
1. 1263-w-94
2. 1263w94
3. 5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1-beta-l-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole
4. Benzimidavir
5. Bw 1263w94
6. Bw-1263w94
7. Gw 1263
8. Gw 257406x
9. Gw-1263
10. Gw-257406x
11. Gw257406x
1. 176161-24-3
2. Benzimidavir
3. 1263w94
4. Livtencity
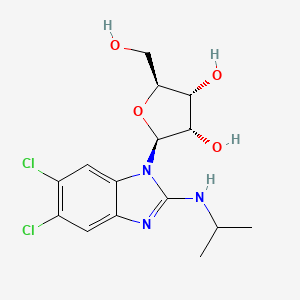
5. (2s,3s,4r,5s)-2-(5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1h-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol
6. Camvia
7. Bw-1263w94
8. Gw-257406x
9. Gw-1263
10. Ptb4x93he1
11. (2s,3s,4r,5s)-2-[5,6-dichloro-2-(propan-2-ylamino)benzimidazol-1-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol
12. 5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1-beta-l-ribofuranosyl-1h-benzimidazole
13. 1263-w-94
14. Gw257406x
15. G1263
16. Maribavir [usan]
17. Unii-ptb4x93he1
18. Maribavir [usan:inn:ban]
19. Camvia(tm)
20. Camvia (tn)
21. Bw 1263w94
22. Maribavir [inn]
23. Maribavir (usan/inn)
24. Maribavir [who-dd]
25. Schembl791309
26. Chembl515408
27. Gtpl12049
28. Dtxsid60170091
29. Zinc3824412
30. Bw1263w94
31. 5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1-(beta-l-ribofuranosyl)-1h-benzimidazole
32. Akos015962194
33. Db06234
34. Gw 1263
35. Gw 257406x
36. 5,6-dichloro-n-(1-methylethyl)-1-beta-l-ribofuranosyl-1h-benzimidazol-2-amine
37. Ncgc00378559-03
38. Ac-22286
39. As-49903
40. Hy-16305
41. Vp-41263
42. D04859
43. O10059
44. Q6762512
45. Maribavir (1263w94, Benzimidazole D-ribose Derivative)
46. 5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1-beta-l-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole
47. 5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1-(.beta.-l-ribofuranosyl)benzimidazole
48. 5,6-dichloro-2-isopropylamino-1-(beta-l-ribofuranosyl)-1h-benzimidazole
49. 1h-benzimidazol-2-amine, 5,6-dichloro-n-(1-methylethyl)-1-.beta.-l-ribofuranosyl-
50. 1h-benzimidazol-2-amine, 5,6-dichloro-n-(1-methylethyl)-1-beta-l-ribofuranosyl-
51. 5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1-.beta.-l-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole
52. 5,6-dichloro-n-(1-methylethyl)-1-.beta.-l-ribofuranosyl-1h-benzimidazol-2-amine
53. (2s,3s,4r,5s)-2-(5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)-1h-benzo[d]-imidazol-1-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol
54. (2s,3s,4r,5s)-2-[5,6-dichloro-2-(isopropylamino)benzimidazol-1-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol
| Molecular Weight | 376.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H19Cl2N3O4 |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 375.0752615 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 375.0752615 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 99.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 447 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Maribavir is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients (weighing >35kg and at least 12 years old) with post-transplant cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection which is refractory to standard treatment with [ganciclovir], [valganciclovir], [cidofovir], or [foscarnet].
Cytomegaloviral disease
Treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection
Maribavir exerts its antiviral efficacy via an alternative target as compared to traditional CMV antivirals and is thus useful in the treatment of CMV infections that have proven resistant to standard therapy. Maribavir should not be used concomitantly with ganciclovir or valganciclovir, as these molecules both require activation via CMV pUL97 in order to exert their antiviral effect. Taking them alongside maribavir - an inhibitor of this same kinase - will therefore significantly reduce their antiviral activity.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AX - Other antivirals
J05AX10 - Maribavir
Absorption
Population pharmacokinetic modeling in patients receiving maribavir 400mg twice daily showed an AUC0-tau and Cmax of 128 g.h/mL and 17.2 g/mL, respectively. It has a median Tmax of one to three hours.
Route of Elimination
Maribavir is eliminated primarily via hepatic metabolism. Following the oral administration of radiolabeled maribavir, 61% of the dose was excreted in the urine (<2% as unchanged drug) and 14% was excreted in the feces (5.7% as unchanged drug).
Volume of Distribution
The mean apparent steady-state volume of distribution for maribavir was 27.3 L.
Clearance
In post-transplant patients, the mean oral clearance of maribavir was 2.85 L/h.
Maribavir is extensively metabolized following oral administration, primarily by CYP3A4 and, to a lesser extent, by CYP1A2. Its major circulating metabolite is VP 44469, an inactive N-dealkylated metabolite.
In post-transplant patients, the mean half-life of elimination was 4.32 hours.
Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a herpesvirus commonly causing infection in patients following stem cell or organ transplants. As with other herpesviruses, CMV tends to persist in the host and become reactivated under immunosuppressive conditions - patients requiring multiple immunosuppressive medications to combat transplant rejection are thus at a much higher risk of developing serious CMV infections. Maribavir belongs to a class of anti-cytomegalovirus antivirals called benzimidazole ribosides. It competitively inhibits the human CMV pUL97 viral protein kinase, which results in viable but severely defective viruses upon replication, although the reasons for this remain poorly defined. In addition, maribavir also inhibits viral release from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by inhibiting pUL97-dependent phosphorylation of the nuclear lamina component lamin A/C, although the extent to which this activity contributes to its antiviral efficacy is unclear.