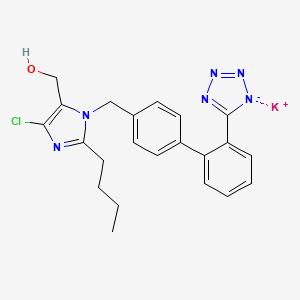

1. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-((2'-(1h-etrazol-5-yl) (1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl)methyl)-1h-imidazole-5-methanol
2. Cozaar
3. Dup 753
4. Dup-753
5. Dup753
6. Losartan
7. Losartan Monopotassium Salt
8. Mk 954
9. Mk-954
10. Mk954
11. Monopotassium Salt, Losartan
12. Potassium, Losartan
13. Salt, Losartan Monopotassium
1. 124750-99-8
2. Cozaar
3. Losartan Potassium Salt
4. Lorzaar
5. Losacar
6. Losaprex
7. Hyzaar
8. Dup 753
9. Nu-lotan
10. Mk 954
11. Lortaan
12. Losata
13. Tancin
14. Mk-0954
15. Losartanpotassium
16. Losartan Potassium (dup 753)
17. Mk0954
18. L-158086
19. Losartan Monopotassium Salt
20. 3st302b24a
21. Aradois
22. Zaart
23. Dup-753
24. Presartan-50
25. E-3340
26. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-(p-(o-1h-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl)imidazole-5-methanol, Monopotassium Salt
27. 124750-99-8 (ka+)
28. Potassium;[2-butyl-5-chloro-3-[[4-[2-(1,2,3-triaza-4-azanidacyclopenta-2,5-dien-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazol-4-yl]methanol
29. Lifezar
30. Lorzaan
31. Losacor
32. Tenopres
33. Lotim
34. Niten
35. Ocsaar
36. Du Pont-753
37. Neo Lotan
38. 1h-imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-((2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)(1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl)methyl)-, Monopotassium Salt
39. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-1h-imidazole-5-methanol, Monopotassium Salt
40. Mfcd09850721
41. Mk-954
42. Du Pont 753
43. Losartan Potassium [usan]
44. Covance
45. Unii-3st302b24a
46. Losartan Potassium [usan:usp]
47. Potassium 5-(4'-((2-butyl-4-chloro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1h-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)biphenyl-2-yl)tetrazol-1-ide
48. Cozaar (tn)
49. Dup-753 Potassium
50. Mk 0954
51. Losartan Potassium,(s)
52. Schembl42079
53. Mls001401407
54. Ex-89
55. Dtxsid3044209
56. Losartan Potassium [jan]
57. Losartan Potassium (jp17/usp)
58. Losartan Potassium [hsdb]
59. Hms2051m12
60. Hms2090o22
61. Hms2235f20
62. Hms3369f08
63. Hms3393m12
64. Losartan Potassium [vandf]
65. Losartan Potassium [mart.]
66. Act02618
67. Bcp05332
68. Bcp29397
69. Losartan Potassium [usp-rs]
70. Losartan Potassium [who-dd]
71. Akos015955543
72. Akos025310168
73. Ac-1072
74. Ccg-100869
75. Losartan Potassium, Analytical Standard
76. Nc00119
77. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-(2'-(tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)-1h-imidazole-5-methanol Potassium
78. Losartan Monopotassium Salt [mi]
79. Losartan Potassium [orange Book]
80. Losartan Potassium [ep Monograph]
81. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)-1,1'-biphenyl-4-yl]methyl]imidazole-5-methanol Potassium Salt
82. Bl164642
83. Epo
84. Hyzaar Component Losartan Potassium
85. Losartan Potassium [usp Monograph]
86. Smr000469593
87. Ft-0625705
88. L-185
89. L0232
90. Losartan Potassium Component Of Hyzaar
91. D00357
92. Ab01275507-01
93. 750l998
94. A805291
95. Sr-05000001514
96. Sr-05000001514-1
97. Q27257991
98. Losartan Potassium, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
99. Losartan Potassium Is Known As A Potent, Synthetic At1 Receptor Antagonist.
100. Losartan Potassium, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
101. Losartan Potassium, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
102. [2-butyl-5-chloro-3-[[4-[2-(1,2,3-triaza-4-azanidacyclopenta-2,5-dien-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazol-4-yl]methanol; Potassium;losartan Potassium
103. 1h-imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-((2-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)(1,1-biphenyl)-4-yl)methyl)-, Monopotassium Salt
104. Potassium;[2-butyl-5-chloro-3-[[4-[2-(1,2,3-triaza-4-azanidacyclopenta-2,5-dien-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazol-4-yl]methanol.
| Molecular Weight | 461.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H22ClKN6O |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 460.1180685 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 460.1180685 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 77.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 526 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cozaar |
| PubMed Health | Losartan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent, Renal Protective Agent |
| Drug Label | COZAAR1(losartan potassium) is an angiotensin II receptor (type AT1) antagonist. Losartan potassium, a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt.Its... |
| Active Ingredient | Losartan potassium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 100mg; 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Merck Sharp Dohme |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Losartan potassium |
| Drug Label | Losartan potassium tablets USP are an angiotensin II receptor (type AT1) antagonist. Losartan potassium, USP a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium... |
| Active Ingredient | Losartan potassium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 100mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Upsher Smith; Teva; Apotex; Alembic Pharms; Aurobindo Pharma; Torrent Pharms; Lupin; Sandoz; Prinston; Roxane; Watson Labs; Macleods Pharms; Ipca Labs; Vivimed Labs; Micro Labs Ltd India; Cadista Pharms; Zydus Pharms Usa; Mylan |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cozaar |
| PubMed Health | Losartan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent, Renal Protective Agent |
| Drug Label | COZAAR1(losartan potassium) is an angiotensin II receptor (type AT1) antagonist. Losartan potassium, a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt.Its... |
| Active Ingredient | Losartan potassium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 100mg; 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Merck Sharp Dohme |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Losartan potassium |
| Drug Label | Losartan potassium tablets USP are an angiotensin II receptor (type AT1) antagonist. Losartan potassium, USP a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium... |
| Active Ingredient | Losartan potassium |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 25mg; 100mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Upsher Smith; Teva; Apotex; Alembic Pharms; Aurobindo Pharma; Torrent Pharms; Lupin; Sandoz; Prinston; Roxane; Watson Labs; Macleods Pharms; Ipca Labs; Vivimed Labs; Micro Labs Ltd India; Cadista Pharms; Zydus Pharms Usa; Mylan |
Indicated in adult and paediatric patients for the: - treatment of anemia due to Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in patients on dialysis and not on dialysis. - treatment of anemia due to zidovudine in patients with HIV-infection. - treatment of anemia due to the effects of concomitant myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and upon initiation, there is a minimum of two additional months of planned chemotherapy. - reduction of allogeneic RBC transfusions in patients undergoing elective, noncardiac, nonvascular surgery.
FDA Label
Proteinuria, Treatment of heart failure, Treatment of hypertension
Erythropoietin and epoetin alfa are involved in the regulation of erythrocyte differentiation and the maintenance of a physiological level of circulating erythrocyte mass. It is reported to increase the reticulocyte count within 10 days of initiation, followed by increases in the RBC count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, usually within 2 to 6 weeks. Depending on the dose administered, the rate of hemoglobin increase may vary. In patients receiving hemodialysis, a greater biologic response is not observed at doses exceeding 300 Units/kg 3 times weekly. Epoetin alfa serves to restore erythropoietin deficiency in pathological and other clinical conditions where normal production of erythropoietin is impaired or compromised. In anemic patients with chronic renal failure (CRF), administration with epoetin alfa stimulated erythropoiesis by increasing the reticulocyte count within 10 days, followed by increases in the red cell count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, usually within 2 to 6 weeks. Epoetin alfa was shown to be effective in increasing hematocrit in zidovudine-treated HIV-infected patients and anemic cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers
Agents that antagonize ANGIOTENSIN II TYPE 1 RECEPTOR. Included are ANGIOTENSIN II analogs such as SARALASIN and biphenylimidazoles such as LOSARTAN. Some are used as ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B03 - Antianemic preparations
B03X - Other antianemic preparations
B03XA - Other antianemic preparations
B03XA01 - Erythropoietin
Absorption
The time to reach peak concentration is slower via the subcutaneous route than the intravenous route which ranges from 20 to 25 hours, and the peak is always well below the peak achieved using the intravenous route (510% of those seen with IV administration). The bioavailability of subcutaneous injectable erythropoietin is much lower than that of the intravenously administered product and is approximately 20-40%. **Adult and paediatric patients with CRF:** Following subcutaneous administration, the peak plasma levels are achieved within 5 to 24 hours. **Cancer patients receiving cyclic chemotherapy:** The average time to reach peak plasma concentration was approximately 13.3 12.4 hours after 150 Units/kg three times per week (TIW) subcutaneous (SC) dosing. The Cmax is expected be 3- to 7- fold higher and the Tmax is expected to be 2- to 3-fold longer in patients receiving a 40,000 Units SC weekly dosing regimen.
Route of Elimination
Erythropoietin and epoetin alfa are cleared via uptake and degradation via the EPO-R-expressing cells, and may also involve other cellular pathways in the interstitium, probably via cells in the reticuloendothelial scavenging pathway or lymphatic system. Only a small amount of unchanged epoetin alfa is found in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
In healthy volunteers, the volume of distribution of intravenous epoetin alfa was generally similar to the plasma volume (range of 4063.80 mL/kg), indicating limited extravascular distribution.
Clearance
**Healthy volunteers: *
In male volunteers receiving intravenous epoetin alfa, the total body clearance was approximately 8.12 1.00 mL/h/kg. **Cancer patients receiving cyclic chemotherapy:*
The average clearance was approximately 20.2 15.9 mL/h/kg after 150 Units/kg three times per week (TIW) subcutaneous (SC) dosing. The patients receiving a 40,000 Units SC weekly dosing regimen display a lower clearance (9.2 4.7 mL/h/kg).
Binding of erythropoietin and epoetin alfa to EPO-R leads to cellular internalization, which involves the degradation of the ligand. Erythropoietin and epoetin alfa may also be degraded by the reticuloendothelial scavenging pathway or lymphatic system.
**Healthy volunteers:*
The half life is approximately 4 hours in healthy volunteers receiving an intravenous injection. A half-life of approximately 6 hours has been reported in children. **Adult and paediatric patients with CRF:*
The elimination half life following intravenous administration ranges from 4 to 13 hours, which is about 20% longer in CRF patients than that in healthy subjects. The half life is reported to be similar between adult patients receiving or not receiving dialysis. **Cancer patients receiving cyclic chemotherapy:*
Following subcutaneous administration, the average half life is 40 hours with range of 16 to 67 hours.
Erythropoietin or exogenous epoetin alfa binds to the erythropoietin receptor (EPO-R) and activates intracellular signal transduction pathways. The affinity (Kd) of EPO for its receptor on human cells is 100 to 200 pM. Upon binding to EPO-R on the surface of erythroid progenitor cells, a conformational change is induced which brings EPO-R-associated Janus family tyrosine protein kinase 2 (JAK2) molecules into close proximity. JAK2 molecules are subsequently activated via phosphorylation, then phosphorylate tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain of the EPO-R that serve as docking sites for Src homology 2-domain-containing intracellular signaling proteins. The signalling proteins include STAT5 that once phosphorylated by JAK2, dissociates from the EPO-R, dimerizes, and translocates to the nucleus where they serve as transcription factors to activate target genes involved in cell division or differentiation, including the apoptosis inhibitor Bcl-x. The inhibition of apoptosis by the EPO-activated JAK2/STAT5/Bcl-x pathway is critical in erythroid differentiation. Via JAK2-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation, erythropoietin and epoetin alfa also activates other intracellular proteins involved in erythroid cell proliferation and survival, such as Shc , phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), and phospholipase C-1.