
1. Heptahydrate Magnesium Sulfate
2. Magnesium Sulfate, Heptahydrate
3. Sulfate, Magnesium
1. 7487-88-9
2. Magnesium Sulphate
3. Magnesium Sulfate Anhydrous
4. Mgso4
5. Sulfuric Acid Magnesium Salt (1:1)
6. Magnesium Sulfate (1:1)
7. Magnesiumsulfat
8. Magnesiumsulfate
9. Magnesium Sulfate, Anhydrous
10. Sulfuric Acid Magnesium Salt
11. Magnesium(ii) Sulfate
12. Magnesium;sulfate
13. Magnesium Sulphate Anhydrous
14. Sulfato De Magnesio
15. Chebi:32599
16. Mfcd00011110
17. Magnesium Sulfate,anhydrous
18. Ml30mj2u7i
19. Magnesium Sulphate, Anhydrous
20. Magnesium Sulfate Anhydrous
21. Sulfuric Acid, Mono-c10-16-alkyl Esters, Magnesium Salts
22. Sal Angalis
23. Sal De Sedlitz
24. Tomix Ot
25. 139939-75-6
26. Ot-s (drying Agent)
27. Ot-s
28. 68081-97-0
29. Sulfuric Acid Magnesiumsalt (1:1), Hydrate (8ci,9ci)
30. Caswell No. 534
31. Magnesii Sulfas
32. Magnesii Sulfas; Magnesium Sulfate; Magnesium Sulphate; Mg-ok; Ot-s
33. Anhydrous Magnesium Sulfate
34. Sulfuric Acid Magnesium Salt (van)
35. Arrosalt 2327
36. Hsdb 664
37. Einecs 231-298-2
38. Unii-ml30mj2u7i
39. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 050503
40. Magnesium Sulfate In Plastic Container
41. Nsc 146179
42. Magnesium Sulfate, Unspecified
43. Sda 15-062-07
44. Ccris 8411
45. Sn 00
46. Einecs 242-691-3
47. Einecs 268-365-0
48. Sulfuric Acid, C10-16 Alkyl Ester, Magnesium Salt
49. Sulphate Of Magnesia
50. (c10-c16) Alkylalcohol Sulfuric Acid, Magnesium Salt
51. Magnesium Sulfate In Dextrose 5% In Plastic Container
52. Ai3-02029
53. Epitope Id:158536
54. Ec 231-298-2
55. C10-c16 Alkyl Alcohol Sulfuric Acid Magnesium Salt
56. Magnesium Sulfate [mi]
57. Chembl2021423
58. Dtxsid6042105
59. Magnesium Sulfate [hsdb]
60. Magnesium Sulfate, Anhydrous Powder
61. Magnesium Sulfate, Anhydrous Granular
62. Akos015902894
63. Db00653
64. Magnesium Sulfate, 1m Aqueous Solution
65. Magnesium Sulfate Anhydrous [ii]
66. 18939-43-0
67. Magnesium Sulfate,anhydrous [vandf]
68. Ft-0628097
69. M1890
70. Magnesium Sulfate Anhydrous [orange Book]
71. Magnesium Sulfate Heptahydrate Solution, 2.25%
72. Magnesium Sulfate, 1m Aqueous Solution, Sterile
73. Magnesium Sulfate Anhydrous [usp Monograph]
74. Q288266
75. Sr-01000944338
76. J-014575
77. J-519590
78. Sr-01000944338-1
79. Magnesium Sulfate, Anhydrous Powder Trace Metals Grade, 99.95%
80. Magnesium Sulfate, Anhydrous Granular Trace Metals Grade, 99.95%
81. Suprep Bowel Prep Kit Component Magnesium Sulfate Anhydrous
82. Magnesium Sulfate Anhydrous Component Of Suprep Bowel Prep Kit
| Molecular Weight | 120.37 g/mol |
|---|---|
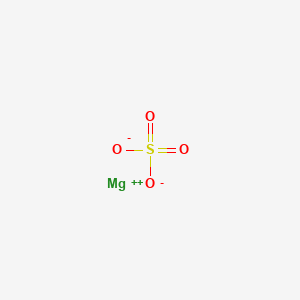
| Molecular Formula | MgO4S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 119.9367713 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 119.9367713 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 88.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 62.2 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Magnesium sulfate |
| PubMed Health | Magnesium Sulfate |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Anticonvulsant, Laxative, Laxative, Hyperosmotic, Parenteral Mineral-Trace Mineral, Renal-Urologic Agent |
| Drug Label | Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate in water for injection. May contain sulfuric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. The pH is 4.5 (3.5 to 6.5). It is available in... |
| Active Ingredient | Magnesium sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira; Fresenius Kabi Usa |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Magnesium sulfate in plastic container |
| Active Ingredient | Magnesium sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 4gm/100ml (40mg/ml); 4gm/50ml (80mg/ml); 2gm/50ml (40mg/ml); 20gm/500ml (40mg/ml); 40gm/1000ml(40mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Magnesium sulfate |
| PubMed Health | Magnesium Sulfate |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Anticonvulsant, Laxative, Laxative, Hyperosmotic, Parenteral Mineral-Trace Mineral, Renal-Urologic Agent |
| Drug Label | Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate in water for injection. May contain sulfuric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. The pH is 4.5 (3.5 to 6.5). It is available in... |
| Active Ingredient | Magnesium sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira; Fresenius Kabi Usa |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Magnesium sulfate in plastic container |
| Active Ingredient | Magnesium sulfate |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 4gm/100ml (40mg/ml); 4gm/50ml (80mg/ml); 2gm/50ml (40mg/ml); 20gm/500ml (40mg/ml); 40gm/1000ml(40mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
Analgesics; Anesthetics; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Anticonvulsants; Calcium Channel Blockers; Cathartics; Tocolytic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
AN EFFECTIVE & WIDELY EMPLOYED SALINE CATHARTIC. /HEPTAHYDRATE, USP/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 743
FULL DOSES OF SALINE CATHARTICS (15 G MAGNESIUM SULFATE OR ITS EQUIVALENT) PRODUCE A SEMIFLUID OR WATERY EVACUATION IN 3 HR OR LESS. LOW DOSES PRODUCE A LAXATIVE EFFECT WITH GREATER LATENCY.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1005
A COLD, WET COMPRESS OF MAGNESIUM SULFATE SOLN IN WATER HAS BEEN EMPLOYED IN TREATMENT OF SUCH SKIN DISORDERS AS ERYSIPELAS. HOT CONCN AQ SOLN...(ABOUT 1 LB/PINT OF WATER) ARE SOMETIMES USED IN TREATMENT OF DEEP-SEATED INFECTIONS, CLOTHS BEING SATURATED & APPLIED WHILE HOT. ACTION MUCH LIKE THAT OF POULTICE. /HEPTAHYDRATE/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 743
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for MAGNESIUM SULFATE (32 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
SOME ABSORPTION OF COMPONENT IONS OF SALINE CATHARTICS DOES OCCUR, & IN CERTAIN INSTANCES THEY MAY PRODUCE SYSTEMIC TOXICITY. IN AN INDIVIDUAL WITH IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION, ACCUM OF MAGNESIUM IONS IN BODY FLUIDS MAY BE SUFFICIENT TO CAUSE INTOXICATION. MAGNESIUM CATHARTICS SHOULD BE ADMIN ONLY IF RENAL FUNCTION IS ADEQUATE.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1005
THE DRUG IS GENERALLY SAFE BUT CAN CAUSE TEMPORARY LOSS OF DEEP TENDON REFLEXES IN MOTHER & MAY SUPPRESS SKELETAL MUSCLE ACTIVITY IN NEONATE. IT SHOULD NOT BE USED IN PT WITH HEART DISEASE...
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations. 4th ed. Chicago: American Medical Association, 1980., p. 798
NEONATE MAY BE DROWSY & EXHIBIT RESP DIFFICULTIES & DIMINISHED MUSCLE TONE. HOWEVER...NO RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PLASMA MAGNESIUM CONCN OF BLOOD COLLECTED FROM UMBILICAL CORD & THE APGAR SCORE /HAS BEEN FOUND/.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 882
Patients receiving parenteral magnesium sulfate shold be observed carefully, and serum magnesium concn should be monitored to avoid overdosage. ... An IV preparation of a calcium salt (e.g., calcium gluconate) should be readily available for use when magnesium sulfate is given IV. /Magnesium sulfate injection/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2163
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for MAGNESIUM SULFATE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used for immediate control of life-threatening convulsions in the treatment of severe toxemias (pre-eclampsia and eclampsia) of pregnancy and in the treatment of acute nephritis in children. Also indicated for replacement therapy in magnesium deficiency, especially in acute hypomagnesemia accompanied by signs of tetany similar to those of hypocalcemia. Also used in uterine tetany as a myometriat relaxant.
Magnesium sulfate is a small colorless crystal used as an anticonvulsant, a cathartic, and an electrolyte replenisher in the treatment of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. It causes direct inhibition of action potentials in myometrial muscle cells. Excitation and contraction are uncoupled, which decreases the frequency and force of contractions. Magnesium sulfate is gaining popularity as an initial treatment in the management of various dysrhythmias, particularly torsades de pointes, and dyrhythmias secondary to TCA overdose or digitalis toxicity.
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Analgesics
Compounds capable of relieving pain without the loss of CONSCIOUSNESS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics.)
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
Tocolytic Agents
Drugs that prevent preterm labor and immature birth by suppressing uterine contractions (TOCOLYSIS). Agents used to delay premature uterine activity include magnesium sulfate, beta-mimetics, oxytocin antagonists, calcium channel inhibitors, and adrenergic beta-receptor agonists. The use of intravenous alcohol as a tocolytic is now obsolete. (See all compounds classified as Tocolytic Agents.)
Anesthetics
Agents capable of inducing a total or partial loss of sensation, especially tactile sensation and pain. They may act to induce general ANESTHESIA, in which an unconscious state is achieved, or may act locally to induce numbness or lack of sensation at a targeted site. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A06 - Drugs for constipation
A06A - Drugs for constipation
A06AD - Osmotically acting laxatives
A06AD04 - Magnesium sulfate
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A12 - Mineral supplements
A12C - Other mineral supplements
A12CC - Magnesium
A12CC02 - Magnesium sulfate
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B05 - Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions
B05X - I.v. solution additives
B05XA - Electrolyte solutions
B05XA05 - Magnesium sulfate
D - Dermatologicals
D11 - Other dermatological preparations
D11A - Other dermatological preparations
D11AX - Other dermatologicals
D11AX05 - Magnesium sulfate
V - Various
V04 - Diagnostic agents
V04C - Other diagnostic agents
V04CC - Tests for bile duct patency
V04CC02 - Magnesium sulfate
Route of Elimination
Magnesium is excreted solely by the kidney at a rate proportional to the serum concentration and glomerular filtration.
Magnesium sulfate is excreted by the kidneys at a rate that varies from one patient to another but that is directly proportional to the serum concn and glomerular filtration.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2164
PLASMA CONCN OF MAGNESIUM INCR IN FETUS & APPROACH MATERNAL BLOOD VALUES AFTER MAGNESIUM SULFATE ADMIN IN ECLAMPSIA & PREECLAMPSIA.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 882
None
43.2 hours (for newborns)
Magnesium is the second most plentiful cation of the intracellular fluids. It is essential for the activity of many enzyme systems and plays an important role with regard to neurochemical transmission and muscular excitability. Magnesium sulfate reduces striated muscle contractions and blocks peripheral neuromuscular transmission by reducing acetylcholine release at the myoneural junction. Additionally, Magnesium inhibits Ca2+ influx through dihydropyridine-sensitive, voltage-dependent channels. This accounts for much of its relaxant action on vascular smooth muscle.
CATHARTIC ACTION RESULTS FROM FACT THAT MGSO4 IS NOT ABSORBED FROM INTESTINAL TRACT, & THUS RETAINS SUFFICIENT WATER WITHIN LUMEN OF BOWEL TO MAKE AN ISOTONIC SOLN. IN EVENT...SALT IS GIVEN IN HYPERTONIC SOLN, SOURCE OF WATER WOULD BE BODY FLUIDS, &...DEHYDRATING ACTION IS EXERTED. /HEPTAHYDRATE, USP/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 743
EXACT MECHANISM OF.../CNS/ DEPRESSANT ACTIVITY IS NOT FULLY KNOWN; HOWEVER, EXCESS MAGNESIUM APPEARS TO DECR AMT OF ACETYLCHOLINE LIBERATED BY MOTOR NERVE IMPULSE. /HEPTAHYDRATE INJECTION USP/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2163
Isolated myometrial strips were obtained from humans undergoing elective cesarean section at term pregnancy and Wistar albino rats on gestational days 19-21. These strips were mounted in organ baths for recording of isometric tensions. The effect of magnesium sulfate, isradipine, and ritodrine on the amplitude and frequency of spontaneous contractions was compared. ... Ritodrine (10-8-10-5 M) concentration-dependently inhibited the frequency and amplitude of spontaneous contractions of myometrial strips. At 10-4 M, tachyphylaxis of ritodrine occurred and contractions started again. Magnesium sulfate (10-7-10-4 M) inhibited the frequency but did not change the amplitude of the spontaneous contractions. Isradipine (10-7-10-4 M) had a concentration-related inhibitor effect on both the frequency and amplitude of the spontaneous contractions. The effects of magnesium sulfate, isradipine, and ritodrine were considerably similar in myometrium strips obtained from pregnant rats and humans. ...
PMID:12225296 Kantas E, et al; Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 81(9): 825-830 (2002)