Db-054961
43. Ft-0636234
44. Lithium2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
45. Lithium 3-carboxy-3,5-dihydroxy-5-oxopentanoate
46. Q2351742
| Molecular Weight | 210.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
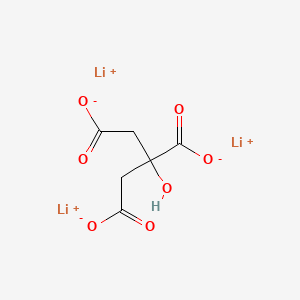
| Molecular Formula | C6H5Li3O7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 210.0515378 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 210.0515378 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 141 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 211 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 4 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lithium citrate |
| Active Ingredient | Lithium citrate |
| Dosage Form | Syrup |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 300mg carbonate/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Wockhardt; Roxane |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lithium citrate |
| Active Ingredient | Lithium citrate |
| Dosage Form | Syrup |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 300mg carbonate/5ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Wockhardt; Roxane |
Lithium is used as a mood stabilizer, and is used for treatment of depression and mania. It is often used in bipolar disorder treatment.
Although lithium has been used for over 50 years in treatment of bipolar disorder, the mechanism of action is still unknown. Lithium's therapeutic action may be due to a number of effects, ranging from inhibition of enzymes such as glycogen synthase kinase 3, inositol phosphatases, or modulation of glutamate receptors.
The precise mechanism of action of Li+ as a mood-stabilizing agent is currently unknown. It is possible that Li+ produces its effects by interacting with the transport of monovalent or divalent cations in neurons. An increasing number of scientists have come to the conclusion that the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate is the key factor in understanding how lithium works. Lithium has been shown to change the inward and outward currents of glutamate receptors (especially GluR3), without a shift in reversal potential. Lithium has been found to exert a dual effect on glutamate receptors, acting to keep the amount of glutamate active between cells at a stable, healthy level, neither too much nor too little. It is postulated that too much glutamate in the space between neurons causes mania, and too little, depression. Another mechanism by which lithium might help to regulate mood include the non-competitive inhibition of an enzyme called inositol monophosphatase. Alternately lithium's action may be enhanced through the deactivation of the GSK-3B enzyme. The regulation of GSK-3B by lithium may affect the circadian clock. GSK-3 is known for phosphorylating and thus inactivating glycogen synthase. GSK-3B has also been implicated in the control of cellular response to damaged DNA. GSK-3 normally phosphorylates beta catenin, which leads to beta catenin degratation. When GSK-3 is inhibited, beta catenin increases and transgenic mice with overexpression of beta catenin express similar behaviour to mice treated with lithium. These results suggest that increase of beta catenin may be a possible pathway for the therapeutic action of lithium.