
1. Carbafos
2. Carbofos
3. Carbophos
4. Cythion
5. Karbofos
6. Prioderm
7. Sadophos
1. 121-75-5
2. Carbophos
3. Carbofos
4. Mercaptothion
5. Karbofos
6. Phosphothion
7. Carbetox
8. Ethiolacar
9. Maldison
10. Prioderm
11. Sadophos
12. Cythion
13. Oleophosphothion
14. Ovide
15. Chemathion
16. Sadofos
17. Carbetovur
18. Fosfothion
19. Fosfotion
20. Malagran
21. Malakill
22. Malaphos
23. Malaspray
24. Malathon
25. Moscarda
26. Cimexan
27. Fyfanon
28. Malafor
29. Malamar
30. Malatol
31. Malatox
32. Malphos
33. Sumitox
34. Taskil
35. Etiol
36. Emmatos Extra
37. Ortho Malathion
38. Siptox I
39. Extermathion
40. Forthion
41. Hilthion
42. Malacide
43. Malation
44. Mercaptotion
45. Kypfos
46. Malasol
47. Malathion E50
48. Malmed
49. Carbethoxy Malathion
50. Malamar 50
51. Kop-thion
52. Compound 4049
53. Insecticide No. 4049
54. Detmol Ma
55. Malathione
56. Emmatos
57. Malataf
58. Malathyl
59. Fosfotion 550
60. Malathion Lv Concentrate
61. Zithiol
62. Staeubol-puder
63. American Cyanamid 4,049
64. Mercaptosuccinic Acid Diethyl Ester
65. Latka 4049
66. Sf 60
67. Diethyl 2-dimethoxyphosphinothioylsulfanylbutanedioate
68. Experimental Insecticide 4049
69. Tm-4049
70. Nci-c00215
71. Ac 26691
72. Diethyl (dimethoxyphosphinothioylthio)succinate
73. Ent 17,034
74. El 4049
75. Four Thousand Forty-nine
76. O,o-dimethyldithiophosphate Diethylmercaptosuccinate
77. 8059hc
78. Dicarboethoxyethyl O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
79. O,o-dimethyl S-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) Dithiophosphate
80. Nsc-6524
81. Mlt
82. Butanedioic Acid, ((dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio)-, Diethyl Ester
83. S-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) O,o-dimethyldithiophosphate
84. Succinic Acid, Mercapto-, Diethyl Ester, S-ester With O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
85. O,o-dimethyl S-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl)phosphorodithioate
86. S-1,2-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl-o,o-dimethyl Thiophosphate
87. U5n7su872w
88. Calmathion
89. Cleensheen
90. Malathiazol
91. Camathion
92. Celthion
93. Dorthion
94. O,o-dimethyl S-1,2-di(ethoxycarbamyl)ethyl Phosphorodithioate
95. Flair
96. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate, O,o-dimethyl Dithiophosphate, S-ester
97. S-(1,2-di(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl) Dimethyl Phosphorothiolothionate
98. O,o-dimethyl-s-1,2-dikarbetoxylethylditiofosfat
99. Diethyl 2-[(dimethoxyphosphorothioyl)thio]succinate
100. Ent-17034
101. Kill-a-mite
102. Malation [polish]
103. O,o-dwumetylo-s-1,2-bis(karboetoksyetylo)-dwutiofosforan
104. S-(1,2-bis(carbethoxy)ethyl) O,o-dimethyl Dithiophosphate
105. Ncgc00091902-05
106. Ncgc00091902-08
107. Malathiozoo
108. ((dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio)butanedioic Acid Diethyl Ester
109. Malaphele
110. Organoderm
111. S-(1,2-bis(etossi-carbonil)-etil)-o,o-dimetil-ditiofosfato
112. Maltox
113. Vetiol
114. S-(1,2-bis(ethoxy-carbonyl)-ethyl)-o,o-dimethyl-dithiofosfaat
115. Vegfru Malatox
116. Butanedioic Acid, [(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio]-, Diethyl Ester
117. Dithiophosphate De O,o-dimethyle Et De S-(1,2-dicarboethoxyethyle)
118. Dsstox_cid_791
119. S-(1,2-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl) O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
120. Mercaptotion [spanish]
121. Derbac-m
122. Hilthion 25wdp
123. Maltox Mlt
124. Diethyl 2-(dimethoxyphosphinothioylthio)succinate
125. Dsstox_rid_75791
126. Succinic Acid, Mercapto-, Diethyl Ester, S-ester With O,o-dimethylphosphorodithioate
127. Dsstox_gsid_20791
128. Latka 4049 [czech]
129. Sadofos 30
130. Kop-thionkypfosmalacide
131. Fog 3
132. [(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio]butanedioic Acid Diethyl Ester
133. Malathyne
134. [(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio]butanedioic Acid, Diethyl Ester
135. S-(1,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
136. S-[1,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
137. Malathion (usp)
138. Oms 1
139. Ifo 13140
140. Cas-121-75-5
141. Ccris 368
142. Hsdb 665
143. Ovide (tn)
144. Malathion [usp:ban]
145. Malathion ,s-(1,2-dicarbethoxyl)
146. Einecs 204-497-7
147. Brn 1804525
148. S-[1,2-bis(carbethoxy)ethyl] O,o-dimethyl Dithiophosphate
149. Unii-u5n7su872w
150. Gammaxine
151. Radotion
152. Ai3-17034
153. S-[1,2-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl] O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
154. Diethyl(dimethoxythiophosphorylthio)succinate
155. Malathion Ulv
156. Suleo M
157. Diethyl ((dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio)butanedioate
158. Phosphorodithioic Acid, O,o-dimethyl Ester, S-ester With Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate
159. O,o-dimethyl-s-1,2-dikarbetoxylethylditiofosfat [czech]
160. S-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) O,o-dimethylphosphorodithioate
161. Spectrum_001795
162. Specplus_000386
163. Malathion [mi]
164. O,o-dimethyl S-(1,2-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl) Dithiophosphate
165. Malathion [hsdb]
166. Malathion [iarc]
167. O,o-dimethyl-s-1,2-(dicarbaethoxyaethyl)-dithiophosphat [german]
168. O,o-dwumetylo-s-1,2-bis(karboetoksyetylo)-dwutiofosforan [polish]
169. Spectrum2_001228
170. Spectrum3_000813
171. Spectrum4_000653
172. Spectrum5_001936
173. Malathion [vandf]
174. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate S-ester With O,o-dimethylphosphorodithioate
175. S-(1,2-bis(ethoxy-carbonyl)-ethyl)-o,o-dimethyl-dithiofosfaat [dutch]
176. S-(1,2-bis(etossi-carbonil)-etil)-o,o-dimetil-ditiofosfato [italian]
177. Malathion [mart.]
178. Dithiophosphate De O,o-dimethyle Et De S-(1,2-dicarboethoxyethyle) [french]
179. S-(1,2-bis(aethoxy-carbonyl)-aethyl)-o,o-dimethyl-dithiophosphat [german]
180. Malathion [usp-rs]
181. Malathion [who-dd]
182. Schembl27358
183. Bspbio_002305
184. Kbiogr_001025
185. Kbioss_002288
186. S-(1,o-dimetil-ditiofosfato
187. S-1,o-dimethyl Thiophosphate
188. Divk1c_006482
189. Malathion, Analytical Standard
190. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate, O,o-dimethyl Thiophosphate
191. Spbio_001076
192. S-(1,o-dimethyl-dithiofosfaat
193. 1,o-dimethyl Phosphordithioates
194. Chebi:6651
195. Malathion [orange Book]
196. O,2-dikarbetoxylethylditiofosfat
197. S-(1,o-dimethyl-dithiophasphat
198. Chembl1200468
199. Dtxsid4020791
200. Malathion [ep Monograph]
201. O,o-dimethyl-s-1,2-(dicarbaethoxyaethyl)-dithiophosphat
202. Bdbm85372
203. Jxsjbgjigxnwci-uhfffaoysa-
204. Kbio1_001426
205. Kbio2_002286
206. Kbio2_004854
207. Kbio2_007422
208. Kbio3_001805
209. S-[1,o-dimethyl Dithiophosphate
210. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate, O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
211. Malathion [usp Monograph]
212. Nsc6524
213. Chebi:141474
214. 1,2-di(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
215. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinic Acid O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
216. Hms3264a04
217. Pharmakon1600-00330021
218. Hy-b0943
219. S-(1,2-bis(aethoxy-carbonyl)-aethyl)-o,o-dimethyl-dithiophosphat
220. Malathion 100 Microg/ml In Nonane
221. Tox21_111175
222. Tox21_400048
223. Ccg-39152
224. Nsc755848
225. Malathion 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
226. Akos015897264
227. Butanedioic Acid, ((dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)-thio)-, Diethyl Ester, (+-)-
228. Diethyl (+-)-mercaptosuccinate, S-ester With O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
229. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinic Acid, S-ester Of O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
230. Malathion 1000 Microg/ml In Acetone
231. Malathion 1000 Microg/ml In Toluene
232. O,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) Dithiophosphate
233. Tox21_111175_1
234. Cs-4416
235. Db00772
236. Nsc-755848
237. Malathion 100 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
238. Ncgc00091902-01
239. Ncgc00091902-02
240. Ncgc00091902-03
241. Ncgc00091902-06
242. Ncgc00091902-07
243. Ncgc00091902-09
244. Ncgc00091902-11
245. O,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) Phosphorodithioate
246. As-13786
247. Cas_121-75-5
248. Malathion 1000 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
249. O,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) Thiothionophosphate
250. Db-041629
251. Dithiophosphate De O,2-dicarboethoxyethyle)
252. Ft-0701077
253. Malathion, Vial Of 1 G, Analytical Standard
254. O,2-di(ethoxycarbamyl)ethyl Phosphorothioate
255. O,o-dimethyl S-1,2-di(ethoxycarbamyl)ethyl
256. 0,2-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl] Dithiophosphate
257. Malathion, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
258. C07497
259. D00534
260. Wln: 2ov1yvo2 & Sps & O1 & O1
261. Ab00053015_02
262. Diethyl 2-(dimethoxyphosphorothioylthio)succinate
263. O,o-dimethyl S-(1,2-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl)
264. 121m755
265. Diethyl (dimethoxyphosphinothioylthio) Butanedioate
266. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate,o-dimethyl Thiophosphate
267. L001138
268. Q423005
269. Sr-01000942243
270. Diethyl [(dimethoxyphosphinothoiyl)thio]butanedioate
271. J-004630
272. O,o-dimethyl Dithiophosphate Diethylmercaptosuccinate
273. Sr-01000942243-1
274. 1,2-d.(ethoxycarbonyl)dimethyl Phosphorothiolothionate
275. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
276. Malathion, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
277. O,o-dimethyl Dithiophosphate Of Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate
278. 1,2-di(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl O,o-dimethyl Phosphordithioate
279. Diethyl 2-[(dimethoxyphosphorothioyl)sulfanyl]succinate #
280. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinic Acid,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
281. Malathion, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
282. O,o-dimethyl S-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) Phosphorodithioate
283. O,o-dimethyl S-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) Thiothionophosphate
284. O,o-dimethyl S-1,2-di(ethoxycarbamyl)ethyl Phosphorothioate
285. S-(1,2-dicarbethoxyethyl) O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
286. Diethyl 2-((dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)thio)butanedioate
287. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate,o-dimethyl Dithiophosphate, S-ester
288. Malathion, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
289. Mercaptosuccinic Acid Diethyl Ester,o-dimethyl Phosphorothioate
290. O,o-dimethyl S-[1,2-bis(ethoxy Carbonyl)ethyl]dithiophosphate
291. O,o-dimethyl-s-(1,2-di(ethoxycarbonyl)ethyl) Phosphorodithioate
292. S-(1,2-bis(aethoxy-carbonyl)-aethyl)-o,o-dimethyl-dithiophasphat
293. [(dimethoxyphophinothioyl)thio]butanedioic Acid, Diethyl Ester
294. Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate S-ester With O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
295. Succinic Acid, Diethyl Ester, S-ester With 0,0-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
296. Succinic Acid, Diethyl Ester, S-ester With O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
297. 1,4-diethyl 2-{[dimethoxy(sulfanylidene)-$l^{5}-phosphanyl]sulfanyl}butanedioate
298. Butanedioic Acid, ((dimethoxyphosphinothioyl)-thio)-, Diethyl Ester, (+/-)-
299. Diethyl (+/-)-mercaptosuccinate, S-ester With O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
300. Malathion Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Cyclohexane, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
301. Mercaptosuccinic Acid Diethyl Ester, S-ester With O,o-dimethyl Phosphorothioate
302. Phosphorodithioic Acid,0-dimethyl Ester, S-ester With Diethyl Mercaptosuccinate
| Molecular Weight | 330.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
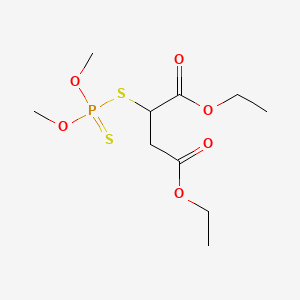
| Molecular Formula | C10H19O6PS2 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 330.03606767 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 330.03606767 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 128 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 341 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Malathion |
| PubMed Health | Malathion (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Pediculicide |
| Drug Label | Malathion Lotion contains 0.005 g of malathion per mL in a vehicle of isopropyl alcohol (78%), terpineol, dipentene, and pine needle oil. The chemical name of malathion is () - [(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl) - thio] butanedioic acid diethyl ester. Mal... |
| Active Ingredient | Malathion |
| Dosage Form | Lotion |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Suven Life |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ovide |
| PubMed Health | Malathion (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Pediculicide |
| Drug Label | OVIDE Lotion contains 0.005 g of malathion per mL in a vehicle of isopropyl alcohol (78%), terpineol, dipentene, and pine needle oil. The chemical name of malathion is () - [(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl) - thio] butanedioic acid diethyl ester. Malathi... |
| Active Ingredient | Malathion |
| Dosage Form | Lotion |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Taro Pharms North |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Malathion |
| PubMed Health | Malathion (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Pediculicide |
| Drug Label | Malathion Lotion contains 0.005 g of malathion per mL in a vehicle of isopropyl alcohol (78%), terpineol, dipentene, and pine needle oil. The chemical name of malathion is () - [(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl) - thio] butanedioic acid diethyl ester. Mal... |
| Active Ingredient | Malathion |
| Dosage Form | Lotion |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Suven Life |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ovide |
| PubMed Health | Malathion (On the skin) |
| Drug Classes | Pediculicide |
| Drug Label | OVIDE Lotion contains 0.005 g of malathion per mL in a vehicle of isopropyl alcohol (78%), terpineol, dipentene, and pine needle oil. The chemical name of malathion is () - [(dimethoxyphosphinothioyl) - thio] butanedioic acid diethyl ester. Malathi... |
| Active Ingredient | Malathion |
| Dosage Form | Lotion |
| Route | Topical |
| Strength | 0.5% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Taro Pharms North |
Malathion Lotion is indicated for patients infected with Pediculus humanus capitis (head lice and their ova) of the scalp hair. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for OVIDE (malathion) lotion (December 2011). Available from, as of January 30, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2024030e-b00d-4fcc-b51d-45dc86933749
Malathion is used for the topical treatment of pediculosis capitis (head lice infestation). The drug also has been used for the topical treatment of pediculosis pubis (pubic lice infestation), pediculosis corporis (body lice infestation), and scabies (mite infestation).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 3535
Pediculicide
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013., p. 1059
(VET): Ectoparasiticide
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2013., p. 1059
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for MALATHION (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Malathion Lotion is contraindicated for neonates and infants because their scalps are more permeable and may have increased absorption of malathion. Malathion Lotion should also not be used on individuals known to be sensitive to malathion or any of the ingredients in the vehicle.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for OVIDE (malathion) lotion (December 2011). Available from, as of January 30, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=2024030e-b00d-4fcc-b51d-45dc86933749
Malathion 0.5% lotion is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the drug or any ingredient in the formulation. The lotion is also contraindicated in neonates and infants. Some clinicians suggest that the malathion preparation commercially available in the US be avoided in patients with asthma and in small children to prevent exposure to fumes from the isopropyl alcohol vehicle.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 3536
Slight stinging or burning has been reported following application of malathion 0.5% lotion, which may be due to the effects of the isopropyl alcohol vehicle. Adverse local effects may include irritation of the skin and scalp, dryness of the hair, and a transient increase in dandruff.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 3536
The manufacturer states that it is not known whether malathion 0.5% lotion has the potential to cause allergic contact sensitization. However, dermatitis of the scalp has been reported in at least one individual following topical application of malathion 5% lotion (10 times the usually recommended dosage) and contact dermatitis has been reported in individuals exposed to agricultural formulations of malathion.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 3536
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for MALATHION (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The lethal dose in mammals is ~1 g/kg.
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 243
For patients infected with Pediculus humanus capitis (head lice and their ova) of the scalp hair.
FDA Label
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide commonly used to control mosquitos and other flying insects. Pharmaceutically, malathion is used to eliminate head lice. The principal toxicological effect of malathion is cholinesterase inhibition, due primarily to malaoxon and to phosphorus thionate impurities.
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
P03AX03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P03 - Ectoparasiticides, incl. scabicides, insecticides and repellents
P03A - Ectoparasiticides, incl. scabicides
P03AX - Other ectoparasiticides, incl. scabicides
P03AX03 - Malathion
Absorption
Malathion in an acetone vehicle has been reported to be absorbed through normal human skin only to the extent of 8% of the applied dose. Absorption may be increased when malathion is applied to damaged skin. Malathion is rapidly and effectively absorbed by practically all routes including the gastrointestinal tract, skin, mucous membranes, and lungs. However, it is readily excreted in the urine, and does not accumulate in organs or tissues.
Concentrations of pesticides and selected metabolites in rat urine and amniotic fluid were determined as biomarker upon oral administration of Wistar rats to two pesticide mixtures consisting of three to five pesticides (bitertanol, propiconazole, cypermethrin, malathion, and terbuthylazine). The pesticides and their metabolites were found in rat amniotic fluid and urine, generally in dose-response concentrations in relation to dosage. The measurement of the substances in the amniotic fluid indicated that the fetus was exposed to the pesticides as well as their metabolites. Moreover, the pesticides detected in urine demonstrated the exposure as well as the ability of the rat to excrete these compounds.
PMID:23736656 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3717736 Bossi R et al; Int J Environ Res Public Health 10 (6): 2271-81 (2013)
O,O,S-Trimethyl phosphorothioate (OOS-TMP) is an impurity present in widely used organophosphorus insecticides such as malathion. Oral treatment of rats with the compound produces prominent bronchiolar epithelial necrosis. Following the administration of [(3)H]OOS-TMP to rats, substantial amounts of radiolabeled material were covalently bound to lung with a concomitant depletion of glutathione (GSH). Other organs showing significant covalently bound radioactivity were liver, kidneys, and ileum. The maximal accumulation occurred in the tissues within 6 hr, and reached a plateau between 6 and 12 hr. Pretreatment of rats with either phenobarbital or piperonyl butoxide decreased the level of radiolabeled material bound in lung, GSH depletion, and the toxicity of OOS-TMP. These results suggest that the covalent binding is due to a metabolite(s) of OOS-TMP and that the metabolite(s) is involved in the mechanism of toxicity of OOS-TMP. ... /(3)H-O,O,S-trimethyl phosphorothioate/
PMID:6710498 Imamura T, Hasegawa L; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 72 (3): 476-83 (1984)
... /The/ objective was to determine the percutaneous absorption of chronically applied malathion in man and to compare chronic absorption to single-dose absorption. The experimental design was to first topically apply [(14)C]malathion to human male volunteers. This procedure was followed by repeated administration of nonradioactive malathion to the same site of application (ventral forearm). [(14)C]Malathion was reapplied (Day 8) when urinary excretion of radioactivity from the first application reached minimum detectable levels. The first [(14)C]malathion absorption was compared to the second [(14)C]malathion application. The percutaneous absorption from the first [(14)C]malathion application was 4.48 +/- 1.3% (SD) of the applied dose. The absorption from the second [(14)C]malathion administration was 3.53 +/- 1.0%, a value not significantly (p greater than 0.05) different from the first application. Therefore, for malathion the single-dose application data are relevant for predicting the toxic potential for longer-term exposure.
PMID:6845371 Wester RC et al; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 68 (1): 116-9 (1983)
Eight autopsy samples from an individual who had ingested a large amount of malathion were analyzed. ... The highest concentrations were found in gastric contents (8621 ppm) and adipose tissue (76.4 ppm). Malaoxon was identified in some tissues at very low levels; a significant amount was found only in fat (8.2 ppm). Malathion monocarboxylic acid & malathion dicarboxylic acid were found in greater abundance: 221 ppm in bile, 106 ppm in kidney, and 103 ppm in the gastric contents.
PMID:7143485 Morgade C, Barquet A; J Toxicol Environ Health 10 (2): 321-5 (1982)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for MALATHION (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
The major metabolites of malathion are the diacid and monoacid metabolites, namely, malathion dicarboxylic acid (DCA) and malathion monocarboxylic acid (MCA). Malaoxon, the active cholinesterase-inhibiting metabolite of malathion, is a minor metabolite. Both malathion and malaoxon are detoxified by carboxyesterases leading to polar, water-soluble compounds that are excreted.
Malathion is either oxidized in the liver to malaoxon by microsomal cytochrome P450 enzymes or to monoacids by a microsomal carboxyesterase. ... The other products of malathion and malaoxon metabolism are detoxification products. Malaoxon is also subject to hydrolysis and carboxyesterase. There is evidence that the linkage at P-S is enzymatically broken by another cytosolic esterase as well (A-esterase) and forms O,O-dimethyl phosphorothioate. There is some evidence that the monoacids can then be S-methylated, and that the C-S bond of either malaoxon or malathion can be further hydrolyzed.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 867
Malathion is rapidly metabolized in vivo principally by hydrolysis of the carboxyl ester linkage to inactive metabolites by carboxylesterases. Because this detoxification reaction occurs much more rapidly in mammals than in susceptible insects, malathion exhibits a relative degree of selective toxicity in insects.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 3538
Malathion ... is oxidized by the hepatic microsomal monooxygenase system to malaoxon, an active, toxic metabolite. Metabolism of malaoxon typically occurs at a faster rate than its formation from malathion, and little accumulation of this highly toxic metabolite occurs in mammals.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 3538
Malathion is metabolically converted to its structurally similar metabolite, malaoxon (oxidation of the P=S moiety to P=O), in insects and mammals. Both malathion and malaoxon are detoxified by carboxyesterases leading to polar, water-soluble, compounds that are excreted. Mammalian systems show greater carboxyesterase activity, as compared with insects, so that the toxic agent malaoxon builds up more in insects than in mammals. This accounts for the increased toxicity of malathion in insects.
EPA/Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxic Substances; Malathion: Updated Revised Human Health Risk Assessment for the Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document (RED) EPA-HQ-OPP-2004-0348-0004. Available from, as of February 2, 2012: https://www.regulations.gov/#!home
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for MALATHION (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
8-24 hours
In a patient who injected about 1.8 g of malathion as a 50% solution IV, the apparent half-life was 2.9 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2016; Drug Information 2016. Bethesda, MD. 2016, p. 3538
Among male volunteers, approximately 90% of an intravenous dose of malathion was excreted in the urine within 5 days and the elimination half-life was 3 hours.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 867
In rats given malathion orally, it is distributed to blood, adipose tissue, muscle, liver, and brain and then eliminated from these tissues at half-lives of 1.4, 2.4, 3.7, 19.4, and 17.6 days, respectively.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V7 866
Malathion is a nonsystemic, wide-spectrum organophosphate insecticide. It inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity of most eukaryotes. Malathion is toxic to aquatic organisms, but has a relatively low toxicity for birds and mammals. The major metabolites of malathion are mono- and di-carboxylic acid derivatives, and malaoxon is a minor metabolite. However, it is malaoxon that is the strongest cholinesterase inhibitor. Cholinesterases catalyze the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetic acid, a reaction necessary to allow a cholinergic neuron to return to its resting state after activation. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of cholinesterase are potent neurotoxins, causing muscle spasms and ultimately death.
Muscle dysfunction in acute organophosphorus (OP) poisoning is a cause of death in human. The present study was conducted to identify the mechanism of action of OP in terms of muscle mitochondrial dysfunction. Electromyography (EMG) was conducted on rats exposed to the acute oral dose of malathion (400 mg/kg) that could inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity up to 70%. The function of mitochondrial respiratory chain and the rate of production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from intact mitochondria were measured. The bioenergetic pathways were studied by measurement of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), lactate, and glycogen. To identify mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic pathways, the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of bax and bcl-2, protein expression of caspase-9, mitochondrial cytochrome c release, and DNA damage were measured. The EMG confirmed muscle weakness. The reduction in activity of mitochondrial complexes and muscular glycogen with an elevation of lactate was in association with impairment of cellular respiration. The reduction in mitochondrial proapoptotic stimuli is indicative of autophagic process inducing cytoprotective effects in the early stage of stress. Downregulation of apoptotic signaling may be due to reduction in ATP and ROS, and genotoxic potential of malathion. The maintenance of mitochondrial integrity by means of artificial electron donors and increasing exogenous ATP might prevent toxicity of OPs.
PMID:23774768 Karami-Mohajeri S et al; Hum Exp Toxicol 33 (3): 251-63 (2014)
... The current study investigates the influence of malathion on insulin signaling pathways and the protective effects of N-acetylcysteine (NAC). Malathion (200 mg/kg) and NAC (2 g/L) were administered orally to rats, during 28 consecutive days. Malathion increases plasma glucose, plasma insulin and glycated hemoglobin levels. Further, we observed an increase of insulin resistance biomarkers and a decrease of insulin sensitivity indices. The GP, GSK3beta and PEPCK mRNA expressions were amplified by malathion while, the expression of glucokinase gene is down-regulated. On the basis of biochemical and molecular findings, it is concluded that malathion impairs glucose homeostasis through insulin resistance and insulin signaling pathways disruptions in a way to result in a reduced function of insulin into hepatocytes. Otherwise, when malathion-treated rats were compared to NAC supplemented rats, fasting glucose and insulin levels, as well as insulin resistance indices were reduced. Furthermore, NAC restored liver GP and PEPCK expression. N-acetylcysteine showed therapeutic effects against malathion-induced insulin signaling pathways disruption in liver. These data support the concept that antioxidant therapies attenuate insulin resistance and ameliorate insulin sensitivity.
PMID:25449180 Lasram MM et al; Gen Comp Endocrinol 215: 88-97 (2015)
The cardiovascular actions of antic-ChE agents are complex, since they reflect both ganglionic and postganglionic effects of accumulated ACh on the heart and blood vessels and actions in the CNS. The predominant effect on the heart from the peripheral action of accumulated ACh is bradycardia, resulting in a fall in cardiac output. Higher doses usually cause a fall in blood pressure, often as a consequence of effects of anti-ChE agents on the medullary vasomotor centers of the CNS. /Anticholinesterase agents/
Brunton, L. Chabner, B, Knollman, B. Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmaceutical Basis of Therapeutics, Twelth Edition, McGraw Hill Medical, New York, NY. 2011, p. 246
/LABORATORY ANIMALS: Acute Exposure/ It was established in experiments on noninbred albino rats that acute intoxication with malathion (0.75 LD50) /administered instramuscularly/ reduced the function of Th1 cells more significantly than the function of Th2 lymphocyte, decreases the activity of B cells and NK cells, blood levels of TNFa, IL-1b and IL-6, IFN-g, IL-2, and IL-4, while not significantly affecting the concentration of IL-10 and IL-13. Atropine (10 mg/kg) under conditions of acute malathion intoxication improved the function of T cells and B lymphocytes, NK cells, as well as the synthesis of immunoregulatory cytokines IFN-g, IL-2, and IL-4. At the same time, atropine in malathion intoxicated rats had no effect on suppression of the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines TNF, IL-1g and IL-6 as well as the content of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-13.
PMID:26591203 Zabrodskii PF et al; Eksp Klin Farmakol 78 (7): 20-3 (2015)