

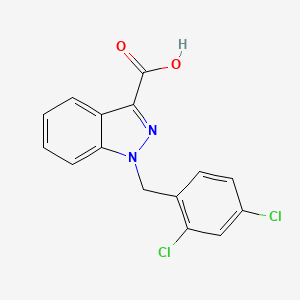

1. 1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)indazole-3-carboxylic Acid
2. Af 1890
3. Diclondazolic Acid
1. 50264-69-2
2. 1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-1h-indazole-3-carboxylic Acid
3. Diclondazolic Acid
4. Doridamina
5. Lonidamina
6. Lonidaminum
7. Lonidamin
8. 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-1h-indazole-3-carboxylic Acid
9. Af 1890
10. 1-(2,4-dichlorbenzyl)-indazole-3-carboxylic Acid
11. Lonidamine (inn)
12. 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]indazole-3-carboxylic Acid
13. 1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)indazole-3-carboxylic Acid
14. Nsc-741419
15. Nsc-758419
16. Af-1890
17. Mls000028822
18. U78804bidr
19. Chebi:50138
20. 1h-indazole-3-carboxylic Acid, 1-((2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl)-
21. 1h-indazole-3-carboxylic Acid, 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-
22. Af-1890;diclondazolic Acid;dica
23. Ncgc00015609-03
24. Smr000058467
25. Lonidamine [inn]
26. Dsstox_cid_782
27. Dsstox_rid_75787
28. Dsstox_gsid_20782
29. Lonidaminum [inn-latin]
30. Lonidamina [inn-spanish]
31. Doridamina (tn)
32. Dichlondazolic Acid
33. Cas-50264-69-2
34. Ccris 3516
35. Lonidamine [inn:ban]
36. Sr-01000075961
37. Einecs 256-510-0
38. Brn 0894483
39. Unii-u78804bidr
40. Kn-228
41. Mfcd00866285
42. Th-070
43. Tocris-1646
44. Lonidamine [mi]
45. Lopac-l-4900
46. L 4900
47. Lonidamine [mart.]
48. Schembl7134
49. Lonidamine [who-dd]
50. Lopac0_000718
51. Cid_39562
52. Zinc1632
53. Chembl1257030
54. Dtxsid5020782
55. Bdbm59775
56. 1h-indazole-3-carboxylic Acid, 1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-
57. Hms2234h24
58. Hms3262o17
59. Hms3268k09
60. Hms3369i01
61. Hms3412p05
62. Hms3651f09
63. Hms3676p05
64. Hms3874d03
65. Pharmakon1600-01503225
66. 1h-indazole-3-carboxylicacid, 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-
67. Act02617
68. Bcp06555
69. Hy-b0486
70. Tox21_110181
71. Tox21_202306
72. Tox21_500718
73. Af1890
74. Nsc741419
75. Nsc758419
76. S2610
77. Akos012842739
78. Tox21_110181_1
79. Ac-5626
80. Ccg-204803
81. Db06266
82. Lp00718
83. Nsc 741419
84. Nsc 758419
85. Sdccgsbi-0050696.p003
86. Ncgc00015609-01
87. Ncgc00015609-02
88. Ncgc00015609-04
89. Ncgc00015609-05
90. Ncgc00015609-06
91. Ncgc00015609-07
92. Ncgc00015609-08
93. Ncgc00015609-09
94. Ncgc00015609-16
95. Ncgc00025244-01
96. Ncgc00025244-02
97. Ncgc00025244-03
98. Ncgc00259855-01
99. Ncgc00261403-01
100. As-11653
101. Sbi-0050696.p002
102. Am20060642
103. Eu-0100718
104. Ft-0650359
105. L0283
106. Sw219810-1
107. Lonidamine, Mitochondrial Hexokinase Inhibitor
108. D07257
109. Ab00597141_08
110. Ab00597141_10
111. 264l692
112. A929099
113. Q-201318
114. Q3836670
115. Sr-01000075961-1
116. Sr-01000075961-3
117. Sr-01000075961-6
118. Brd-k78513633-001-03-3
119. Brd-k78513633-001-06-6
120. Z1741977188
121. 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-3-indazolecarboxylic Acid
122. 1-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-1h-indazole-3-carboxylicacid
| Molecular Weight | 321.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H10Cl2N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 320.0119330 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 320.0119330 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 55.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 396 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate disorders, and cancer/tumors (unspecified).
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Radiation-Sensitizing Agents
Drugs used to potentiate the effectiveness of radiation therapy in destroying unwanted cells. (See all compounds classified as Radiation-Sensitizing Agents.)
Antispermatogenic Agents
Agents, either mechanical or chemical, which destroy spermatozoa in the male genitalia and block spermatogenesis. (See all compounds classified as Antispermatogenic Agents.)
Trypanocidal Agents
Agents destructive to the protozoal organisms belonging to the suborder TRYPANOSOMATINA. (See all compounds classified as Trypanocidal Agents.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XX - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XX07 - Lonidamine
Lonidamine has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[1-[(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)methyl]indazole-3-carbonyl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Lonidamine is an orally administered small molecule that inhibits glycolysis by the inactivation of hexokinase. Hexokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes glucose, the first step in glycolysis. The inhibition of hexokinase by lonidamine is well established. In addition, there is evidence that lonidamine may increase programmed cell death. This stems from the observation that mitochondria and mitochondria-bound hexokinase are crucial for induction of apoptosis; agents that directly effect mitochondria may, therefore, trigger apoptosis. Indeed, in vitro models with lonidamine exhibit the hallmarks of apoptosis, including mitochondrial membrane depolarization, release of cytochrome C, phosphatidylserine externalization, and DNA fragmentation. [PMID: 16986057]