


1. Mulpleta
1. 1110766-97-6
2. Mulpleta
3. S-888711
4. 6ll5jfu42f
5. Rsc888711
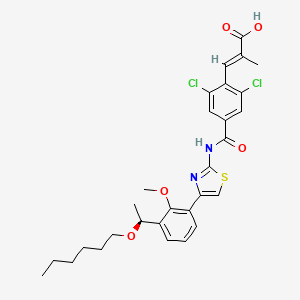
6. (e)-3-[2,6-dichloro-4-[[4-[3-[(1s)-1-hexoxyethyl]-2-methoxyphenyl]-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]carbamoyl]phenyl]-2-methylprop-2-enoic Acid
7. (s,e)-3-(2,6-dichloro-4-((4-(3-(1-(hexyloxy)ethyl)-2-methoxyphenyl)thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)phenyl)-2-methylacrylic Acid
8. (2e)-3-(2,6-dichloro-4-((4-(3-((1s)-1-(hexyloxy)ethyl)-2-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)phenyl)-2-methylprop-2-enoic Acid
9. Lusutrombopag [inn]
10. Unii-6ll5jfu42f
11. Lusutrombopag [usan:inn]
12. Mulpleta (tn)
13. 2-propenoic Acid, 3-(2,6-dichloro-4-(((4-(3-((1s)-1-(hexyloxy)ethyl)-2-methoxyphenyl)-2-thiazolyl)amino)carbonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl-, (2e)-
14. S 888711
15. Lusutrombopags-888711
16. Lusutrombopag [mi]
17. Lusutrombopag [jan]
18. Lusutrombopag [usan]
19. Lusutrombopag [who-dd]
20. Schembl3062080
21. Schembl3062084
22. Chembl2107831
23. Lusutrombopag (jan/usan/inn)
24. Gtpl10032
25. Chebi:136051
26. Dtxsid701027951
27. Lusutrombopag [orange Book]
28. 2-propenoic Acid, 3-[2,6-dichloro-4-[[[4-[3-[(1s)-1-(hexyloxy)ethyl]-2-methoxyphenyl]-2-thiazolyl]amino]carbonyl]phenyl]-2-methyl-, (2e)-
29. Ex-a1290
30. Mfcd28502075
31. S6988
32. Zinc84759273
33. Cs-6137
34. Db13125
35. Ncgc00522464-01
36. (2e)-3-(2,6-dichloro-4-((4-(3-((1s)-1-(hexyloxy)ethyl)- 2-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)carbamoyl)phenyl)-2-methylprop-2-enoic Acid
37. Ac-30601
38. As-52368
39. Hy-19883
40. J3.505.027b
41. D10476
42. A927042
43. S888711
44. Q27265116
45. (e)-3-[2,6-dichloro-4-[4-[3-[(s)-1-hexyloxyethyl]-2-methoxyphenyl]thiazol-2-ylcarbamoyl]phenyl]-2-methylacrylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 591.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H32Cl2N2O5S |
| XLogP3 | 7.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 13 |
| Exact Mass | 590.1408987 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 590.1408987 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 126 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 822 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Lusutrombopag is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a medical or dental procedure.
FDA Label
Mulpleo is indicated for the treatment of severe thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic liver disease undergoing invasive procedures
Treatment of thrombocytopenia secondary to liver disease
The AUC of lusutrombopag was found to correlate the increased platelet counts. Following administration of 3 mg daily dose in patients with chronic liver disease and thrombocytopenia, the mean (standard deviation) maximum platelet count in patients (N=74) without platelet transfusion was 86.9 (27.2) 10^9/L, and the median time to reach the maximum platelet count was 12.0 (5 to 35) days. Lusutrombopag was not shown to induce any clinically significant QTc prolongation at a dose 8 times the recommended dosage.
B02BX
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B02 - Antihemorrhagics
B02B - Vitamin k and other hemostatics
B02BX - Other systemic hemostatics
B02BX07 - Lusutrombopag
Absorption
Lusutrombopag is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. It exhibited a doseproportional pharmacokinetic profile over the single dose range of 1 mg to 50 mg, which was similar in both healthy subjects and those with chronic liver disease. A geometric mean (%CV) maximal concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC) in healthy subjects receiving 3 mg of lusutrombopag were 111 (20.4) ng/mL and 2931 (23.4) ng.hr/mL. The accumulation ratios of Cmax and AUC were approximately 2 with oncedaily multipledose administration, and steadystate plasma lusutrombopag concentrations were achieved after Day 5. The time to reach peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) were approximately 6 to 8 hours after oral administration in patients with chronic liver disease. Food consumption is not reported to affect the absorption and bioavailability of lusutrombopag.
Route of Elimination
About 1% of the administered dose of lusutrombopag undergoes urinary excretion. Fecal excretion accounted for 83% of the total dose, where 16% of the dose was excreted as unchanged parent compound.
Volume of Distribution
The mean (%CV) lusutrombopag apparent volume of distribution in healthy adult subjects was 39.5 (23.5) L.
Clearance
The approximate mean (%CV) clearance of lusutrombopag in patients with chronic liver disease is estimated to be 1.1 (36.1) L/hr.
CYP4 enzymes predominantly contribute to the metabolism of lusutrombopag, especially CYP4A11. Lusutrombopag is reported to mainly undergo - and -oxidation, as well as glucuronidation.
In healthy adult subjects, the terminal elimination halflife (t1/2) was approximately 27 hours.
Lusutrombopag mimics the biological actions of endogenous thrombopoietin (TPO) by acting as an agonist for the thrombopoietin receptor (TPOR) expressed on megakaryocytes. It binds to the transmembrane domain of the receptor and induces thrombocytopoiesis by targeting the same signal transduction system as that of endogenous TPO, which involves the activation of JAK and STAT pathways. It stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow progenitor cells into megakaryocytes, which undergoes maturation to act as precursor cells for platelets. A single megakaryocyte produces and releases thousands of platelets upon maturation and series of remodeling events. Lusutrombopag displays high specificity towards human TPORs when compared to murine TPORs. Lusutrombopag may affect other hematopoietic lineages as well, including erythroid, granulocytic and lymphoid lineages. One case of increased leukocyte and erythrocyte counts that prolonged for over 120 days was reported following administration in a patient with liver cirrhosis (LC) due to hepatitis C virus.