
1. Act 064992
2. Act-064992
3. Act064992
4. Actelion-1
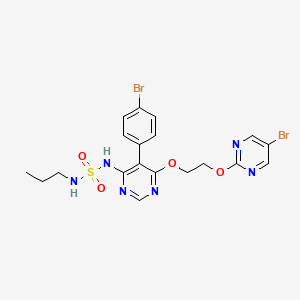
5. N-(5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-(2-(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yloxy)ethoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)-n'-propylaminosulfonamide
6. Opsumit
1. 441798-33-0
2. Opsumit
3. Act-064992
4. Act 064992
5. N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-n'-propylsulfamide
6. Act064992
7. Z9k9y9wmvl
8. 5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-[2-(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxyethoxy]-n-(propylsulfamoyl)pyrimidin-4-amine
9. N-(5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-(2-((5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy)ethoxy)-4-pyrimidinyl)-n'-propylsulfamide
10. Chebi:76607
11. Actelion-1
12. Macitentan [inn]
13. N-(5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-(2-((5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxy)ethoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)-n'-propylsulfamide
14. N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-{2-[(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]ethoxy}pyrimidin-4-yl]-n'- Propylsulfamide
15. Macitentan [usan:inn]
16. Unii-z9k9y9wmvl
17. Macitentanum
18. Sulfamide, N-(5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-(2-((5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy)ethoxy)-4-pyrimidinyl)-n'-propyl-
19. Sulfamide, N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-n'-propyl-
20. Macitentan- Bio-x
21. Opsumit (tn)
22. Macitentan [mi]
23. Macitentan [jan]
24. Macitentan (jan/usan)
25. Macitentan [usan]
26. Macitentan [vandf]
27. (non-labelled)macitentan-d7
28. Macitentan [who-dd]
29. Mls006011174
30. Gtpl7352
31. Schembl1445625
32. Chembl2103873
33. Macitentan [orange Book]
34. Dtxsid50196063
35. Ex-a544
36. Hms3653n06
37. Hms3747e09
38. Cas:441798-33-0;macitentan
39. Bcp05309
40. Bdbm50395626
41. Mfcd17167076
42. S8051
43. Zinc43202140
44. Akos024463406
45. Am81244
46. Ccg-270155
47. Cs-0686
48. Db08932
49. Sb14841
50. Macitentan (actelion-1,act-064992)
51. Ncgc00346456-01
52. Ncgc00346456-05
53. Ac-30102
54. As-74590
55. Bm162771
56. Hy-14184
57. N-(5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-(2-(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yloxy)ethoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)-n'-propylaminosulfonamide
58. Smr004702943
59. Db-070519
60. Ft-0696675
61. Sw219473-1
62. Act 064992; Act-064992
63. D10135
64. Q6724151
65. {[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-{2-[(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]ethoxy}pyrimidin-4-yl]sulfamoyl}(propyl)amine
66. N-(5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-(2-((5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxi)ethoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)-n'-propylsulfuric Diamide
67. N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)-oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-n'-propylsulfamide
68. N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-n'-propyl-sulfamide
69. N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-{2-[(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]ethoxy}pyrimidin-4-yl]-n'-propylsulfuric Diamide
| Molecular Weight | 588.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H20Br2N6O4S |
| XLogP3 | 3.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 587.96130 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 585.96335 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 137 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 642 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Opsumit |
| PubMed Health | Macitentan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive |
| Drug Label | OPSUMIT (macitentan) is an endothelin receptor antagonist. The chemical name of macitentan is N-[5-(4-Bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-N'-propylsulfamide. It has a molecular formula of C19H20Br2N6O4S and a molecula |
| Active Ingredient | Macitentan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actelion Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Opsumit |
| PubMed Health | Macitentan (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antihypertensive |
| Drug Label | OPSUMIT (macitentan) is an endothelin receptor antagonist. The chemical name of macitentan is N-[5-(4-Bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-N'-propylsulfamide. It has a molecular formula of C19H20Br2N6O4S and a molecula |
| Active Ingredient | Macitentan |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Actelion Pharms |
Investigated for use/treatment in cardiovascular disorders, hypertension, and pulmonary hypertension.
Macitentan is indicated for the treatment of WHO group 1 pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) both alone and in combination with tadalafil.
FDA Label
Opsumit, as monotherapy or in combination, is indicated for the long-term treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in adult patients of WHO Functional Class (FC) II to III.
Efficacy has been shown in a PAH population including idiopathic and heritable PAH, PAH associated with connective tissue disorders, and PAH associated with corrected simple congenital heart disease.
Treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH)
Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension, Treatment of systemic sclerosis
Treatment of functional single ventricle heart disease with total cavo-pulmonary connection
Macitentan acts primarily by reducing vasoconstriction and cell proliferation due to endothelin overexpression.
Endothelin A Receptor Antagonists
Compounds and drugs that bind to and inhibit or block the activation of ENDOTHELIN A RECECPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Endothelin A Receptor Antagonists.)
Endothelin B Receptor Antagonists
Compounds and drugs that bind to and inhibit or block the activation of ENDOTHELIN B RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Endothelin B Receptor Antagonists.)
C02KX04
C02KX04
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C02 - Antihypertensives
C02K - Other antihypertensives
C02KX - Antihypertensives for pulmonary arterial hypertension
C02KX04 - Macitentan
Absorption
Macitentan has a median Tmax of 8h although some studies have found up to 30h at higher doses. Although the bioavailability has not been experimentally determined, pharmacokinetic modeling has estimated it at 74%. Food has not been found to have a significant effect on absorption.
Route of Elimination
Eliminated 50% through urine and 24% through feces. Of the 50% excreted through the urine, none of the recovered dose was in the form of the parent drug nor the active metabolite.
Volume of Distribution
Macitentan has an apparent volume of distribution of 40-50L.
Clearance
Clearance data was not found.
Macitentan undergoes oxidative depropylation of the sulfonamide moiety via CYP3A4, 2C8, 2C9, and 2C19 to form the active metabolite M6. The ethylene glycol moiety undergoes oxidative cleavage via CYP2C9 to the alcohol metabolite M4. M4 is oxidized to its corresponding acid, M5, then hydrolyzed to the metabolite termed m/z 324. Oxidative depropylation of a distal carbon atom via CYP2C8, 2C9, and 2C19 forms M7. Hydrolysis of both macitentan and M5 produces M3. Finally M5 may be further metabolized via hydrolysis and hydroxylation to M2 or via glucuronidation to a glucuronide metabolite, M1.
The half-life of elimination of macitentan is 16 hours. The half-life of elimination of the active metabolite is 40-66h
Through complete blockade of tissular endothelin, Actelion-1 is expected to protect tissue from the damaging effect of elevated endothelin, specifically in the cardiovascular system. In pre-clinical studies, Actelion-1 also exhibited effects suggesting that it maintains the integrity of the vascular wall and improves long-term outcome. Accordingly, Actelion-1 may provide therapeutic benefit in a wide range of cardiovascular indications.
Macitentan is an antagonist which binds to the endothelin A and B receptors (EA and EB) and blocks signaling from endothelin-1 and -2. Pulmonary arterial hypertension has many different mechanisms which contribute to the development of endothelial dysfunction including elevated cytosolic calcium, genetic factors, epigenetic changes, and mitochondrial dysfunction. The focus of macitentan's mechanism relates to the role of overexpressed endothelin from the vascular endothelium. Endothelins are released in both a constitutive fashion from secretory vesicles and in response to stimuli via Weibel-Palade storage granules. Endothelins bind to the EA and EB receptors, with endothelins -1 and -2 having more affinity than endothelin-3. Binding to the Gq coupled EA receptor triggers Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of smooth muscle cells via the phospholipase C (PLC) pathway. Downstream protein kinase C activation may also contribute to increased Ca2+ sensitivity of the contractile apparatus. EA receptor activation is also known to contribute to pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation. The binding of endothelins to the EB receptors acts in opposition to EA signaling by activating the same PLC cascade in endothelial cells to activate endothelial nitric oxide synthase. The subsequent release of nitric oxide produces vasodilation through the cyclic guanosine monophosphate cascade. Despite the greater presence of EB receptors on endothelial cells, they are still present on smooth muscle cells and may contribute to cell proliferation through the same mechanisms as EA receptors. Macitentan is thought to provide its therapeutic effect primarily via blocking signaling through EA which produces both decreased vasoconstriction via reduced smooth muscle cell contractility and attenuation of the hyperproliferation of smooth muscle cells found in PAH. Blockade of EB is less likely to contribute to a therapeutic effect as this signaling is responsible for the counter-regulatory vasodilatory signal.