


1. Hydrochloride, Lymecycline
2. Lymecycline Hydrochloride
3. Lysine, Tetracycline-l-methylene
4. Lysine, Tetracyclinemethylene
5. N Lysinomethyltetracycline
6. N-lysinomethyltetracycline
7. Tetracycline L Methylene Lysine
8. Tetracycline-l-methylene Lysine
9. Tetracyclinemethylene Lysine
1. Tetralysal
2. N-lysinomethyltetracycline
3. Limeciclina
4. Lymecyclinum
5. Tetracycline-l-methylenelysine
6. Ciclolysal
7. Mucomycin
8. 992-21-2
9. Tetracycline-l-methylene Lysine
10. Ciclolysine
11. Tetracyclinemethylenelysine
12. Lymecycline (inn)
13. (+)-n-(5-amino-5-carboxypentylaminomethyl)-4-dimethylamino-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxonaphthacene-2-carboxamide
14. Tetralisal
15. 7d6em3s13p
16. N6-((4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamido)methyl)lysine
17. Chebi:59040
18. N(2)-(((+)-5-amino-5-carboxypentylamino)methyl)tetracycline
19. Lymecycline [inn]
20. L-lysine,n6-[[[[(4s,4as,5as,6s,12as)-4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenyl]carbonyl]amino]methyl]-
21. N(6)-[({[(4s,4as,5as,6s,12as)-4-(dimethylamino)-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracen-2-yl]carbonyl}amino)methyl]-l-lysine
22. Infaciclina
23. Lisinbiotic
24. Vebicyclysal
25. Ciclisin
26. Armyl
27. Tetraciclina-l-metilenlisina
28. (2s)-6-[[[(4s,4as,5as,6s,12ar)-4-(dimethylamino)-1,6,10,11,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-3,12-dioxo-4,4a,5,5a-tetrahydrotetracene-2-carbonyl]amino]methylamino]-2-aminohexanoic Acid
29. Lymecycline [inn:ban]
30. Lymecyclinum [inn-latin]
31. Limeciclina [inn-spanish]
32. Tetracycline, Lysinomethyl-
33. Unii-7d6em3s13p
34. Einecs 213-592-2
35. Tetraciclina-l-metilenlisina [italian]
36. Lymecycline (85%)
37. Lymecycline [mi]
38. Lymecycline [mart.]
39. Lymecycline [who-dd]
40. Schembl149162
41. Tetracycline-l Methylene-lysine
42. Chembl2103929
43. Schembl23248015
44. Gtpl10912
45. Lymecycline [ep Monograph]
46. N(sup 2)-(((+)-5-amino-5-carboxypentylamino)methyl)tetracycline
47. Zinc53682936
48. Akos016340328
49. Db00256
50. Ks-1366
51. 2-naphthacenecarboxamide, 4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-, Lysinemethylene Deriv.
52. D06884
53. Q897051
54. N2-(((+)-5-amino-5-carboxypentylamino)methyl)tetracycline
55. L-lysine, N6-(((((4s,4as,5as,6s,12as)-4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenyl)carbonyl)amino)methyl)-
56. L-lysine, N6-((((4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenyl)carbonyl)amino)methyl)-, (4s-(4alpha,4aalpha,6beta,12aalpha))-
57. Lysine, N(sup 6)-((4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamido)methyl)-, (+)-
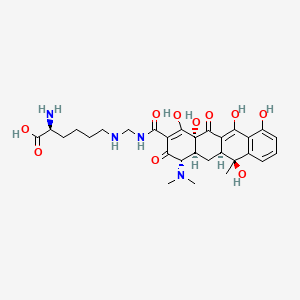
| Molecular Weight | 602.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H38N4O10 |
| XLogP3 | -4.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 13 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 602.25879342 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 602.25879342 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 243 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 43 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1230 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Lymecycline is used for the treatment of acne in addition to other susceptible infections; propionibacterium is often the cause of acne. Some of the infections that can be treated with lymecycline include upper respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, bronchitis, chlamydial infections, and rickettsial infections.
Lymecycline, like other tetracyclines, exerts bacteriostatic actions on intracellular and extracellular bacteria, treating susceptible bacterial infections. It has been shown to be safe and effective in the treatment of moderate to severe acne. It is important to note that like other tetracyclines, lymecycline may cause esophageal irritation and ulceration, which can be prevented by drinking adequate fluids during administration. It also has the potential to cause photosensitivity. Lymecycline can lead to renal tubular acidosis or hepatic toxicity. It is not recommended to administer this drug in patients with renal disease or severe hepatic disease.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01A - Tetracyclines
J01AA - Tetracyclines
J01AA04 - Lymecycline
Absorption
Lymecycline is 77-88% absorbed after oral administration with a relative bioavailability of 70%. The Cmax of lymecycline is 2.1 mg/L and is achieved about 3 hours after administration. The AUC is 21.9 4.3 mgh/L.
Route of Elimination
Lymecycline is 25% eliminated in the urine. Based on being a member of the tetracycline drug class, fecal elimination is likely another route of elimination.
Volume of Distribution
Lymecycline is lipophilic and easily crosses the cell membrane and passively diffuses through bacterial porin channels. As a second-generation tetracycline, the concentration in the bile ranges from 10 to 25 times higher than plasma concentration. In general, the volume of distribution of tetracyclines ranges from 1.31.7 L/kg or 100130 L.
Clearance
Lymecycline is partially cleared by the kidneys, like other tetracyclines.
The half-life of lymecycline is approximately 8 hours.
Normally, the ribosome synthesizes proteins through the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the mRNA-ribosome complex. Lymecycline binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit, preventing amino-acyl tRNA from binding to the A site of the ribosome, which prevents the elongation of polypeptide chains. This results in bacteriostatic actions, treating various infections.
