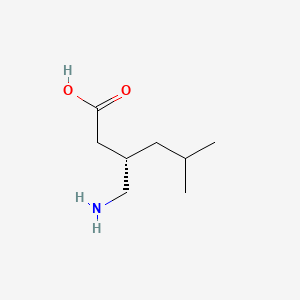

1. (r-)-3-isobutyl Gaba
2. (s)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic Acid
3. (s+)-3-isobutyl Gaba
4. 1008, Ci
5. 3 Isobutyl Gaba
6. 3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic Acid
7. 3-isobutyl Gaba
8. Ci 1008
9. Ci-1008
10. Ci1008
11. Gaba, 3-isobutyl
12. Lyrica
1. 148553-50-8
2. Lyrica
3. (s)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic Acid
4. 3-isobutyl Gaba
5. (3s)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic Acid
6. Ci-1008
7. (s)-pregabalin
8. Hexanoic Acid, 3-(aminomethyl)-5-methyl-, (3s)-
9. Vronogabic
10. Ci 1008
11. Pregabalin Mylan
12. Pregabalin Sandoz
13. Pd 144723
14. Pd-144723
15. Pregabalin Zentiva
16. Pregabalin Sandoz Gmbh
17. (s)-3-isobutyl Gaba
18. Chembl1059
19. Chebi:64356
20. (3s)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methyl-hexanoic Acid
21. 55jg375s6m
22. Ynp-1807
23. Nsc-759256
24. Hexanoic Acid, 3-(aminomethyl)-5-ethyl-, (3s)-
25. (r-)-3-isobutyl Gaba
26. Pregabalin [usan]
27. Hexanoic Acid, 3-(aminomethyl)-5-methyl-, (s)-
28. Pregabalina
29. Pregabaline
30. Nervalin
31. Pregablin
32. Unii-55jg375s6m
33. Hsdb 7530
34. Pregabalin [usan:inn:ban:jan]
35. Ncgc00095186-01
36. Pregabalin- Bio-x
37. Lyrica (tn)
38. Mfcd00917044
39. Lyrica Cr
40. Pregabalin [mi]
41. (s)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoicacid
42. Pregabalin [inn]
43. Pregabalin [jan]
44. Pregabalin [hsdb]
45. Pregabalin [vandf]
46. Pregabalin [mart.]
47. Schembl8227
48. Dsstox_cid_25950
49. Dsstox_rid_81246
50. Pregabalin [usp-rs]
51. Pregabalin [who-dd]
52. Dsstox_gsid_45950
53. Pregabalin (jan/usan/inn)
54. Pregabalin [ema Epar]
55. Pregabalin Mylan Pharma
56. (s)-(+)-4-amino-3-(2-methylpropyl)butanoic Acid
57. Gtpl5484
58. Zinc5152
59. Dea No. 2782
60. Pregabalin, >=97% (nmr)
61. Dtxsid1045950
62. Pregabalin [orange Book]
63. Pregabalin [ep Monograph]
64. Hms3715j16
65. Pregabalin [usp Monograph]
66. Pregabalin 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
67. Tox21_111475
68. Bdbm50164279
69. Akos001476611
70. Akos005145504
71. Lyrica;ci-1008;pd-144723
72. Ac-1158
73. Ccg-221247
74. Cs-1247
75. Db00230
76. Ks-5378
77. Nsc 759256
78. (s)-3-aminomethyl-5-methylhexanoic Acid
79. Ncgc00346738-01
80. 121ge001
81. Bp163672
82. Hy-17414
83. (s)-3-aminomethyl-5-methyl-hexanoic Acid
84. Am20080369
85. Cas-148553-50-8
86. P2840
87. En300-92104
88. (3s)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methyl Hexanoic Acid
89. (s)-(+)-3-aminomethyl-5-methylhexanoic Acid
90. D02716
91. Ab01563007_01
92. 553p508
93. A808784
94. Q412174
95. Sr-01000942257
96. Sr-01000942257-2
97. Pregabalin, Europepharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
98. Z2757554242
99. 1414928-41-8
| Molecular Weight | 159.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H17NO2 |
| XLogP3 | -1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 159.125928785 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 159.125928785 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 123 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lyrica |
| PubMed Health | Pregabalin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant, Neuropathic Pain Agent |
| Drug Label | Pregabalin is described chemically as (S)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. The molecular formula is C8H17NO2 and the molecular weight is 159.23. The chemical structure of pregabalin is:Pregabalin is a white to off-white, crystalline solid with... |
| Active Ingredient | Pregabalin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Solution |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 20mg/ml; 200mg; 25mg; 150mg; 300mg; 75mg; 100mg; 50mg; 225mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pf Prism; Cp Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pregabalin |
| PubMed Health | Pregabalin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant, Neuropathic Pain Agent |
| Drug Label | Pregabalin is described chemically as (S)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. The molecular formula is C8H17NO2 and the molecular weight is 159.23. The chemical structure of pregabalin is:Pregabalin is a white to off-white, crystalline solid with... |
| Active Ingredient | Pregabalin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Solution |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 20mg/ml; 200mg; 25mg; 150mg; 300mg; 75mg; 100mg; 50mg; 225mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Apotex; Lupin; Sandoz; Watson Labs; Actavis Elizabeth; Teva Pharms; Wockhardt Usa |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lyrica |
| PubMed Health | Pregabalin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant, Neuropathic Pain Agent |
| Drug Label | Pregabalin is described chemically as (S)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. The molecular formula is C8H17NO2 and the molecular weight is 159.23. The chemical structure of pregabalin is:Pregabalin is a white to off-white, crystalline solid with... |
| Active Ingredient | Pregabalin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Solution |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 20mg/ml; 200mg; 25mg; 150mg; 300mg; 75mg; 100mg; 50mg; 225mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pf Prism; Cp Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pregabalin |
| PubMed Health | Pregabalin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant, Neuropathic Pain Agent |
| Drug Label | Pregabalin is described chemically as (S)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. The molecular formula is C8H17NO2 and the molecular weight is 159.23. The chemical structure of pregabalin is:Pregabalin is a white to off-white, crystalline solid with... |
| Active Ingredient | Pregabalin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Solution |
| Route | oral; Oral |
| Strength | 20mg/ml; 200mg; 25mg; 150mg; 300mg; 75mg; 100mg; 50mg; 225mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms; Apotex; Lupin; Sandoz; Watson Labs; Actavis Elizabeth; Teva Pharms; Wockhardt Usa |
Pregabalin is indicated for management of post-herpetic neuralgia. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 2412
Pregabalin is indicated for management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. /Included in US product labe/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 2412
Pregabalin is indicated as an adjunctive therapy for adult patients with partial onset seizures. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007., p. 2412
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration ... has approved Lyrica (pregabalin), the first drug to treat fibromyalgia, a disorder characterized by pain, fatigue and sleep problems.
FDA; FDA News (P07-107). Available from, as of July 31, 2007: https://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/NEWS/2007/NEW01656.html
Known hypersensitivity to pregabalin or any ingredient in the formulation.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2247
Because of the possibility of increased seizure frequency, anticonvulsant drugs, including pregabalin, should be withdrawn gradually and dosage reduced slowly over at least 1 week. Abrupt discontinuance of pregabalin has been associated with insomnia, nausea, headache, and diarrhea.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2247
In controlled studies, blurred vision, which was reported in 6 or 2% of patients receiving pregabalin or placebo, respectively, resolved in the majority of cases with continued dosing; less than 1% of patients required discontinuance of the drug. In addition, decreased visual acuity was reported in 7 or 5% of patients receiving pregabalin or placebo, respectively, while visual field changes were detected in 13 or 12% of patients receiving the drug or placebo, respectively, and funduscopic changes were observed in 2% of patients receiving pregabalin or placebo. The clinical importance of these ophthalmologic findings has not been elucidated. If visual disturbance persists, further ocular assessment should be considered, while more frequent assessment is recommended in patients who already are monitored for ocular conditions.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2247
Weight gain, which was related to dosage and duration of exposure to pregabalin, has been reported in patients receiving pregabalin. Weight gain did not appear to be associated with baseline body mass index (BMI), gender, or age and was not limited to patients with edema.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2247
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PREGABALIN (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Pregabalin is indicated for the management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, fibromyalgia, neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury, and as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in patients 1 month of age and older.
FDA Label
* Neuropathic pain:
- Lyrica is indicated for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults.
* Epilepsy :
- Lyrica is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
* Generalised anxiety disorder:
- Lyrica is indicated for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults.
* Epilepsy :
Pregabalin Mylan Pharma is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
* Generalised Anxiety Disorder:
Pregabalin Mylan Pharma is indicated for the treatment of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) in adults.
* Neuropathic pain:
Pregabalin Mylan is indicated for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults.
* Epilepsy :
Pregabalin Mylan is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
* Generalised Anxiety Disorder:
Pregabalin Mylan is indicated for the treatment of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) in adults.
Neuropathic pain
- Pregabalin Pfizer is indicated for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults.
Epilepsy
- Pregabalin Pfizer is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
Generalised Anxiety Disorder
- Pregabalin Pfizer is indicated for the treatment of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) in adults.
* Neuropathic pain:
- Pregabalin Zentiva k. s. is indicated for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults.
* Epilepsy :
- Pregabalin Zentiva k. s. is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
* Generalised anxiety disorder:
- Pregabalin Zentiva k. s. is indicated for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults.
Epilepsy
- Pregabalin Accord is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
Generalised Anxiety Disorder
- Pregabalin Accord is indicated for the treatment of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) in adults.
* Neuropathic pain:
- Pregabalin Zentiva is indicated for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults.
* Epilepsy :
- Pregabalin Zentiva is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
* Generalised anxiety disorder:
- Pregabalin Zentiva is indicated for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) in adults.
* Epilepsy :
Pregabalin Sandoz GmbH is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
* Generalised Anxiety Disorder:
Pregabalin Sandoz GmbH is indicated for the treatment of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) in adults.
* Neuropathic pain:
Pregabalin Sandoz is indicated for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults.
* Epilepsy :
Pregabalin Sandoz is indicated as adjunctive therapy in adults with partial seizures with or without secondary generalisation.
* Generalised Anxiety Disorder:
Pregabalin Sandoz is indicated for the treatment of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) in adults.
Alleviation of acute anxiety and fear associated with transportation and veterinary visits.
Although the structure of pregabalin is similar to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it binds the alpha2-delta subunit of presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. Pregabalin does not modulate dopamine receptors, serotonin receptors, opiate receptors, sodium channels or cyclooxygenase activity.
Anti-Anxiety Agents
Agents that alleviate ANXIETY, tension, and ANXIETY DISORDERS, promote sedation, and have a calming effect without affecting clarity of consciousness or neurologic conditions. ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS are commonly used in the symptomatic treatment of anxiety but are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Anxiety Agents.)
Analgesics
Compounds capable of relieving pain without the loss of CONSCIOUSNESS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics.)
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
N03AX16
N03AX16
N03AX16
N03AX16
N03AX16
N03AX16
N03AX16
N03AX16
N03AX16
QN03AX16
N03AX16
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AX - Other antiepileptics
N03AX16 - Pregabalin
Absorption
After oral dosing administered in the fasted state, pregabalin absorption is rapid, and extensive. Pregabalin oral bioavailability is reported to be 90% regardless of the dose. Cmax is attained within 1.5 hours after single or multiple doses, and steady state is attained within 24-48 hours with repeated administration. Both Cmax and AUC appear to be dose proportional. Food decreases the rate of pregabalin absorption and as a result, lowers the Cmax by an estimated 25-30% and increases the Tmax to approximately 3 hours. However, the effect of food does not appear to impact the total absorption of pregabalin in a way that is clinically relevant. As a result, pregabalin can be administered with or without food.
Route of Elimination
Pregabalin is almost exclusively eliminated in the urine. Further, based on preclinical studies, pregabalin does not appear to undergo racemization to the R enantiomer in the body.
Volume of Distribution
After oral administration of pregabalin, the reported apparent volume of distribution is roughly 0.5 L/kg. Although pregabalin is not very lipophilic, it is able to cross the blood brain barrier(BBB). System L transporters facilitate the transport of large amino acids across the BBB and it has been confirmed that pregabalin is a substrate. This information suggests that system L transporters are responsible for pregabalin uptake into the BBB. In rat models, pregabalin has been shown to cross the placenta.
Clearance
In young healthy subjects the mean renal clearance is estimated to be 67.0 to 80.9 mL mL/min. Given pregabalin's lack of plasma protein binding, this clearance rate suggests that renal tubular reabsorption is involved.
Pregabalin is well absorbed after oral administration ...
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 2539
Following oral administration of pregabalin capsules under fasting conditions, peak plasma concentrations occur within 1.5 hours. Pregabalin oral bioavailability is >/=90% and is independent of dose. Following single- (25 to 300 mg) and multiple-dose (75 to 900 mg/day) administration, maximum plasma concentrations (C max ) and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) values increase linearly. Following repeated administration, steady state is achieved within 24 to 48 hours. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics can be predicted from single-dose data.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 2539
The rate of pregabalin absorption is decreased when given with food, resulting in a decrease in Cmax of approximately 25% to 30% and an increase in Tmax to approximately 3 hours. However, administration of pregabalin with food has no clinically relevant effect on the total absorption of pregabalin. Therefore, pregabalin can be taken with or without food.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 2539
Pregabalin does not bind to plasma proteins. The apparent volume of distribution of pregabalin following oral administration is approximately 0.5 L/kg. Pregabalin is a substrate for system L transporter which is responsible for the transport of large amino acids across the blood brain barrier. Although there are no data in humans, pregabalin has been shown to cross the blood brain barrier in mice, rats, and monkeys. In addition, pregabalin has been shown to cross the placenta in rats and is present in the milk of lactating rats.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 2539
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PREGABALIN (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Less than 2% of pregabalin is metabolized and it is excreted virtually unchanged in the urine.
Pregabalin undergoes negligible metabolism in humans. Following a dose of radiolabeled pregabalin, approximately 90% of the administered dose was recovered in the urine as unchanged pregabalin. The N-methylated derivative of pregabalin, the major metabolite of pregabalin found in urine, accounted for 0.9% of the dose. In preclinical studies, pregabalin (S-enantiomer) did not undergo racemization to the R-enantiomer in mice, rats, rabbits, or monkeys.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 2540
The elimination half life of pregabalin is 6.3 hours.
Pregabalin is eliminated from the systemic circulation primarily by renal excretion as unchanged drug with a mean elimination half-life of 6.3 hours in subjects with normal renal function.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 2540
Although the mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated, studies involving structurally related drugs suggest that presynaptic binding of pregabalin to voltage-gated calcium channels is key to the antiseizure and antinociceptive effects observed in animal models. By binding presynaptically to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, pregabalin modulates the release of several excitatory neurotransmitters including glutamate, substance-P, norepinephrine, and calcitonin gene related peptide. In addition, pregabalin prevents the alpha2-delta subunit from being trafficked from the dorsal root ganglia to the spinal dorsal horn, which may also contribute to the mechanism of action. Although pregabalin is a structural derivative of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not bind directly to GABA or benzodiazepine receptors.
Pregabalin is an anticonvulsant that is structurally related to the inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Pregabalin also has demonstrated analgesic activity. Although pregabalin was developed as a structural analog of GABA, the drug does not bind directly to GABA-A, GABA-B, or benzodiazepine receptors; does not augment GABA-A responses in cultured neurons; and does not alter brain concentrations of GABA in rats or affect GABA uptake or degradation. However, in cultured neurons, prolonged application of pregabalin increases the density of GABA transporter protein and increases the rate of functional GABA transport.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2248
Pregabalin binds with high affinity to the alpha2-delta site (an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels) in CNS tissues. ... In vitro, pregabalin reduces the calcium-dependent release of several neurotransmitters, including glutamate, norepinephrine, and substance P, possibly by modulation of calcium channel function.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2248
Pregabalin does not block sodium channels, is not active at opiate receptors, and does not alter cyclooxygenase enzyme activity. It is inactive at serotonin and dopamine receptors and does not inhibit dopamine, serotonin, or noradrenaline reuptake.
Physicians Desk Reference 61st ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2007., p. 2539
Pregabalin is a potent ligand for the alpha-2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system that exhibits potent anticonvulsant, analgesic, and anxiolytic activity in a range of animal models. ... Potent binding to the alpha-2-delta site reduces depolarization-induced calcium influx with a consequential modulation in excitatory neurotransmitter release. Pregabalin has no demonstrated effects on GABAergic mechanisms. ...
PMID:15315511 Ben-Menachem E; Epilepsia 45 Suppl 6: 13-8 (2004)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for PREGABALIN (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.