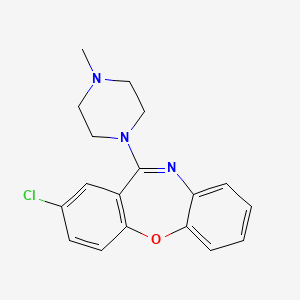

1. 2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-dibenz(b,f)(1,4)oxazepine
2. Cl 71,563
3. Cl-71,563
4. Cl71,563
5. Cloxazepine
6. Hydrochloride, Loxapine
7. Loxapine Hydrochloride
8. Loxapine Monohydrochloride
9. Loxapine Succinate
10. Loxapinsuccinate
11. Loxipine Maleate
12. Loxipine Succinate
13. Loxitane
14. Maleate, Loxipine
15. Oxilapine
16. Succinate, Loxapine
1. 1977-10-2
2. Cloxazepine
3. Oxilapine
4. Loxitane
5. Loxapin
6. Dibenzacepin
7. Dibenzoazepine
8. Adasuve
9. Loxapina
10. Loxapinum
11. Sum 3170
12. Cl-62362
13. Sum-3170
14. Hf3170
15. Hf 3170
16. Lw 3170
17. 2-chloro-11-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)dibenzo[b,f][1,4]oxazepine
18. Dibenz[b,f][1,4]oxazepine, 2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-
19. S-805
20. 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine
21. Chembl831
22. Cl 62,362
23. Chebi:50841
24. 2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)dibenz(b,f)(1,4)oxazepine
25. Dibenz(b,f)(1,4)oxazepine, 2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-
26. Ler583670j
27. Lossapina [dcit]
28. Hydrofluoride 3170
29. 2-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)dibenz[b,f][1,4]oxazepine
30. Loxapinum [inn-latin]
31. Loxapina [inn-spanish]
32. Lossapina
33. Loxapine [usan:inn:ban]
34. Az-004
35. Loxapine (usan/inn)
36. Cl 62362
37. S 805
38. Staccato Loxapine
39. Hsdb 3111
40. Loxapine (water)
41. Loxapine (dmso)
42. Adasuve (tn)
43. Einecs 217-835-3
44. Loxitane Intramuscular
45. Brn 0626753
46. Spectrum_000355
47. 2-chloro-11-(4-methylpiperazino)dibenzo(b,f)(1,4)oxazepine
48. Cl71,563
49. Loxapine [hsdb]
50. Loxapine [usan]
51. Specplus_000823
52. 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzo[b][1,5]benzoxazepine
53. Loxapine [inn]
54. Loxapine [mi]
55. Loxapine [vandf]
56. Prestwick0_000132
57. Prestwick1_000132
58. Prestwick2_000132
59. Prestwick3_000132
60. Spectrum2_001737
61. Spectrum3_001830
62. Spectrum5_001857
63. Loxapine [mart.]
64. Loxapine [who-dd]
65. Loxitane-c Oral Suspension
66. Lopac0_000720
67. Schembl94146
68. Bspbio_000204
69. Bspbio_003479
70. Gtpl205
71. Kbioss_000835
72. Divk1c_006919
73. Unii-ler583670j
74. Spbio_001814
75. Spbio_002143
76. Loxapine [orange Book]
77. Bpbio1_000226
78. Dtxsid7023229
79. Bdbm22871
80. Kbio1_001863
81. Kbio2_000835
82. Kbio2_003403
83. Kbio2_005971
84. Kbio3_002983
85. Pdsp1_001058
86. Pdsp2_001042
87. S5197
88. Zinc19796158
89. Ccg-204805
90. Cs-1105
91. Db00408
92. Sdccgsbi-0050698.p003
93. Qtl1_000050
94. Ncgc00021145-01
95. Ncgc00021145-02
96. Ncgc00021145-03
97. Ncgc00021145-04
98. Ncgc00021145-05
99. Ncgc00021145-06
100. Ncgc00021145-07
101. Ncgc00021145-08
102. Ncgc00021145-23
103. Ncgc00022279-03
104. Ncgc00022279-04
105. Ncgc00022279-05
106. Hy-17390
107. C07104
108. D02340
109. Q58614
110. Ab00053735_15
111. Ab00053735_16
112. 977l102
113. L001085
114. Brd-k39915878-036-04-6
115. Brd-k39915878-036-05-3
116. Brd-k39915878-036-15-2
117. 2-chloro-11-(4-methylpiperazino)dibenz[b,f][1,4]oxazepine
118. 8-chloro-6-(4-methylpiperazino)benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine;succinic Acid
119. 13-chloro-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxa-9-azatricyclo[9.4.0.0^{3,8}]pentadeca-1(11),3(8),4,6,9,12,14-heptaene
120. 13-chloro-10-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-oxa-9-azatricyclo[9.4.0.0^{3,8}]pentadeca-1(11),3,5,7,9,12,14-heptaene
| Molecular Weight | 327.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H18ClN3O |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 327.1138399 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 327.1138399 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 28.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 450 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adasuve |
| PubMed Health | Loxapine |
| Drug Classes | Antipsychotic |
| Drug Label | ADASUVE, a typical antipsychotic, is an inhalation powder of loxapine supplied in a single-use, disposable inhaler containing 10 mg of loxapine base. ADASUVE is a drug-device combination product.Active Ingredient: Loxapine (base). Loxapine, a dibenzo... |
| Active Ingredient | Loxapine |
| Dosage Form | Powder |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adasuve |
| PubMed Health | Loxapine |
| Drug Classes | Antipsychotic |
| Drug Label | ADASUVE, a typical antipsychotic, is an inhalation powder of loxapine supplied in a single-use, disposable inhaler containing 10 mg of loxapine base. ADASUVE is a drug-device combination product.Active Ingredient: Loxapine (base). Loxapine, a dibenzo... |
| Active Ingredient | Loxapine |
| Dosage Form | Powder |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
Antipsychotic Agents; Dopamine Antagonists
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
THIS DIBENZOXAZEPINE DERIVATIVE IS EFFECTIVE IN TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA BUT IT IS NOT CLEAR WHETHER IT HAS ANY ADVANTAGE OVER OTHER ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS. /SUCCINATE/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 447
Loxapine is indicated for the management of symptoms and characteristics of psychotic conditions. /Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 1905
Loxapine has been used to treat anxiety neurosis with depression. /NOT included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 1905
...LOXAPINE SHOULD BE RESERVED FOR USE IN PT WHO ARE REFRACTORY TO ESTABLISHED ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS. /SUCCINATE/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 447
Safe use of loxapine during pregnancy has not been established; therefore, the drug should not be used in pregnant women or women who might become pregnant unless the potential benefits outweigh the possible risk to the woman or fetus.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1891
Pending accumulation of clinical data on the use of the drug in children, loxapine is not recommended for use in children younger than 16 years of age.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1891
Loxapine should be used with caution, particularly in conjunction with anticholinergic antiparkinsonian agents and in patients with glaucoma or a tendency toward urinary retention because of possible anticholinergic activity. Since loxapine may have an aniemetic effect, it is possible that the drug could mask the sign of overdosage of toxic agents or interfere with the diagnosis of such conditions as intestinal obstruction or brain tumor. Loxapine is contraindicated in comatose patients, patients who have severe CNS depression from any cause, or known hypersensitivity to the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1891
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for LOXAPINE (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
A 2500 mg ingestion ... proved fatal ...
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 667
For the management of the manifestations of psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia
Adasuve is indicated for the rapid control of mild-to-moderate agitation in adult patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Patients should receive regular treatment immediately after control of acute agitation symptoms.
Loxapine, a dibenzoxazepine compound, represents a subclass of tricyclic antipsychotic agents, chemically distinct from the thioxanthenes, butyrophenones, and phenothiazines. Pharmacologically, Loxapine is a tranquilizer for which the exact mode of action has not been established, however, it is believed that by antagonising dopamine and serotonin receptors, there is a marked cortical inhibition which can manifest as tranquilization and suppression of aggression.
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Dopamine Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate DOPAMINE RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine or exogenous agonists. Many drugs used in the treatment of psychotic disorders (ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS) are dopamine antagonists, although their therapeutic effects may be due to long-term adjustments of the brain rather than to the acute effects of blocking dopamine receptors. Dopamine antagonists have been used for several other clinical purposes including as ANTIEMETICS, in the treatment of Tourette syndrome, and for hiccup. Dopamine receptor blockade is associated with NEUROLEPTIC MALIGNANT SYNDROME. (See all compounds classified as Dopamine Antagonists.)
N05AH01
N - Nervous system
N05 - Psycholeptics
N05A - Antipsychotics
N05AH - Diazepines, oxazepines, thiazepines and oxepines
N05AH01 - Loxapine
Absorption
Systemic bioavailability of the parent drug was only about one third that after an equivalent intramuscular dose (25 mg base) in male volunteers
Route of Elimination
Metabolites are excreted in the urine in the form of conjugates and in the feces unconjugated.
Animal studies with radioactive drug indicate that loxapine and/or its metabolites are widely distributed in body tissues with highest concentrations in brain, lungs, heart, liver, and pancreas. The drug appears in the CSF.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1890
Loxapine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI tract. The drug is also almost completely absorbed following IM administration.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1889
RAPIDLY & ALMOST COMPLETELY ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT. PEAK LOXAPINE SERUM LEVELS /WITHIN 2 HR, RANGE FROM 0.006 TO 0.013 MCG/ML AFTER/ 25 MG ORAL DOSE...MAJOR /ACTIVE/ METABOLITE IN SERUM IS 8-HYDROXYLOXAPINE /MAX CONCN 0.012-0.038 MCG/ML WITHIN 2-4 HR AFTER ORAL LOXAPINE. HUMAN/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1976
LOXAPINE AND/OR METABOLITES...WIDELY DISTRIBUTED IN BODY TISSUES...HIGHEST CONCN IN BRAIN, LUNGS, HEART, LIVER, & PANCREAS...APPEARS IN CSF...CROSSES PLACENTA...IN MILK OF NURSING MOTHERS /ANIMALS, RADIOACTIVE DRUG/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1976
METABOLITES /7- & 8-HYDROXY-, 7- & 8-HYDROXYDESMETHYLLOXAPINE; N-OXIDES OF LOXAPINE, 7- & 8-HYDROXYLOXAPINE/ EXCRETED IN URINE & FECES. LITTLE OR NO UNMETABOLIZED DRUG...FOUND...METABOLITES /PRIMARILY GLUCURONIDE OR SULFATE CONJUGATES IN URINE, PRIMARILY UNCONJUGATED IN FECES. HUMAN, ORAL/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1976
Hepatic
RAPIDLY & EXTENSIVELY METABOLIZED IN LIVER BY AROMATIC HYDROXYLATION, N-DEMETHYLATION & N-OXIDATION. MAJOR METABOLITES...8-HYDROXYLOXAPINE, & 7-HYDROXYLOXAPINE WHICH ARE ACTIVE...8-HYDROXYDESMETHYLLOXAPINE, 7-HYDROXYDESMETHYLLOXAPINE & LOXAPINE-N-OXIDE WHICH ARE INACTIVE /HUMAN, ORAL/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1976
SIGNIFICANT AMT OF N-OXIDES OF /7-HYDROXY- & 8-HYDROXYLOXAPINES, METABOLITES FORMED BY HYDROXYLATION & N-OXIDATION/, PRESENT...LOXAPINE METABOLITES ARE EXCRETED IN URINE PRIMARILY AS GLUCURONIDE OR SULFATE CONJUGATES /HUMAN, ORAL/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1976
2 METABOLITES: 8-HYDROXYLOXAPINE & 8-HYDROXYAMOXAPINE, INCR ON ORAL MEDICATION.
SAKALIS G, GERSHON S; PARENTERAL LOXAPINE IN ACUTE SCHIZOPHRENIA; CURR THER RES CLIN EXP 25(FEB) 330-4 (1979)
Loxapine is rapidly and extensively metabolized in the liver by aromatic hydroxylation, N-oxidation. The major metabolites of loxapine are 8-hydroxyloxapine and 7-hydroxyloxapine which are active and 8-hydroxydesmethylloxapine, 7-hydroxydesmethylloxapine, and loxapine N-oxide which are inactive. Significant amounts of the N-oxides of the hydroxyloxapines are also present.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service-Drug Information 19 98. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1998 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1890
Loxepine has known human metabolites that include Loxepine N-glucuronide.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Oral-4 hours
SERUM LEVELS OF LOXAPINE & METABOLITES DECLINE IN BIPHASIC MANNER. HALF-LIFE DURING 1ST PHASE...5 HR...DURING 2ND PHASE...19 HR. /AFTER SINGLE 25 MG ORAL DOSE, SEDATIVE EFFECT BEGINS IN 20-30 MIN; PEAK EFFECT WITHIN 1.5-3 HR; DURATION APPROX 12 HR. HUMAN/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1976
Loxapine is a dopamine antagonist, and also a serotonin 5-HT2 blocker. The exact mode of action of Loxapine has not been established, however changes in the level of excitability of subcortical inhibitory areas have been observed in several animal species in association with such manifestations of tranquilization as calming effects and suppression of aggressive behavior.
STUDIES HAVE SHOWN THAT LOXAPINE PRODUCES SEDATION & PRONOUNCED EXTRAPYRAMIDAL REACTIONS, DECR CONVULSIVE THRESHOLD, & HAS ANTIADRENERGIC & ANTICHOLINERGIC EFFECTS. /SUCCINATE/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 447