


1. Ckd 501
2. Ckd-501
3. Ckd501
1. 607723-33-1
2. Lobeglitazone [inn]
3. My89f08k5d
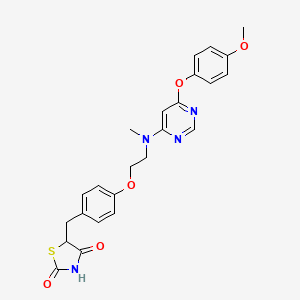
4. 5-(4-(2-((6-(4-methoxyphenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)(methyl)amino)ethoxy)benzyl)thiazolidine-2,4-dione
5. Unii-my89f08k5d
6. Ckd501
7. Lobeglitazone [who-dd]
8. Schembl2742697
9. Chembl3585580
10. Chebi:136052
11. Db09198
12. Sb16869
13. 5-[[4-[2-[[6-(4-methoxyphenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl]-methylamino]ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione
14. Db-090849
15. Q18350076
16. (5rs)-5((4-(2-((6-(4-methoxyphenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)methylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione
17. 2,4-thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-((6-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-4-pyrimidinyl)methylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-
| Molecular Weight | 480.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H24N4O5S |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 480.14674105 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 480.14674105 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 128 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 670 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Lobeglitazone was approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (South Korea) in 2013, and is being monitored by postmarketing surveillance until 2019. Lobeglitazone is not approved for use by either the Food and Drug Administration (USA), Health Canada, or by the European Medicines Agency for use in the management of diabetes.
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BG - Thiazolidinediones
A10BG04 - Lobeglitazone
Absorption
In rat studies, the AUC for the doses 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/kg, AUC values were determined to be 459, 514, and 481 ug min/mL respectively. Absoprtion occurs rapidly after administration, with Tmax of 67.5 and 48.8 min and a Cmax of 0.962 and 0.4.94 ug/mL following doses of 0.5 and 2 mg/kg, respectively. Absolute bioavailability after oral administration was nearly complete and apparently not affected by the dosage; 92.1% following a 0.5 mg/kg dose and 99.0% following a 2 mg/kg dose. Furthermore, the extent of LB remaining in the GI tract at 24 h was found to be negligible, with values less than 0.2% of the oral dose, suggesting that the intestinal absorption is complete in rats at the dose range studied.
Route of Elimination
It has been reported that the combined extent of the excretion of lobeglitazone to the bile, urine and intestine is low (less than 10% of total dose), suggesting that the major route of elimination for the drug involves its metabolism.
Volume of Distribution
The steady state volume of distribution (Vss) of lobeglitazone was found to be 189276 mL/kg. Vss was not found to vary statistically with the dose, suggesting that lobeglitazone follows linear kinetics.
Clearance
In rat studies, systemic clearance was found to be between 1.95 and 2.19 mL/min/kg regardless of dosage.
Rat studies with lobeglitazone have suggested that it is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isozymes, however the exact enzymes involved in its metabolism have yet to be elucidated. The structure of Lobeglitazone's five major metabolites have been characterized along with their pharmacokinetic parameters, and can be seen in the metabolism section below. In rat studies, demethylation and hydroxylation appear to be the primary metabolic pathways. The most abundant metabolite found in these studies was confirmed in vivo as M1, a demethylated derivative of lobeglitazone; its rate of formation was found to be approximately 0.216 0.252 mL/min/kg, representing approximately 9.76% of the total lobeglitazone elimination in vivo in rats.
Following an intravenous dosage of 1 mg/kg, the half life was found to be 110 min.
Lobeglitazone acts as an insulin sensitizer by binding and activating Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPAR) gamma within fat cells. By promoting the binding of insulin at fat cells, lobeglitazone has been shown to reduce blood sugar levels, lower hemoglobain A1C (HbA1C) levels, and improve lipid and liver profiles. Unlike [DB01132], which is a dual PPAR agonist at PPAR-alpha and PPAR-gamma, Lobeglitazone is a pure PPAR-alpha agonist.